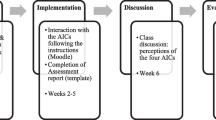
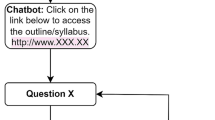
Abstract
Chatbots are tools that have the potential to effectively support interpersonal communication and interaction. Chatbots can provide great opportunities in education. The use of chatbots in education can be used to employ interactive methods, to provide learners information and different types of info, and to guide learners. Indeed, chatbots promise to enhance learning experiences by creating more interaction than traditional teaching practices provide. In this context, the purpose of this study is to apply chatbot technology as a guidance tool in educational environments and to model its effects on visual design self-efficacy, engagement, satisfaction, and learner autonomy at the end of the process. The participants of the study are 86 university students. In this study, data were collected with 4 different scales. Data were analyzed using the variance-based structural equation model with the partial least square method. As a result of the study, it was found that students with higher chatbot usage satisfaction had higher visual design self-efficacy. Chatbot usage satisfaction positively affects some aspects of course satisfaction. Chatbot usage satisfaction affects engagement. The effects of the study results in terms of research and practice were discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamopoulou, E., & Moussiades, L. (2020). An overview of chatbot technology. In I. Maglogiannis, L. Iliadis, & E. Pimenidis (Eds.), Artificial intelligence applications and innovations. AIAI 2020. IFIP advances in information and communication technology (584 vol., pp. 373–383). Springer
Alkan, M. F., & Arslan, M. (2019). Learner autonomy of pre-service teachers and its associations with academic motivation and self-efficacy. Malaysian Journal of Learning and Instruction, 16(2), 75–96
Axelson, R. D., & Flick, A. (2010). Defining student engagement. Change: The magazine of higher learning, 43(1), 38–43
Dekker, I., De Jong, E. M., Schippers, M. C., De Bruijn-Smolders, M., Alexiou, A., & Giesbers, B. (2020). Optimizing students’ mental health and academic performance: AI-enhanced life crafting. Frontiers in Psychology, 11(June), 1–15
Dixson, M. D. (2010). Creating Effective Student Engagement in Online Courses: What Do Students Find Engaging? Journal of the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 10(2), 1–13
Dixson, M. D. (2015). Measuring student engagement in the online course: The Online Student Engagement scale (OSE). Online Learning, 19(4), n4
Geçer, A. K., & Topal, A. D. (2015). Development of Satisfaction Scale For E-Course: Reliability and Validity Study. Eğitimde Kuram ve Uygulama, 11(4), 1272–1287
Gonda, D. E., Luo, J., Wong, Y. L., & Lei, C. U. (2019). Evaluation of developing educational chatbots based on the seven principles for good teaching. Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE international conference on teaching, assessment, and learning for engineering, TALE 2018, Australia, 446–453. IEEE
Gülbahar, Y. (2012). Study of developing scales for assessment of the levels of readiness and satisfaction of participants in e-learning environments. Ankara University Journal of Faculty of Educational Sciences (JFES), 45(2), 119–138
Haristiani, N., & Rifai, M. M. (2021). Chatbot-based application development and implementation as an autonomous language learning medium. Indonesian Journal of Science and Technology, 6(3), 561–576
Haristiani, N., Danuwijaya, A. A., Rifai, M. M., & Sarila, H. (2019). Gengobot: A chatbot-based grammar application on mobile instant messaging as language learning medium. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 14(6), 3158–3173
Hill, J., Ford, W. R., & Farreras, I. G. (2015). Real conversations with artificial intelligence: A comparison between human–human online conversations and human–chatbot conversations. Computers in Human Behavior, 49, 245–250
Huang, W., Hew, K. F., & Fryer, L. K. (2021). Chatbots for language learning—Are they really useful? A systematic review of chatbot-supported language learning.Journal of Computer Assisted Learning
Hwang, G. J., & Chang, C. Y. (2021). A review of opportunities and challenges of chatbots in education.Interactive Learning Environments,1–14
Khan, A., Ranka, S., Khakare, C., & Karve, S. (2019). NEEV: An education informational chatbot. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 6(4), 492–495
Kılıç, K. (2020). An action research on computer assisted illustration practices within the scope of elective graphic design course. Unpublished PhD thesis. Ondokuz Mayıs University, Turkey
Kim, N. Y., Cha, Y., & Kim, H. S. (2019). Future English learning: Chatbots and artificial intelligence. Multimedia-Assisted Language Learning, 22(3), 32–53
Kumar, J. A. (2021). Educational chatbots for project-based learning: investigating learning outcomes for a team-based design course. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 18(1), 1–28
Martín-Rodríguez, Ó., Fernández-Molina, J. C., Montero-Alonso, M., & González-Gómez, F. (2015). The main components of satisfaction with e-learning. Technology Pedagogy and Education, 24(2), 267–277
Muniasamy, A., & Alasiry, A. (2020). Deep learning: The impact on future eLearning. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning, 15(1), 188–199
Newman, F. M., Wehlage, G. G., & Lamborn, S. D. (1992). Taking students seriously. Student engagement and achievement in American secondary schools. New York: Teachers College, Columbia University
Nguyen, Q. N., Sidorova, A., & Torres, R. (2021a). User interactions with chatbot interfaces vs. Menu-based interfaces: An empirical study.Computers in Human Behavior,107093
Nguyen, Q. N., Sidorova, A., & Torres, R. (2021b). User interactions with chatbot interfaces vs. Menu-based interfaces: An empirical study.Computers in Human Behavior,107093
Pereira, J., Fernández-Raga, M., Osuna-Acedo, S., Roura-Redondo, M., Almazán-López, O., & Buldón-Olalla, A. (2019). Promoting learners’ voice productions using chatbots as a tool for improving the learning process in a MOOC. Technology Knowledge and Learning, 24(4), 545–565
Pérez, J. Q., Daradoumis, T., & Puig, J. M. M. (2020). Rediscovering the use of chatbots in education: A systematic literature review. Computer Applications in Engineering Education, 28(6), 1549–1565
Polat, E., Hopcan, S., & Kamalı Arslantaş, T. (2022). Çevrimiçi Öğrenci Bağlılık Ölçeğinin Türkçe’ye Uyarlanması: Geçerlik ve Güvenirlik Çalışması. Eğitim Teknolojisi Kuram ve Uygulama, 12(1), 41–56
Poncette, A. S., Rojas, P. D., Hofferbert, J., Sosa, A. V., Balzer, F., & Braune, K. (2020). Hackathons as stepping stones in health care innovation: Case study with systematic recommendations.Journal of Medical Internet Research, 22(3), e17004
Rheu, M., Shin, J. Y., Peng, W., & Huh-Yoo, J. (2021). Systematic review: trust-building factors and implications for conversational agent design. International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction, 37(1), 81–96
Schmulian, A., & Coetzee, S. A. (2019). The development of Messenger bots for teaching and learning and accounting students’ experience of the use thereof. British Journal of Educational Technology, 50(5), 2751–2777
Smutny, P., & Schreiberova, P. (2020). Chatbots for learning: A review of educational chatbots for the Facebook Messenger. Computers & Education, 151, 103862
Uzunboylu, H., & Oz, C. (2016). Graphics Development for the Self-efficacy Scale: A Study of Validity and Reliability. International Journal of Educational Sciences, 15(1–2), 269–278
Wang, J., Hwang, G., & Chang, C. (2021). Directions of the 100 most cited chatbot-related human behavior research: A review of academic publications. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 2, 1–12
Wu, E. H. K., Lin, C. H., Ou, Y. Y., Liu, C. Z., Wang, W. K., & Chao, C. Y. (2020). Advantages and constraints of a hybrid model K-12 E-Learning assistant chatbot. Ieee Access : Practical Innovations, Open Solutions, 8, 77788–77801
Yuan, C. C., Li, C. H., & Peng, C. C. (2021). Development of mobile interactive courses based on an artificial intelligence chatbot on the communication software LINE.Interactive Learning Environments,1–15
Zhou, L., Gao, J., Li, D., & Shum, H. Y. (2020). The design and implementation of xiaoice, an empathetic social chatbot. Computational Linguistics, 46(1), 53–93
Yildiz Durak, H. (2019). Investigation of nomophobia and smartphone addiction predictors among adolescents in Turkey: Demographic variables and academic performance. The Social Science Journal, 56(4), 492–517. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soscij.2018.09.003
Yildiz Durak, H., & Saritepeci, M. (2019). Modeling the Effect of New Media Literacy Levels and Social Media Usage Status on Problematic Internet Usage Behaviours among High School Students. Education and Informations Technologies, 24(4), 2205–2223. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-019-09864-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
YILDIZ DURAK, H. Conversational agent-based guidance: examining the effect of chatbot usage frequency and satisfaction on visual design self-efficacy, engagement, satisfaction, and learner autonomy. Educ Inf Technol 28, 471–488 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11149-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11149-7