Abstract
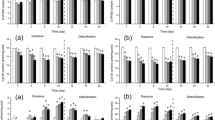
The ability of African sharptooth catfish (Clarias gariepinus) in inducing cytochrome P-450 class 1A (CYP1A) and glutathione S-transferase (GST) biomarkers was determined in liver and gill filaments after 4 days of waterborne exposure to the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P). Male (n=6) and female (n=6) fish were exposed to B[a]P added to the water (30 μg/l) corresponding to 5 mg/kg total body weight. Five female and six male fish, exposed to acetone alone added to the water served as controls. The 7-ethoxyresurufin-O-deethylase (EROD) activity was measured in hepatic microsomes and gill filaments. In addition, GST activity was determined in the hepatic cytosolic fraction and fluorescent aromatic compounds (FACs) in bile and biliverdin. Benzo[a]pyrene strongly induced EROD activities in gill filaments of both sex. Levels of FACs per ml of bile were 17-fold higher in exposed fish compared to the controls. Correlations between induction of EROD activities in gill filaments and liver and between induction of EROD activities in gill filaments and levels of biliary FACs metabolites were strong. GST activities in the hepatic cytosolic fraction were similar amongst the treated and control groups. This is the first report on studies determining EROD activities in gill filaments and hepatic tissue, FACs in bile and GST in hepatic tissues of C. gariepinus after waterborne exposure to B[a]P. The findings suggest that the gill filament-based EROD assay in C. gariepinus can be used to monitor the pollution of AhR agonists in aquatic ecosystems in eastern and southern African countries.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson T., Pesonen M., Johansson C., (1985). Differential induction of cytochrome P−45-dependent monooxygenase, epoxide hydrolase, glutathione transferase and UDP glucuronosyltransferase activities in the liver of rainbow trout by β-naphthoflavone or Clophen A50Biochem. Pharmacol. 34: 3309–14
Beyer J., Sandvik M., Hylland K., Fjeld E., Egaas E., Aas E., Skåre J., Goksøyr A., (1996). Contaminant accumulation and biomarker responses in flounder (Platichthys flesus L.) and Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) exposed by caging to polluted sediments in Sorfjorden, Norway Aquat. Toxicol. 36: 75–98
Beyer J., Sandvik M., Skaare J.U., Egaas E., Hylland K., Waagbo R., Goksoy A., (1997). Time and dose-dependent biomarker responses in flounder (Platichthys flesus L.) exposed to benzo[a]pyrene, 2,3,3´,4,4´,5-hexachlorobiphenyl (PCB−156) and cadmiumBiomarkers 2: 35–44
Bradford M.M., (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilising the principle of protein-dye bindingAnal. Biochem. 72: 248–54
Carlsson C., Pärt P., Brunström B., (1999). 7-Ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase induction in cultured gill epithelial cells from rainbow troutAquat. Toxicol. 47: 117–28
Clements W.H., Oris J.T., Wissing T.E., (1994). Accumulation and food chain transfer of Fluoranthene and Benzo[a]pyrene in Chironomus riparius and Lepomis macrochirus Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 26: 261–6
Collier T.K., Varanasi U., (1991). Hepatic activities of xenobiotic metabolising enzymes and biliary levels of xenobiotics in English sole (Parophrys vetulus) exposed to environmental contaminantsArch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 20: 462–73
Datta M., Kaviraj A., (2003). Ascorbic acid supplementation of diet for reduction of deltamethrin induced stress in freshwater catfish Clarias gariepinusChemosphere 53: 883–8
Gadagbui B.K.M., Goksøyr A., (1996). Biomarker studies in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) caged in, and in mudfish (Clarias anguillaris) exposed to sediment from a polluted river in Ghana, West AfricaMarine Environ. Res. 42: 275
Gallagher E.P., Gross T.S., Sheehy K.M., (2001). Decreased glutathione S-transferase expression and activity and altered sex steroids in Lake Apopka brown bullheads (Ameriurus nebulosos)Aquat. Toxicol. 55: 223–37
Goksøyr A., Förlin L., (1992). The cytochrome P−450 system in fish: aquatic toxicology and environmental monitoringAquat. Toxicol. 22: 287–312
Grossbard M.L., Aas E., Beyer J., Goksøyr A., (1987). Fixed wavelength fluorescence (FF) of bile as a monitoring tool for polyaromatic hydrocarbon exposure in fish: an evaluation of compound specificity, inner filter effect and signal interpretationBiomarkers 5: 9–23
Habig W.H., Pabst M.J., Jacoby W.B., (1974). Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymic step in mercapturic acid formationJ. Biol. Chem. 249: 7130–9
Hayes J.D., Pulford D.J., (1995). The glutathione S-Transferase supergene family: regulation of GST and the contribution of the isoenzymes to cancer chemoprotection and drug resistanceCrit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 30: 445–600
Jaward F.M., Barber J.L., Booij K., Jones K.C., (2004). Spatial distribution of atmospheric PAHs and PCNs along a north-south Atlantic transectEnviron. Pollut. 132: 173–81
Jönsson, E.M. (2003). A gill filament EROD assay: development and application in environmental monitoring. Ph.D. Thesis, Uppsala University, Sweden
Jönsson E.M., Abrahamson A., Brunstrom B., Brandt I., Ingebrigtsen K., Jørgensen E.H., (2003). EROD activity in gill filaments of anadromous and marine fish as a biomarker of dioxin-like pollutantsComp. Biochem. Physiol. 136: 235–43
Jönsson E.M., Brandt I., Brunstrom B., (2002). Gill filament-based EROD assay for monitoring waterborne dioxin-like pollutants in fishEnviron. Sci. Technol. 36: 3340–4
Klaassen C., Watkins J.B. III, (1984). Mechanisms of bile formation, hepatic uptake, and biliary excretionPharmacol. Rev. 36: 1–67
Kloepper-Sams P.J., Benton E., (1994). Exposure of fish to biologically treated bleached-kraft effluent: II. Induction of hepatic cytochrome P4501A in mountain whitefish (Prosopium williamsoni) and other species Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 13: 1483–96
Kosmala A., Migeon B., Flammarion P., Garric J., (1998). Impact assessment of a wastewater treatment plant effluent using the fish biomarker Ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase: field and on-site experimentsEcotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 41: 19–28
Krahn M.M., Brown D.W., Collier T.K., Friedman A.J., Jenkins R.G., Malins D.C., (1980). Rapid analysis of naphthalene and its metabolites in biological systems: determination by high performance liquid chromatography/fluorescence detection and by plasma desorption/chemical ionisation mass spectrometryJ. Biochem. Biophys. Meth. 2: 233–46
Krahn M.M., Burrows D.G., Macleod W.D., Malins D.C., (1987). Determination of individual metabolites of aromatic compounds in hydrolyzed bile of English sole (Parophrys vetulus) from polluted sites in Puget sound, WashingtonArch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 16: 511–22
Krahn M.M., Kittle L.J., Macleod W.D., (1986). Evidence for exposure of fish to oil spilled into the Columbia river Marine Environ. Res. 34: 237–41
Leaver M.J., Pirrit L., George S.G., (1992). Expression and tissue distribution of Plaice glutathione S-transferase AMarine Environ. Res. 34: 237–41
Levine S.L., Oris J.T., (1999). CYP1A expression in liver and gill of rainbow trout following waterborne exposure: implications for biomarker determinationAquat. Toxicol. 46: 279–87
Lien N.T., Adriaens D., Janssen C.R., (1997). Morphological abnormalities in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) larvae exposed to malathionChemistry 35: 1475–86
Mbongwe B., Legrand M., Blais J.M., Kimpe L.E., Ridal J.J., Lean D.R., (2003). Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane in the aquatic ecosystem of the Okavango Delta, Botswana, South AfricaEnviron. Toxicol. Chem. 22:7–19
Mccormick S.D., Bern H.A., (1989) In vitro stimulation of Na+–K+-ATPase activity and ouabain binding by cortisol in coho salmon gillAm. J. Physiol. 256: R707–15
Mitchell A.E., Lakritz J., Jones A.D., (2000). Quantification of individual glutathione S-transferase isozymes in hepatic and pulmonary tissues of naphthalene-tolerant miceArch. Toxicol. 74: 215–21
Nguyen L.T., Janssen C.R., Volckaert F.A., (1999). Susceptibility of embryonic and larval African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) to toxicantsBull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 62: 230–7
Olajire A.A., Altenburger R., Küster E., Brack W., (2005). Chemical and ecotoxicological assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon – contaminated sediments of the Niger Delta, Southern NigeriaSci. Tot. Environ. 340: 123–36
Payne J.F., Fancey L.L., Rahimtula A.D., Porter E.L., (1987). Review and perspective on the use of mixed function oxygenase enzymes in biological monitoringComp. Biochem. Physiol. 86: 233–45
Sturm A., Hodson P.V., Carey J.H., Hansen P., (1999). Hepatic UDP-glucuronosyltransferase in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and preliminary assessment of response to pulp mill cooking liquorBull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 62: 608–15
Theron J., Prinsloo J.F., Schoonbee H.J., (1991). Investigations into the effects of concentration and duration of exposure to formalin and malachite green on the survival of the larvae and juveniles of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L). and the sharptooth catfish (Clarias gariepinus) (Burchell)Onderstep J. Vet. Res. 58: 245–51
Timmers R.J., Granneman J.C., Lambert J.G., Van Oordt P.G., (1988). Estrogen−2-hydroxylase in the brain of the male African catfish, Clarias gariepinus Gen. Comp. Endocrin. 72:190–203
Viljoen A., Steyn G.J., Van Vuren J.H., Wade P.W., (2003). Zinc effects on the embryos and larvae of the sharptooth catfish, Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822)Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 70: 1022–27
Acknowledgments
This study was kindly funded by the Norwegian Universities’ Committee for Development Research and Education (NUFU) PRO 08/2002. The experiment was approved by the Animal Use and Care and Research Committees of the Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Pretoria. We express our sincere thanks to the technical assistance we received from Mr. Huyser and Mrs. Mulders, University of Pretoria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MDEGELA, R., MYBURGH, J., CORREIA, D. et al. Evaluation of the Gill Filament-Based EROD Assay in African Sharptooth Catfish (Clarias gariepinus) as a Monitoring Tool for Waterborne PAH-Type Contaminants. Ecotoxicology 15, 51–59 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-005-0041-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-005-0041-5