Abstract
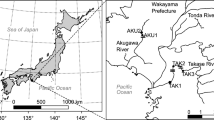
Japanese eels (Anguilla japonica) utilize a broad range of habitats along the marine-freshwater ecotone during their growth phase in inland waters. This study aimed to analyze the foraging behavior of yellow-phase Japanese eels in connected fresh- and brackish water habitats and to connect foraging behavior and habitat use through the analysis of carbon (δ13C) and nitrogen (δ15N) stable isotopes. Stomach contents of eels collected in fresh- and brackish waters were analyzed to identify food sources. Values of δ13C and δ15N were analyzed in eels and their potential food sources, and used to predict the recent foraging patterns of eels in the Matsukawa-ura, a brackish water lagoon, and in three freshwater tributaries. Eels preyed on the benthic river community and the mudflat community of the lagoon. Gobiid fishes were found to be an important food source for eels in fresh- and brackish water habitats, while Japanese mitten crabs (Eriocheir japonica) and shore crabs (Hemigrapsus spp.) were major prey in fresh- and brackish waters respectively. δ13C values of potential eel prey differed significantly between fresh- and brackish waters and were used to classify three recent patterns of foraging by the 73 eels included in this study: 1) freshwater foraging, 2) brackish water foraging, and 3) multiple-habitat foraging. The data suggested that some eels recently or frequently moved between fresh- and brackish water habitats while others demonstrated a higher fidelity to either fresh- or brackish waters. Isotopic characteristics of prey in the respective foraging habitats revealed the plasticity of habitat use of yellow eels in the study area. This study demonstrates an integrated approach to study habitat use and foraging behavior of eels. Furthermore, the study underlines the need to consider freshwater and estuarine habitats and the connectivity between them for eel management and conservation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai T, Kotake A, McCarthy TK (2006) Habitat use by the European eel Anguilla anguilla in Irish waters. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 67:569–578
Arai T, Kotake A, Ohji M, Miller MJ, Tsukamoto K, Miyazaki N (2003) Occurrence of sea eels of Anguilla japonica along the Sanriku coast of Japan. Ichthyol Res 50:78–81
Bearhop S, Thompson DR, Waldron S, Russell IC, Alexander G, Furness RW (1999) Stable isotopes indicate the extent of freshwater feeding by cormorants Phalacrocorax carbo shot at inland fisheries in England. J Appl Ecol 36:75–84
Béguer-Pon M, Castonguay M, Benchetrit J, Hatin D, Legault M, Verreault G, Mailhot Y, Tremblay V, Dodson JJ (2015) Large-scale, seasonal habitat use and movements of yellow American eels in the St. Lawrence River revealed by acoustic telemetry. Ecol Freshw Fish 24:99–111
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method for total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Cabana G, Rasmussen JB (1994) Modelling food chain structure and contaminant bioaccumulation using stable nitrogen isotopes. Nature 372:255–257
Castonguay M, Hodson PV, Couillard CM, Eckersley MJ, Dutil JD, Verreault G (1994) Why is recruitment of the American eel Anguilla rostrata declining in the St. Lawrence River and gulf? Can J Fish Aquat Sci 51:479–488
Chen JZ, Huang SL, Han YS (2014) Impact of long-term habitat loss on the Japanese eel Anguilla japonica. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 151:361–369
Clark FN (1928) The weight–length relationship of the California sardine (Sardina caerulea) at San Pedro. Division of Fish and Game. Fish Bull 12:59
Clément M, Chiasson AG, Veinott G, Cairns DK (2014) What otolith microchemistry and stable isotope analysis reveal and conceal about anguillid eel movements across salinity boundaries. Oecologia 1:1143–1153
Daverat F, Limburg KE, Thibault I, Shiao JC, Dodson JJ, Caron F, Tzeng WN, Iizuka Y, Wickström H (2006) Phenotypic plasticity of habitat use by three temperate eel species, Anguilla anguilla, A. japonica and A. rostrata. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 308:231–241
Dekker W (2003) Did lack of spawners cause the collapse of the European eel, Anguilla anguilla? Fisheries Manag Ecol 10:365–376
DeNiro MJ, Epstein S (1981) Influence of diet on the distribution of nitrogen isotopes in animals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 45:341–351
DeNiro MJ, Epstein S (1977) Mechanism of carbon isotope fractionation associated with lipid synthesis. Science 197:261–263
DeNiro MJ, Epstein S (1978) Influence of diet on the distribution of carbon isotopes in animals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 42:495–506
Dörner H, Skov C, Berg S, Schulze T, Beare DJ, Van Der Velde G (2009) Piscivory and trophic position of Anguilla anguilla in two lakes: importance of macrozoobenthos density. Jour Fish Biol 74:2115–2131
Doucett RR, Hooper W, Power G (1999) Identification of anadromous and nonanadromous adult brook trout and their progeny in the Tabusintac River, New Brunswick, by means of multiple-stable-isotope analysis. Trans Am Fish Soc 128:278–288
Dudgeon D, Arthington AH, Gessner MO, Kawabata ZI, Knowler DJ, Lévêque C, Naiman RJ, Prieur-Richard AH, Soto D, Stiassny MLJ, Sullivan CA (2006) Freshwater biodiversity: importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 81:163–182
Feunteun E (2002) Management and restoration of European eel population (Anguilla anguilla): an impossible bargain. Ecol Eng 18:575–591
Froese R (2006) Cube law, condition factor and weight-length relationships: history, meta-analysis and recommendations. J Appl Ichthyol 22:241–253
Fry B, Sherr EB (1984) δ13C measurments as indicators of carbon flow in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Contrib Mar Sci 27:13–47
Fry B (2002) Conservative mixing of stable isotopes across estuarine salinity gradients: a conceptual framework for monitoring watershed influences on downstream fisheries production. Estuaries 25:264–271
Fuji T, Kasai A, Suzuki KW, Ueno M, Yamashita Y (2010) Freshwater migration and feeding habits of juvenile temperate seabass Lateolabrax japonicus in the stratified Yura River estuary, the sea of Japan. Fish Sci 76:643–652
Garcia AM, Hoeinghaus DJ, Vieira JP, Winemiller KO (2007) Isotopic variation of fishes in freshwater and estuarine zones of a large subtropical coastal lagoon. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 73:399–408
Harada M, Kume M, Mochioka N, Tamura Y, Kanzaki T, Hashiguchi S, Kasai A, Yamashita Y (2018) Japanese eel Anguilla japonica and aquatic animals collected with Ishi-kura net in the Iroha and Katsura Rivers, Oita prefecture, Japan. Nippon Suisan Gakk 84:45–53 (in Japanese, with English abstract)
Haro A, Richkus W, Whalen K, Hoar A, Busch WD, Lary S, Brush T, Dixon D (2000) Population decline of the American eel: implications for research and management. Fisheries 25:7–16
Harrod C, Grey J, McCarthy TK, Morrissey M (2005) Stable isotope analyses provide new insights into ecological plasticity in a mixohaline population of European eel. Oecologia 144:673–683
Hedger RD, Dodson JJ, Hatin D, Caron F, Fournier D (2010) River and estuary movements of yellow-stage American eels Anguilla rostrata, using a hydrophone array. J Fish Biol 76:1294–1311
Hesslein RH, Hallard KA, Ramlal P (1993) Replacement of sulfur, carbon, and nitrogen in tissue of growing broad whitefish (Coregonus nasus) in response to a change in diet traced by δ 34 S, δ 13 C, and δ 15 N. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 50:2071–2076
Hobson KA (1990) Stable isotope analysis of marbled murrelets: evidence for freshwater feeding and determination of trophic level. Condor 92:897–903
Hobson KA (1999) Tracing origins and migration of wildlife using stable isotopes: a review. Oecologia 120:314–326
Hobson KA, Clark RG (1992) Assessing avian diets using stable isotopes I: turnover of 13C in tissues. Condor 94:181–188
Houlihan DF, Carter CG, McCarthy ID (1995) Protein synthesis in fish. In: Hochachka PW, Mommsen TP (eds) Biochemistry and molecular biology of fishes. Metabolic Biochemistry. Elsevier Biomedical, Amsterdam, pp 191–220
Itakura H, Kitagawa T, Miller MJ, Kimura S (2015a) Declines in catches of Japanese eels in rivers and lakes across Japan: have river and lake modifications reduced fishery catches? Land Ecol Eng 11:147–160
Itakura H, Kaino T, Miyake Y, Kitagawa T, Kimura S (2015b) Feeding, condition, and abundance of Japanese eels from natural and revetment habitats in the Tone River, Japan. Environ Biol Fish 98:1871–1888
Itakura H, Miyake Y, Kitagawa T, Kimura S (2017) Site fidelity, diel and seasonal activities of yellow-phase Japanese eels (Anguilla japonica) in a freshwater habitat as inferred from acoustic telemetry. Ecol Freshw Fish 27:737–751
Jacoby DMP, Gollock MJ (2014) Anguilla japonica. The IUCN red list of threatened species 2014:e.T166184A1117791
Jellyman DJ (1977) Summer upstream migration of juvenile freshwater eels in New Zealand. New Zeal J Mar Freshw 11:61–71
Kaifu K, Tamura M, Aoyama J, Katsumi T (2010) Dispersal of yellow phase Japanese eels Anguilla japonica after recruitment in the Kojima Bay-Asahi River system, Japan. Environ Biol Fish 88:273–282
Kaifu K, Miyazaki S, Aoyama J, Kimura S, Tsukamoto K (2012) Diet of Japanese eels Anguilla japonica in the Kojima Bay-Asahi River system, Japan. Environ Biol Fish 96:439–446
Kan K, Sato M, Nagasawa K (2016) Tidal-flat macrobenthos as diets of the Japanese eel Anguilla japonica in western Japan, with a note on the occurrence of a parasitic nematode Heliconema anguillae in eel stomachs. Zool Sci 33:50–62
Keys AB (1928) The weight-length relation in fishes. Proc Nat Acad Sci 14:922–925
Kulbicki M, Guillemot N, Amand M (2005) A general approach to length-weight relationships for New Caledonian lagoon fishes. Cybium 29:235–252
Kume M, Terashima Y, Wada T, Yamashita Y (2019) Longitudinal distribution and microhabitat use of young Japanese eel Anguilla japonica in a small river flowing through paddy areas. J Appl Ichthyol 35:876–883
Kwak TJ, Engman AC, Lilyestrom CG (2019) Ecology and conservation of the American eel in the Caribbean region. Fisheries Manag Ecol 26:42–52
Laffaille P, Feunteun E, Baisez A, Robinet T, Acou A, Legault A, Lek S (2003) Spatial organisation of European eel (Anguilla anguilla L.) in a small catchment. Ecol Freshw Fish 12:254–264
Lasne E, Acou A, Vila-Gispert A, Laffaille P (2008) European eel distribution and body condition in a river floodplain: effect of longitudinal and lateral connectivity. Ecol Freshw Fish 17:567–576
Minagawa M, Wada E (1984) Stepwise enrichment of 15N along food chains: further evidence and the relation between δ15N and animal age. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:1135–1140
Mizutani H, Fukuda M, Kabaya Y, Wada E (1990) Carbon isotope ratio of feathers reveals feeding behavior of cormorants. Auk 107:400–403
Noda T, Wada T, Iwasaki T, Sato T, Narita K, Matsumoto I, Hori T, Mitamura H, Arai N (2019a) Post-release behaviors and movements of cultured and wild Japanese eels (Anguilla japonica) in a shallow brackish water lagoon in northeastern Japan. Environ Biol Fish 107:1435–1456
Noda T, Komaki T, Wada T, Kume M, Kutzer A, Terashima Y, Fujita T, Satoh T, Yamada M, Matsumoto Y, Hori T, Takagi J, Mitamura H, Arai N, Yamashita Y (2019b) Behavioral ecology of wild Japanese eels in brackish waters -comparison with cultured eels-. The Japanese Society of Fisheries Science Spring Meeting 2019. Program and abstracts 38. (in Japanese)
Okamura A, Yamada Y, Yokouchi K, Horie N, Mikawa N, Utoh T, Tanaka S, Tsukamoto K (2007) A silvering index for the Japanese eel Anguilla japonica. Environ Biol Fish 80:77–89
Omweri JO, Suzuki KW, Edouard L, Yokoyama H, Yamashita Y (2018) Seasonality and occurrence of the dominant mysid Neomysis awatschensis (Brandt, 1851) in the Yura River estuary, central sea of Japan. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 211:188–198
Owen SF (2001) Meeting energy budgets by modulation of behaviour and physiology in the eel (Anguilla anguilla L.). Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 128:629–642
Park JM, Kwak SN, Lee WC (2020) Dietary study using set-nets produces bias in prey choice of fish: a case of three coastal fishes inhabiting southern Korean waters. J Sea Res 157:101846
Parker S (1995) Homing ability and home range of yellow-phase American eels in a tidally dominated estuary. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 75:127–140
Peterson BJ, Fry B (1987) Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 18:293–320
Post DM (2002) Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: models, methods and assumptions. Ecology 8:703–718
R Core Team (2017) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. http://www.r-project.org/. Accessed in October, 2017
Sakano H, Fujiwara E, Nohara S, Ueda H (2005) Estimation of nitrogen stable isotope turnover rate of Oncorhynchus nerka. Environ Biol Fish 72:13–18
Schoeninger MJ, DeNiro MJ (1984) Nitrogen and carbon isotopic composition of bone collagen from marine and terrestrial animals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:625–639
Smith RJ, Hobson KA, Koopman HN, Lavigne DM (1996) Distinguishing between populations of fresh- and salt-water harbour seals (Phoca vitulina) using stable-isotope ratios and fatty acid profiles. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 53:272–279
Suzuki KW, Kasai A, Nakayama K, Tanaka M (2005) Differential isotopic enrichment and half-life among tissues in Japanese temperate bass (Lateolabrax japonicus) juveniles: implications for analyzing migration. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 626:71–678
Takahashi T, Kameda K, Kawamura M, Nakajima T (2006) Food habits of great cormorant Phalacrocorax carbo hanedae at Lake Biwa, Japan, with special reference to ayu Plecoglossus altivelis altivelis. Fish Sci 72:477–484
Tatsukawa K (2003) Eel resources in East Asia. In Eel Biology. Springer Japan, Tokyo, pp 293–298
Tayasu I, Hirasawa R, Ogawa NO, Ohkouchi N, Yamada K (2011) New organic reference materials for carbon- and nitrogen-stable isotope ratio measurements provided by Center for Ecological Research, Kyoto University, and Institute of Biogeosciences, Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology. Limnology 12:261–266
Tesch FW (2003) The Eel, 5th edn. Blackwell Science Ltd, Oxford, England
Thibault I, Dodson J, Caron F, Tzeng W, Iizuka Y, Shiao J (2007) Facultative catadromy in American eels: testing the conditional strategy hypothesis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 344:219–229
Tieszen LL, Boutton TW, Tesdahl KG, Slade NA (1983) Fractionation and turnover of stable carbon isotopes in animal tissues: implications for δ13C analysis of diet. Oecologia 57:32–37
Tsukamoto K, Aoyama J, Miller MJ (2002) Migration, speciation, and the evolution of diadromy in anguillid eels. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 59:1989–1998
Tsukamoto K (2006) Spawning of eels near a seamount. Nature 439:929–929
Tsukamoto K, Arai T (2001) Facultative catadromy of the eel Anguilla japonica between freshwater and seawater habitats. Mar 220:265–276
Tsukamoto K, Nakai I, Tesch WV (1998) Do all freshwater eels migrate? Nature 396:635–636
Verhelst P, Reubens J, Pauwels I, Buysse D, Aelterman B, Van Hoey S, Goethals P, Moens T, Coeck J, Mouton A (2018) Movement behaviour of large female yellow European eel (Anguilla anguilla L.) in a freshwater polder area. Ecol Freshw Fish 27:471–480
Wada T, Kamiyama K, Shimamura S, Matsumoto I, Mizuno T, Nemoto Y (2011) Habitat utilization, feeding, and growth of wild spotted halibut Verasper variegatus in a shallow brackish lagoon: Matsukawa-ura, northeastern Japan. Fish Sci 77:785–793
Walsh CT, Pease BC (2002) The use of clove oil as an anaesthetic for the longfinned eel, Anguilla reinhardtii (Steindachner). Aquac Res 33:627–635
Wasserman RJ, Pereira-da-Conceicoa LL, Strydom NA, Weyl O (2012) Diet of Anguilla mossambica (Teleostei, Anguillidae) elvers in the Sundays River, eastern cape, South Africa. Afr J Aquat Sci 37:347–349
Winter HV, Jansen HM, Bruijs MCM (2006) Assessing the impact of hydropower and fisheries on downstream migrating silver eel, Anguilla anguilla, by telemetry in the river Meuse. Ecol Freshw Fish 15:221–228
Yokouchi K, Fukuda N, Miller MJ, Aoyama J, Daverat F, Tsukamoto K (2012) Influences of early habitat use on the migratory plasticity and demography of Japanese eels in Central Japan. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 107:132–140
Yokoyama H, Ishihi Y (2003) Feeding of the bivalve Theora lubrica on benthic microalgae: isotopic evidence. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 255:303–309
Yokoyama H, Ishihi Y (2006) Variation in δ13C and δ15N among different tissues of three estuarine bivalves: implications for dietary reconstructions. Plankton Benthos Res 1:178–182
Yokoyama H, Sakami T, Ishihi Y (2009) Food sources of benthic animals on intertidal and subtidal bottoms in inner Ariake sound, southern Japan, determined by stable isotopes. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 82:243–253
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere thanks to the staff of the Soma Branch of Fukushima Prefectural Fisheries Experimental Station, Nobuaki Arai, Hiromichi Mitamura, Takuji Noda, Hideki Sawada, Takuhei Komaki, Junichi Takagi, Tomoya Hori of Kyoto University, Akihide Kasai, Seokjin Yoon, Yousuke Sadayuki of Hokkaido University, Naoki Fushimi of Futaba Koken LTD, and Hiromi Uno of the Center of Ecological Research, Kyoto University for supporting the field work. We are grateful to Hisashi Yokoyama for his kind help with analyzing stable isotope ratios. The stable isotope analysis was conducted using the Cooperative Research Facilities (Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer) of the Center for Ecological Research, Kyoto University. Sampling procedures in this study were performed in accordance with the “Guidelines for the Use of Fishes in Research” published by the Ichthyological Society of Japan in 2003 (http://www.fish-isj.jp/6nglish/guidelines.html).
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI (16H02563) to Yoh Yamashita and by the Link Again Program of the Nippon Foundation - Kyoto University Joint Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 24 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kutzer, A., Lavergne, E., Kume, M. et al. Foraging behavior of yellow-phase Japanese eels between connected fresh- and brackish water habitats. Environ Biol Fish 103, 1061–1077 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-020-01002-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-020-01002-6