Abstract
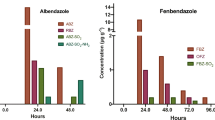
Avermectins are widely used veterinary medicines. They bind strongly to faeces in their non-metabolized form and their half-life in faeces depends on field conditions. There are conflicting data regarding the behaviour of avermectins in the environment. Therefore, we investigated the degradation of abamectin and doramectin on sheep grazed pasture under field conditions in soil, soil–faeces and faeces samples from day 6 to day 70 (abamectin) or to day 50 (doramectin) after sheep treatment. Field conditions were recorded periodically during the experiment. Degradation of abamectin in sheep faeces and in soil–faeces was observed until day 60, with small amounts present in faeces until 70 days post treatment. Because the concentration of abamectin residues in soil was very low on day 6 after treatment, further significant degradation could not be measured. The concentration of doramectin in all analysed matrices decreased rapidly until day 50. It can be concluded that high concentrations of both avermectins were present during the first 20 days after treatment and that field conditions have an important role in degradation of avermectins on grazed pasture of treated animals. Clear identification of the consequences of avermectin exposure and the period of the greatest environmental risk will require further investigations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell W.C., Benz G.W., (1984). Ivermectin: a review of efficacy and safety J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 7:1–16
Cook D.F., (1993). Effect of avermectin residues in sheep dung on mating of the Australian sheep blowfly Lucilia cuprina Vet. Parasitol. 48:205–14
De Montigny P., Shim J.S.K., Pivnichny J.V., (1990). Liquid chromatographic determination of ivermectin in animal plasma with trifluoroacetic anhydride and N-methylimidazole as the derivatization reagent J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 8(6):507–11
Fisher M.H., Mrozik H., (1992). The chemistry and pharmacology of avermectins Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 32:537–53
Forbes A.B., (1996). Environmental assessments in veterinary parasitology: A balanced perspective Int. J. Parasitol. 26(5): 567–69
Halley B.A., Nessel R.J., Lu A.Y.H., (1989). Environmental aspect of ivermectin usage in livestock: general considerations In: Campbell W.C., (Eds) Ivermectin and Abamectin New York Springer Verlag 163–72 pp
Halley B.A., VandenHeuvel W.J.A., Wislocki P.G., (1993). Environmental effects of the usage of avermectins in livestock Vet. Parasitol. 48:109–25
Herd R., (1995). Endectocidal drugs: Ecological risks and counter-measures Int. J. Parasitol. 25(8): 875–85
Herd R., (1996). Ecotoxicity of the avermectins: A reply to Forbes Int. J. Parasitol. 26(5): 571–72
Holter P., Sommer C., Grønvold J., (1993). Attractiveness of dung from ivermectin-treated cattle to Danish and afrotropical scarabaeid dung beetles Vet. Parasitol. 48:159–69
King K.L., (1993). Methods for assessing the impact of avermectins on the decomposer community of sheep pastures Vet. Parasitol. 48:87–97
Kolar L., Kužner J., Kožuh Eržen N., (2004). Determination of abamectin and doramectin in sheep faeces using HPLC with fluorescence detection Biomed. Chromatogr. 18:117–24
Kožuh Eržen N., Cerkvenik Flajs V., (2003). Simultaneous determination of abamectin and doramectin in soil from a grazed pasture Acta Chim. Slov. 50:301–08
Kožuh Eržen N., Kobal S., Cerkvenik Flajs V., 2003. Veterinary pharmaceuticals and environment In: Dobeic M., Vudrag M., Berger T., (Eds) Proceedings of 1st Interdisciplinary Symposium “DDD, Health and Environment” Ljubljana Slovenia 139–145 pp
Kužner J., Kožuh Eržen N., Kolar L., Kobal S., Marc I., Cerkvenik Flajs V., Pogačnik M., (2003). Time profile of excretion and behaviour of abamectin in soil from a grazed pasture of treated animals. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther., Suppl. 26 (suppl. 1), 257
Lumaret J.P., Errouissi F., (2002). Use of anthelmintics in herbivores and evaluation of risks for the non target fauna of pastures Vet. Res. 33(2):547–62
Mahon R.J., Wardhaugh K.G., van Gerwen A.C.M., Whitby W.A., (1993). Reproductive development and survival of Lucilia cuprina Wiedemann when fed sheep dung containing ivermectin Vet. Parasitol. 48:193–204
McKellar Q.A., Benchaoui H.A., (1996). Avermectins and milbemycins J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 19:331–51
McKellar Q.A., (1997). Ecotoxicology and residues of anthelmintic compounds Vet. Parasitol. 72:413–35
Moore J.C., DeRuiter P.C., Hunt H.W., (1993). Soil invertebrate/micro-invertebrate interactions: disproportionate effects of species on food web structure and function Vet. Parasitol. 48:247–60
Ridsdill-Smith T.J., (1993). Effect of avermectin residues in cattle dung on dung beetle (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) reproduction and survival Vet. Parasitol. 48:27–137
Sommer C., Steffansen B., (1993). Changes with time after treatment in the concentrations of ivermectin in fresh cow dung and in cow pats aged in the field Vet. Parasitol. 48:67–73
Suarez V.H., (2002). Helminthic control on grazing ruminants and environmental risks in South America Vet. Res. 33:563–73
Steel J.W., Wardhaugh K.G., (2002). Ecological impact of macrocyclic lactones on dung fauna In: Vercruysse J., Rew R.S., (Eds) Macrocyclic Lactones and Antiparasitic Therapy Wallingford CAB International 141–162 pp
Strong L., James S., (1993). Some effects of ivermectin on the yellow dung fly, Scatophaga stercoraria Vet. Parasitol. 48:181–91
Taylor S.M., (1999). Sheep scab – environmental considerations of treatment with doramectin Vet. Parasitol. 83:309–17
Wardhaugh K.G., Mahon R.J., Axelsen A., Rowland M.W., Wanjura W., (1993). Effects of ivermectin residues in sheep dung on the development and survival of the bushfly, Musca vetustissima Walker and a scarabaeine dung beetle, Euoniticellus fulvus Goeze Vet. Parasitol. 48:139–57
Wislocki P.G., Grosso L.S., Dybas R.A., (1989). Environmental aspects of abamectin use in crop protection In: Campbell W.C., (Eds) Ivermectin and Abamectin New York Springer Verlag 182–200 pp
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Sport of Slovenia and Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Food of Slovenia (CRP V4-0476-01 and RP P4-0092). The authors thank Katarina Adamič, Boštjan Drolc and Andrej Škibin, DVM for their technical assistance and also Marko Zupan, M.Sc. of the Center for Soil and Environmental Sciences, Agronomy Department, Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana for physical characterization of the soil samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ERŽEN, N.K., KOLAR, L., FLAJS, V.C. et al. Degradation of Abamectin and Doramectin on Sheep Grazed Pasture. Ecotoxicology 14, 627–635 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-005-0012-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-005-0012-x