Abstract
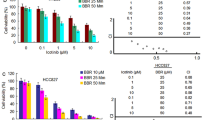
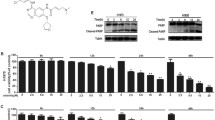
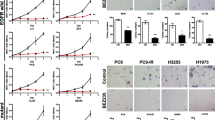
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Combination of drugs targeting independent signaling pathways would effectively block the proliferation of cancer cells with lower concentrations and stronger synergy effects. Dasatinib, a multi-targeted protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting BCR-ABL and kinases of SRC family, has been successfully applied in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). BMS-754807, an inhibitor targeting the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-IR) and insulin receptor (IR) family kinases, has been in phase I development for the treatment of a variety of human cancers. Herein, we demonstrated that dasatinib in combination with BMS-754807 inhibited lung cancer cell growth, while induced autophagy as well as cell cycle arrest at the G1 phase. Dasatinib in combination with BMS-754807 suppressed the expression of cell cycle marker proteins, Rb, p-Rb, CDK4, CDK6 and Cyclin D1, and the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Dasatinib in combination with BMS-754807 induced autophagy in lung cancer cells, evidenced by the upregulation of LC3B II and beclin-1, the downregulation of LC3B I and SQSTM1/p62, and the autophagic flux observed with a confocal fluorescence microscopy. Furthermore, dasatinib (18 mg/kg) in combination with BMS-754807 (18 mg/kg) inhibited the growth of tumors in NCI-H3255 xenografts without changing the bodyweight. Overall, our results suggest that dasatinib in combination with BMS-754807 inhibits the lung cancer cell proliferation in vitro and tumor growth in vitro, which indicates promising evidence for the application of the drug combination in lung cancer therapy.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Wang M, Herbst RS, Boshoff C (2021) Toward personalized treatment approaches for non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Med 27(8):1345–1356
Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, Akerley W, Bauman JR, Bharat A, Bruno DS et al (2022) Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 3.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 20(5):497–530
Bade BC, Dela Cruz CS (2020) Lung cancer 2020: epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin Chest Med 41(1):1–24
Boumahdi S, de Sauvage FJ (2020) The great escape: tumour cell plasticity in resistance to targeted therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 19(1):39–56
Shen J, Li L, Yang T, Cohen PS, Sun G (2020) Biphasic mathematical model of cell-drug interaction that separates target-specific and off-target inhibition and suggests potent targeted drug combinations for multi-driver colorectal cancer cells. Cancers (Basel) 12(2):436
Alkebsi L, Wang X, Ohkawara H, Fukatsu M, Mori H, Ikezoe T (2021) Dasatinib induces endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human vascular-endothelial cells: counteracted by cotreatment with bosutinib. Int J Hematol 113(3):441–455
Liu C, Zhu X, Jia Y, Chi F, Qin K, Pei J, Zhang C et al (2021) Dasatinib inhibits proliferation of liver cancer cells, but activation of Akt/mTOR compromises dasatinib as a cancer drug. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 53(7):823–836
Huang WC, Kuo KT, Wang CH, Yeh CT, Wang Y (2019) Cisplatin resistant lung cancer cells promoted M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages via the Src/CD155/MIF functional pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):180
Hsu PC, Yang CT, Jablons DM, You L (2020) The crosstalk between src and Hippo/YAP signaling pathways in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Cancers (Basel) 12(6):1361
Fan PD, Narzisi G, Jayaprakash AD, Venturini E, Robine N, Smibert P, Germer S et al (2018) YES1 amplification is a mechanism of acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors identified by transposon mutagenesis and clinical genomics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(26):E6030–E6038
Fuentes-Baile M, Ventero MP, Encinar JA, García-Morales P, Poveda-Deltell M, Pérez-Valenciano E, Barberá VM et al (2020) Differential effects of IGF-1R small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors BMS-754807 and OSI-906 on human cancer cell lines. Cancers (Basel) 12(12):3717
Xue L, Chen F, Yue F, Camacho L, Kothapalli S, Wei G, Huang S et al (2021) Metformin and an insulin/IGF-1 receptor inhibitor are synergistic in blocking growth of triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 185(1):73–84
Zeng B, Liao X, Liu L, Zhang C, Ruan H, Yang B (2021) Thyroid hormone mediates cardioprotection against postinfarction remodeling and dysfunction through the IGF-1/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Life Sci 267:118977
Franks SE, Jones RA, Briah R, Murray P, Moorehead RA (2016) BMS-754807 is cytotoxic to non-small cell lung cancer cells and enhances the effects of platinum chemotherapeutics in the human lung cancer cell line A549. BMC Res Notes 9:134
Dong AQ, Kong MJ, Ma ZY, Qian JF, Xu XH (2007) Down-regulation of IGF-IR using small, interfering, hairpin RNA (siRNA) inhibits growth of human lung cancer cell line A549 in vitro and in nude mice. Cell Biol Int 31(5):500–507
Reinmuth N, Kloos S, Warth A, Risch A, Muley T, Hoffmann H, Thomas M et al (2014) Insulin-like growth factor 1 pathway mutations and protein expression in resected non-small cell lung cancer. Hum Pathol 45(6):1162–1168
Siddle K (2011) Signalling by insulin and IGF receptors: supporting acts and new players. J Mol Endocrinol 47(1):R1–10
Lehman CE, Spencer A, Hall S, Shaw JJP, Wulfkuhle J, Petricoin EF, Bekiranov S et al (2021) IGF1R and src inhibition induce synergistic cytotoxicity in HNSCC through inhibition of FAK. Sci Rep 11(1):10826
Shen J, Li L, Yang T, Cheng N, Sun G (2019) Drug sensitivity screening and targeted pathway analysis reveal a multi-driver proliferative mechanism and suggest a strategy of combination targeted therapy for colorectal cancer cells. Molecules 24(3):623
Awasthi N, Zhang C, Ruan W, Schwarz MA, Schwarz RE (2012) BMS-754807, a small-molecule inhibitor of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor/insulin receptor, enhances gemcitabine response in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 11(12):2644–2653
Camidge DR, Otterson GA, Clark JW, Ignatius Ou SH, Weiss J, Ades S, Shapiro GI et al (2021) Crizotinib in patients with MET-amplified NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol 16(6):1017–1029
Chen Z, Chen Q, Cheng Z, Gu J, Feng W, Lei T, Huang J et al (2020) Long non-coding RNA CASC9 promotes gefitinib resistance in NSCLC by epigenetic repression of DUSP1. Cell Death Dis 11(10):858
Liu R, Chen Y, Liu G, Li C, Song Y, Cao Z, Li W et al (2020) PI3K/AKT pathway as a key link modulates the multidrug resistance of cancers. Cell Death Dis 11(9):797
Nepstad I, Hatfield KJ, Grønningsæter IS, Reikvam H (2020) The PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in human acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells. Int J Mol Sci 21(8):2907
Tan AC (2020) Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Thorac Cancer 11(3):511–518
Bostner J, Karlsson E, Pandiyan MJ, Westman H, Skoog L, Fornander T, Nordenskjöld B et al (2013) Activation of akt, mTOR, and the estrogen receptor as a signature to predict tamoxifen treatment benefit. Breast Cancer Res Treat 137(2):397–406
Lee S, Rauch J, Kolch W (2020) Targeting MAPK signaling in cancer: mechanisms of drug resistance and sensitivity. Int J Mol Sci 21(3):1102
Drosten M, Barbacid M (2020) Targeting the MAPK pathway in KRAS-driven tumors. Cancer Cell 37(4):543–550
Martínez-Alonso D, Malumbres M (2020) Mammalian cell cycle cyclins. Semin Cell Dev Biol 107:28–35
Hume S, Dianov GL, Ramadan K (2020) A unified model for the G1/S cell cycle transition. Nucleic Acids Res 48(22):12483–12501
Levy JMM, Towers CG, Thorburn A (2017) Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 17(9):528–542
Li X, Yang KB, Chen W, Mai J, Wu XQ, Sun T, Wu RY et al (2021) CUL3 (cullin 3)-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of BECN1 (beclin 1) inhibit autophagy and promote tumor progression. Autophagy 17(12):4323–4340
Jia R, Bonifacino JS (2021) The ubiquitin isopeptidase USP10 deubiquitinates LC3B to increase LC3B levels and autophagic activity. J Biol Chem 296:100405
Wen W, Li X, Yin M, Wang H, Qin L, Li H, Liu W et al (2021) Selective autophagy receptor SQSTM1/ p62 inhibits Seneca Valley virus replication by targeting viral VP1 and VP3. Autophagy 17(11):3763–3775
Harrison PT, Vyse S, Huang PH (2020) Rare epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 61:167–179
Belli S, Esposito D, Servetto A, Pesapane A, Formisano L, Bianco R (2020) c-Src and EGFR inhibition in molecular cancer therapy: what else can we improve? Cancers (Basel) 12(6):1489
Chen Z, Oh D, Dubey AK, Yao M, Yang B, Groves JT, Sheetz M (2018) EGFR family and src family kinase interactions: mechanics matters? Curr Opin Cell Biol 51:97–102
Shen J, Li L, Howlett NG, Cohen PS, Sun G (2020) Application of a biphasic mathematical model of cancer cell drug response for formulating potent and synergistic targeted drug combinations to triple negative breast cancer cells. Cancers (Basel) 12(5):1087
Zhang Y, Wang L, Meng L, Cao G, Wu Y (2019) Sirtuin 6 overexpression relieves sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by promoting autophagy. Cell Cycle 18(4):425–436
Lőrincz P, Juhász G (2020) Autophagosome-Lysosome Fusion. J Mol Biol 432(8):2462–2482
Chang C, Jensen LE, Hurley JH (2021) Autophagosome biogenesis comes out of the black box. Nat Cell Biol 23(5):450–456
Mareninova OA, Jia W, Gretler SR, Holthaus CL, Thomas DDH, Pimienta M, Dillon DL et al (2020) Transgenic expression of GFP-LC3 perturbs autophagy in exocrine pancreas and acute pancreatitis responses in mice. Autophagy 16(11):2084–2097
Salazar G, Cullen A, Huang J, Zhao Y, Serino A, Hilenski L, Patrushev N et al (2020) SQSTM1/p62 and PPARGC1A/PGC-1alpha at the interface of autophagy and vascular senescence. Autophagy 16(6):1092–1110
Funding
This work was supported by the grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30901821 and 81172136), Natural Science Basic Project of Shanxi Province, China (No. 20210302124183), Scientific and Technological Innovation Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi (No. 2021L339), Nature Science Project of Shanxi Province, China (Nos. 201701D121165 and 201901D111190), Natural Science Foundation for Young Scientists of Shanxi Province, China (No. 201801D221069), Research Project Supported by Shanxi Scholarship Council of China (Nos. 2020 − 194 and 2021 − 165), Open Fund from Key Laboratory of Cellular Physiology (Shanxi Medical University), Ministry of Education, China (No. KLMEC/SXMU-202011), Shanxi ‘1331 Project’ Key Subjects Construction, China (No. 1331KSC), Outstanding Youth Foundation of Shanxi Province, China (No. 201901D211547), Scientific research project of Shanxi Provincial Health Commission, China (No. 2019059), “136” College-level open fund, China (No. 2021YZ03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: CZ, CL, BY. Performed the experiments: CZ, XZ, ZW. Analyzed the data: CZ, CL. Contributed reagents/materials/analytical tools: CZ, XZ, ZW, TG, HZ, DZ, YN, XL, XZ, GL, XD, LZ, JX. Wrote the paper: CZ, CL, BY.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Zhao, X., Wang, Z. et al. Dasatinib in combination with BMS-754807 induce synergistic cytotoxicity in lung cancer cells through inhibiting lung cancer cell growth, and inducing autophagy as well as cell cycle arrest at the G1 phase. Invest New Drugs 41, 438–452 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-023-01360-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-023-01360-9