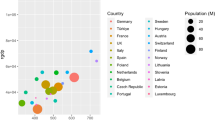
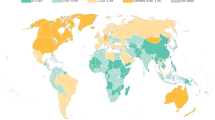
Abstract
Waste generation and waste disposal are becoming increasingly prominent in the environmental arena, from a policy perspective and in the context of delinking analysis. In general, waste generation is still increasing proportionally with income, and economic and environmental costs associated to landfilling are also increasing. This paper provides a comprehensive analysis of waste generation, incineration and landfill dynamics based on panel data for the EU25, to assess the effects of different drivers (economic, structural, policy) and the eventual differences between Western and Eastern EU countries. We show that for waste generation there is still no Waste Kuznets Curve (WKC) trend, although elasticity to income drivers appears lower than in the past. Landfill and other policy effects do not seem to provide backward incentives for waste prevention, and in terms of landfill and incineration, as expected, they are respectively decreasing and increasing, with policy acting as a strong driver. Eastern countries appear to be performing generally quite well, thus benefiting from EU membership and related policies in terms of environmental performance. We can conclude that although absolute delinking is far from being achieved for waste generation, there are some first positive signs of an increasing relative delinking for waste generation and robust landfill diversion, and varying evidence of a significant role of the EU waste policies implemented in the late 1990s and early 2000s. Our evidence suggests that if while landfill diversion is currently associated to a delinking partly explained by EU policies, waste prevention must be the next objective of waste regulation efforts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpay S, Caliskan A, Mahmud S (2006) Environmental policy performance, economic growth and trade liberalization: a cross country empirical analysis. Department of Economics, Bilkent University, mimeo
Andersen F, Larsen H, Skovgaard M, Moll S, Isoard S (2007) A European model for waste and material flows. Resour Conserv Recycl 49(4): 421–435
André F, Cerda E (2004) Landfill construction and capacity expansion. Environ Resour Econ 28: 409–434
Andreoni J, Levinson A (2001) The simple analytics of the Environmental Kuznets Curve. J Public Econ 80(2): 269–286
Arellano M, Bond S (1991) Some tests of specification for panel data: Monte Carlo evidence and an application to employment equations. Rev Econ Stud 58: 277–297
Beede D, Bloom D (1995) Economics of the generation and management of MSW. NBER Working Paper 5116, Cambridge, Mass: NBER
Berglund C, Soderholm P (2003) An econometric analysis of global waste paper recovery and utilization. Environ Resour Econ 26: 429–456
Berrens R, Bohara A, Gawande K, Wang P (1998) Testing the inverted U hypothesis for US hazardous waste an application of the generalized gamma model. Econ Lett 55(3): 435–440
Bluffstone R, Deshazo JR (2003) Upgrading municipal environmental services to EU level: a case study of household willingness to pay in Lithuania. Environ Dev Econ 8: 637–654
Brisson I, Pearce D (1995) Benefit transfer for disamenity from waste disposal. CSERGE working paper No 6, UCL, London
Brock W, Taylor S (2004) The green solow model. NBER working paper No 10557. National Bureau of Economic Research, Cambridge, Massachusetts
Bruno GSF (2005) Approximating the Bias of the LSDV estimator for dynamic unbalanced panel data models. Econ Lett 87(3): 361–366
Cagatay S, Mihci H (2003) Industrial pollution, environmental suffering and policy measures: an index of environmental sensitivity performance. J Environ Assess Policy Manag 5: 205–245
Cagatay S, Mihci H (2006) Degree of environmental stringency and the impact on trade patterns. J Econ Stud 33(1): 30–51
Callan J, Thomas S (1999) Adopting a unit pricing system for MSW: policy and socio-economic determinants. Environ Resour Econ 14: 503–518
Callan S, Thomas J (2006) Analyzing demand for disposal and recycling services: a systems approach. East Econ J 32(2): 221–240
Caplan A, Grijalva T, Jackson-Smith D (2007) Using choice question formats to determine compensable values: the case of a landfill-siting process. Ecol Econ 60: 834–846
Chavas JP (2004) On impatience, economic growth and the EKC: a dynamic analysis of resource management. Environ Resour Econ 28(2): 123–152
Choe C, Fraser I (1999) An economic analysis of household waste management. J Environ Econ Manag 38: 234–246
Cole M (2005) Re-examining the pollution-income relationship: a random coefficients approach. Econ Bull 14: 1–7
Cole M, Rayner A, Bates J (1997) The EKC: an empirical analysis. Environ Dev Econ 2: 401–416
Cole M, Elliott R, Shimamoto K (2005) Industrial characteristics, environmental regulations and air pollution: an analysis of the UK manufacturing sector. J Environ Econ Manag 50: 121–143
Cole M, Elliott R, Fredrikkson P (2006) Endogenous pollution haves: does FDI influence environmental regulations?. Scand J Econ 108(1): 157–178
DEFRA (2005) A study to estimate the disamenity costs of landfill in Great Britain. DEFRA, London
DEFRA/DTI (2003) Sustainable consumption and production indicators. DEFRA, London
Dijkgraaf E, Vollebergh H (2004) Burn or bury? A social cost comparison of final waste disposal methods. Ecol Econ 50: 233–247
Dinda S (2005) Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis: a survey. Ecol Econ 49: 431–455
EC (2008) Directive 2008/98/EC of the European parliament and of the council of 19 November 2008 on waste and repealing certain directives. European Commission, Bruxelles
EEA (2006) Market-based instruments for environmental policy in Europe (technical report No 8/2005). European Environment Agency, Copenhagen
EEA (2007) The road from landfilling to recycling: common destination different routes. European Environment Agency, Copenhagen
El-Fadel M, Findikakis A, Leckie J (1997) Environmental impacts of solid waste landfilling. J Environ Manag 50(1): 1–25
Eliste P, Fredrikkson PG (1998) Does open trade result in a race to the bottom? Cross country evidence. The World Bank, mimeo
Eshet T, Ayalon O, Shechter M (2004) A meta analysis of waste management externalities: a comparative study of economic and non economic valuation methods. University of Haifa, Israel, mimeo
European Commission (EC) (2003a) Towards a thematic strategy for waste prevention and recycling, COM (2003) 301. European Commission, Brussels
European Commission (EC) (2003b) Towards a thematic strategy on sustainable use of natural resources COM (2003) 572. European Commission, Brussels
Ferrara I, Missios P (2005) Recycling and waste diversion effectiveness: evidence from Canada. Environ Resour Econ 30: 221–238
Fischer-Kowalski M, Amann C (2001) Beyond IPAT and Kuznets Curves: globalization as a vital factor in analyzing the environmental impact of socio economic metabolism. Popul Environ 23: 7–47
Fredriksson P (2000) The siting of hazardous waste facilities in federal systems. Environ Resour Econ 15: 75–87
Gallagher L, Ferreira S, Convery F (2008) Host community attitudes towards solid waste infrastructures: comprehension before compensation. J Environ Plan manag 51(2): 233–257
Gawande K, Berrens R, Bohara A (2001) A consumption based theory of the EKC. Ecol Econ 37(1): 101–112
Glachant M (2004) Changing product characteristics to reduce waste generation. In: OECD (2004), Addressing the Economics of waste. OECD: Paris
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1994) Economic growth and the environment. NBER Working papers 4634. National Bureau of Economic Research, Cambridge, Massachusetts
Highfill J, McCasey M (2001) Landfilling versus backstop recycling when income is growing. Environ Resour Econ 19: 37–52
Holtz-Eakin D, Selden TM (1992) Stoking the fires? CO2 emissions and economic growth. NBER working papers 4248. National Bureau of Economic Research, Cambridge, Massachusetts
Huhtala A (1997) A post consumer waste management model for determining optimal levels of recycling and landfilling. Environ Resour Econ 10: 310–314
Jacobsen H, Mazzanti M, Moll S, Simeone MG, Pontoglio S, Zoboli R (2004) Methodology and indicators to measure decoupling, resource efficiency, and waste prevention. ETC/WMF, European topic centre on waste and material flows. European Environment Agency, Copenhagen
Jenkins R, Maguire K, Morgan C (2004) Host community compensation and municipal solid waste landfills. Land Econ 80: 513–528
Johnstone N, Labonne J (2004) Generation of household solid waste in OECD countries. An empirical analysis using macroeconomic data. Land Econ 80(4): 529–538
Karousakis K (2009) MSW generation disposal and recycling: empirical evidence from OECD countries. In: Mazzanti M, Montini A (eds) Waste & environmental policy. Routledge, London
Kiviet JF (1995) On Bias inconsistency and efficiency of various estimators in dynamic panel data models. J Econom 68: 53–78
Lang JC (2005) Zero landfill zero waste: the greening of industry in Singapore. Int J Environ Sustain Dev 4: 331–351
Lieb CM (2004) The Environmental Kuznets Curve and flow versus stock pollution: the neglect of future damages. Environ Resour Econ 29(4): 483–506
List JA, Gallet CA (1999) Does one size fits all?. Ecol Econ 31: 409–424
Martin A, Scott I (2003) The effectiveness of the UK landfill tax. J Environ Plan Manag 46(5): 673–689
Mazzanti M (2008) Is waste generation de-linking from economic growth?. Appl Econ Lett 15(4): 287–291
Mazzanti M, Montini A (eds) (2009) Waste & environmental policy. Routledge, London
Mazzanti M, Zoboli R (2005) Delinking and Environmental Kuznets Curves for waste indicators in Europe. Environ Sci 2(4): 409–425
Mazzanti M, Montini A, Zoboli R (2008) Municipal waste generation socio-economic drivers and waste management instruments. J Environ Dev 17: 51–69
Miranda ML, Miller J, Jacobs T (2000) Talking trash about landfills: using quantitative scoring schemes in landfill siting processes. J Policy Anal manag 19(1): 3–22
Ozawa T (2005) Hotelling rule and the landfill exhaustion problem: case of Tokyo city. Stud Reg Sci 35: 215–230
Pearce DW (2004) Does European Union waste policy pass a cost benefit test?. World Econ 5(3): 115–137
Powell J, Brisson I (1995) Benefit transfer for disamenity from waste disposal. CSERGE working paper. UCL, London
Raymond L (2004) Economic growth as environmental policy? Reconsidering the Environmental Kuznets Curve. J Public Policy 24: 27–48
Rothman D (1998) EKC real progress or passing the buck? A case for consumption based approaches. Ecol Econ 25: 177–194
Seppala T, Haukioja T, Kaivo-Oja J (2001) The EKC hypothesis does not hold for direct material flows: EKC hypothesis tests for DMF in four industrial countries. Population and the environment 23(2): 217–238
Stern D (1998) Progress on the Environmental Kuznets Curve?. Environ Dev Econ 3: 173–196
Stern D (2004) The rise and fall of the Environmental Kuznets Curve. World Dev 32(8): 1419–1438
Sterner T, Bartelings H (1999) Household waste management in a Swedish municipality: determinants of waste disposal, recycling and composting. Environ Resour Econ 13: 473–491
Swamy PA (1970) Efficient inference in a random coeffcient regression model. Econometrica 38: 311–323
Taseli B (2007) The impact of the European landfill directive on waste management strategy and current legislation in Turkey’s specially protected areas. Resour Conserv Recycl 52: 119–135
Wang P, Bohara A, Berrens R, Gawande K (1998) A risk based Environmental Kuznets Curve for US hazardous waste sites. Appl Econ Lett 5: 761–763
Watson M, Bulkeley H, Hudson R (2008) Unpicking environmental policy integration from tales of waste management. Environ Plan C 26: 481–498
Wooldridge J (2003) Econometric analysis of cross section and panel data. The MIT press, Cambridge Mass
World Bank (1992) Development and the environment, World bank Report. Oxford University Press, Washington, DC
Yang HL, Innes R (2007) Economic incentives and residential waste management in Taiwan: an empirical investigation. Environ Resour Econ 37: 489–519
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mazzanti, M., Zoboli, R. Municipal Waste Kuznets Curves: Evidence on Socio-Economic Drivers and Policy Effectiveness from the EU. Environ Resource Econ 44, 203–230 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-009-9280-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-009-9280-x
Keywords
- Waste Kuznets Curves
- Delinking
- Waste management
- Waste policies
- Policy evaluation
- Landfill diversion
- Waste generation
- Incineration
- Waste prevention