Abstract
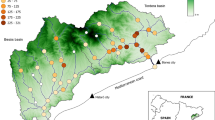
Catalysts for species decline are difficult to identify and are rarely single. The use of predictive models that incorporate multiple factors have proven useful in recognizing major drivers of species declines in multiple systems. In this study, a geographic information systems model was used to evaluate factors contributing to the decline of the Slackwater Darter throughout its distributional range. The species has suffered a precipitous decline, and it is essential to understand conservation threats and to prioritize habitat for restoration and protection. Variables incorporated into the habitat model included land use/land cover, soil and geographic descriptions, hydrologic variables, and others. Habitat where the species has become extirpated or undetectable by conventional sampling was compared to extant populations to identify factors contributing to population loss. Land cover and farm pond density were identified as potential drivers of extirpation. Finally, a model of suitable habitat was used to predict spawning areas in Limestone Creek, where the species was recently discovered. This model identified eight new spawning sites for Slackwater Darter in the system where breeding sites were unknown, and was 44% accurate in its predictive capabilities; however, positive detections were noticeably clustered and indicate the likely influence of some untested variable. With the information provided by this analysis, a framework for habitat protection can be created to assist with restoration of this species.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan JD (2004) Landscapes and riverscapes: the influence of land use on stream ecosystems. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 35:25–284
Bernal NA, DeAngelis DL, Schofield PJ, Sealey KS (2015) Predicting spatial and temporal distribution of indo-Pacific lionfish (Pterois volitans) in Biscayne Bay through habitat suitability modeling. Biol Invasions 17:1603–1614
Boschung, HT, (1976) 1. An evaluation of the Slackwater Darter Etheostoma boschungi, relative to its range, critical habitat, and reproductive habits in the Cypress Creek watershed and adjacent streamsystems. 2. An assessment of the probable impacts of the Cypress Creek watershed project on the Slackwater Darter and its critical habitat. Auburn, Alabama
Clausen R, York R (2008) Global biodiversity decline of marine and freshwater fish: a cross-national analysis of economic, demographic, and ecological influences. Soc Sci Res 37:1310–1320
Cummings KS, Mayer CA, Szafoni RE (1998) Endangered freshwater mussels (Mollusca: Unionidae) in the north fork Vermilion River, Illinois with comments on the federally endangered clubshell, Pleurobema clava (Lamarck, 1819). Trans Ill State Acad Sci 91:91–102
Daniels RA (1989) Habitat of the eastern sand darter, Ammocrypta pellucida. J Freshw Ecol 8:287–295
Darling JA, Mahon AR (2011) From molecules to management: adopting DNA-based methods for monitoring biological invasions in aquatic environments. Environ Res 111:978–988
Ficetola GF, Miaud C, Pompanon F, Taberlet P (2008) Species detection using environmental DNA from water samples. Biol Lett 4:423–425
Ficetola GF, Pansu J, Bonin A, Coissac E, Giguet-Covex C, De Barba M, Gielly L, Lopes CM, Boyer F, Pompanon F, Raye T (2015) Replication levels, false presences and the estimation of the presence/absence from eDNA metabarcoding data. Mol Ecol Resour 15:543–556
Fluker BL, Kuhajda BR, Harris PM (2011) Conservation genetics of spring associated darters in Alabama. Tuscaloosa, Alabama
Germer S, Neill C, Rusche AV, Elsenbeer H (2010) Influence of land-use change on near-surface hydrological processes: undisturbed forest to pasture. Hydrology 380:473–480
Janosik AM, Johnston CE (2015) Environmental DNA as an effective tool for detection of imperiled fishes. Environ Biol Fish 98:1889–1893
Januchowski-Hartley SR, McIntyre PB, Diebel M, Doran PJ, Infante DM, Joseph C, Allan JD (2013) Restoring aquatic ecosystem connectivity requires expanding inventories of both dams and road crossings. Front Ecol Environ 11:211–217
Jenks, GF (1967) The data model concept in statistical mapping. International Yearbook of Cartography 7:186–190
Jerde CL, Chadderton WL, Mahon AR, Renshaw MA, Corush J, Budny ML, Mysorekar S, Lodge DM (2013) Detection of Asian carp DNA as part of a Great Lakes basin-wide surveillance program. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 70:522–526
Johnston CE, Henderson AR, Hartup WW (2013) Precipitous decline and conservation of Slackwater darter (Etheostoma boschungi) in tributaries of the Tennessee River, Tennessee and Alabama. Biodivers Conserv 22:3247–3259
McGregor SW, Shepard TE (1995) Investigations of Slackwater darter, Etheostoma boschungi, populations, 1992-94. Geol Surv Ala 184:1–33
Mckelvey KS, Young MK, Knotek WL, Carim KJ, Wilcox TM, Padgett-Stewart TM, Schwartz MK (2016) Sampling large geographic areas for rare species using environmental DNA: a study of bull trout Salvelinus confluenus occupancy in western Montana. J Fish Biol 88:1215–1222
Oliver MA, Webster R (1990) Kriging: a method of interpolation for geographical information systems. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 4:99–107
Pfleger MO, Rider SJ, Johnston CE, Janosik AM (2016) Saving the doomed: using eDNA to aid in detection of rare sturgeon for conservation (Acipenseridae). Global Ecol Conserv 8:99–107
Richman NI, Bohm M, Adams SB, Alvarez F, Bergey EA, Bunn JJS, Burnham Q, Cordeiro J, Coughran J, Crandall KA et al (2015) Multiple drivers of decline in the global status of freshwater crayfish (Decapoda: Astacidea). Philosophical T Roy Soc B. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2014.0060
Scanlon BR, Reedy RC, Stonestrom DA, Dennchy KF (2005) Impact of land use and land cover change on groundwater recharge and quality in the southwestern U. S. Glob Change Biol 11:1577–1593
Stanbury KB, Starr RM (1999) Applications of geographic information systems (GIS) to habitat assessment and marine resource management. Oceanol Acta 22:699–703
Stendera, S., Adrian, R., Bonada, N., Canedo-Arguelles, M., Hugueny, B., Januschke, Pletterbauer, F., Hering, D (2012) Drivers and stressors of freshwater biodiversity across different ecosystems and scales: a review. Hydrobiologia 696: 1–28
Steinman AD, Conklin J, Bohlen PJ, Uzarski DG (2003) Influence of cattle grazing and pasture land use on macroinvertebrate communities in freshwater wetlands. Wetlands 23:877–889
Taylor CA, Burr BM, Cook KM (1994) Status and distribution of three rare Illinois fishes: Blacktail shiner (Cyprinella venusta), northern Starhead topminnow (Fundulus dispar), and cypress darter (Etheostoma proeliare). Trans Ill State Acad Sci 87:71–82
US Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS) (2008) Slackwater darter (Etheostoma boschungi) 5-year review: summary and evaluation. Jackson, Mississippi
Utz RM, Hilderbrand RH, Raesly RL (2010) Regional differences in patterns of fish species loss with changing land use. Biol Conserv 143:688–699
Wall BR, Williams JD (1974) Etheostoma boschungi, a new percid fish from the Tennessee drainage in northern Alabama and western Tennessee. Tulane Stud Zool 18:172
Wang L, Lyons J, Kanchl P, Gatti R (1997) Influences of watershed landuse on habitat quality and biotic integrity in Wisconsin streams. Fisheries 22:6–12
Zhang C, Jordan C, Higgins A (2007) Using neighborhood statistics and GIS to quantify and visualize spatial variation in geochemical variables: an example using Ni concentrations in the topsoils of Northern Ireland. Geoderma 137:466–476
Acknowledgements
We thank Jenna, Crovo, Warren Stiles, Davis Todd, Drew Jarrett, Jeffy Zeyl Eve Brantley and Brian Helms for their invaluable suggestions and assistance with the multiple components of this project Project funding was provided by the Alabama Department of Conservation and Natural Resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix 1
Appendix 2 External ArcGIS data sources
*All downloaded datasets were transformed and projected into WGS 84/UTM Zone 16 N.
Roads data
Streams data
-
Tennessee: http://www.tngis.org/water.htm
County outlines:
State outlines were downloaded from the USA State Boundaries Layer Package provided by esri on arggis.com
https://www.arcgis.com/home/item.html?id=540003aa59b047d7a1f465f7b1df1950
Soils data were downloaded from ArcGIS.com as a data download package derived from the 2014 NRCS SSURGO data: https://www.arcgis.com/home/item.html?id=a23eb436f6ec4ad6982000dbaddea5ea
Land cover data was obtained from the 2011 National Land Cover Dataset: https://www.mrlc.gov/nlcd2011.php
Watershed boundaries were clipped from the National Hydrography Dataset: https://nhd.usgs.gov/wbd.html
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, M.B., Johnston, C.E. & Janosik, A. A habitat risk assessment and breeding site projection for Slackwater darter (Etheostoma boschungi) (Percidae) in Alabama and Tennessee USA. Environ Biol Fish 102, 685–703 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-019-00862-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-019-00862-x