Summary
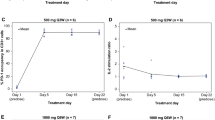
Purpose This study investigated the relationship between the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of everolimus in patients with metastatic breast cancer (mBC) in real-world practice.Methods Twenty-two patients with mBC treated with everolimus plus exemestane were enrolled. Blood everolimus concentrations were measured at outpatient visits. The inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) activity in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) was examined. The efficacy and safety endpoints were progression-free survival (PFS) and the cumulative incidence of dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs), respectively. Results Blood samples were obtained from 19 consenting patients. Everolimus did not completely inhibit mTOR activity in PBMCs at therapeutic concentrations (~ 56 % maximal inhibition). The most common adverse event was stomatitis (any grade 77 %). The trough concentration (Ctrough) was significantly higher in patients experiencing DLTs than in those without any DLTs (P = 0.030). The optimal Ctrough cutoff predicting DLT development was 17.3 ng/mL. The cumulative incidence of DLTs was significantly higher in patients with Ctrough ≥17.3 ng/mL than in other patients (sub-hazard ratio 4.87, 95 % confidence interval [CI] 1.53–15.5; P = 0.007). Furthermore, the median PFS was numerically longer in patients who maintained a steady-state Ctrough below the threshold than in those who did not (327 days [95 % CI 103–355 days] vs. 194 days [95 % CI 45 days–not estimable]; P = 0.35). Conclusions The suggested upper threshold for the therapeutic window of everolimus Ctrough was 17.3 ng/mL. Pharmacokinetically guided dosing may improve the efficacy and safety of everolimus for mBC, warranting further investigation in a larger study.
Clinical trial registry: Not applicable.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available because of privacy or ethical restrictions.
References
Budde K, Becker T, Arns W, Sommerer C, Reinke P, Eisenberger U, Kramer S, Fischer W, Gschaidmeier H, Pietruck F, ZEUS Study Investigators (2011) Everolimus-based, calcineurin-inhibitor-free regimen in recipients of de-novo kidney transplants: an open-label, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 377:837–847
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, Hutson TE, Porta C, Bracarda S, Grünwald V, Thompson JA, Figlin RA, Hollaender N, Urbanowitz G, Berg WJ, Kay A, Lebwohl D, Ravaud A, RECORD-1 Study Group (2008) Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Lancet 372:449–456
Yao JC, Shah MH, Ito T, Bohas CL, Wolin EM, Van Cutsem E, Hobday TJ, Okusaka T, Capdevila J, de Vries EG, Tomassetti P, Pavel ME, Hoosen S, Haas T, Lincy J, Lebwohl D, Öberg K; RAD001 in Advanced Neuroendocrine Tumors, Third Trial (RADIANT-3) Study Group (2011) Everolimus for advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. N Engl J Med 364:514–523
Franz DN, Belousova E, Sparagana S, Bebin EM, Frost M, Kuperman R, Witt O, Kohrman MH, Flamini JR, Wu JY, Curatolo P, de Vries PJ, Whittemore VH, Thiele EA, Ford JP, Shah G, Cauwel H, Lebwohl D, Sahmoud T, Jozwiak S (2013) Efficacy and safety of everolimus for subependymal giant cell astrocytomas associated with tuberous sclerosis complex (EXIST-1): a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 381:125–132
Bissler JJ, Kingswood JC, Radzikowska E, Zonnenberg BA, Frost M, Belousova E, Sauter M, Nonomura N, Brakemeier S, de Vries PJ, Whittemore VH, Chen D, Sahmoud T, Shah G, Lincy J, Lebwohl D, Budde K (2013) Everolimus for angiomyolipoma associated with tuberous sclerosis complex or sporadic lymphangioleiomyomatosis (EXIST-2): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 381:817–824
Baselga J, Campone M, Piccart M, Burris HA 3rd, Rugo HS, Sahmoud T, Noguchi S, Gnant M, Pritchard KI, Lebrun F, Beck JT, Ito Y, Yardley D, Deleu I, Perez A, Bachelot T, Vittori L, Xu Z, Mukhopadhyay P, Lebwohl D, Hortobagyi GN (2012) Everolimus in postmenopausal hormone-receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 366:520–529
Kovarik JM, Kahan BD, Kaplan B, Lorber M, Winkler M, Rouilly M, Gerbeau C, Cambon N, Boger R, Rordorf C, Everolimus Phase 2 Study Group (2001) Longitudinal assessment of everolimus in de novo renal transplant recipients over the first post-transplant year: pharmacokinetics, exposure-response relationships, and influence on cyclosporine. Clin Pharmacol Ther 69:48–56
Kovarik JM, Tedesco H, Pascual J, Civati G, Bizot MN, Geissler J, Schmidli H (2004) Everolimus therapeutic concentration range defined from a prospective trial with reduced-exposure cyclosporine in de novo kidney transplantation. Ther Drug Monit 26:499–505
Franz DN, Belousova E, Sparagana S, Bebin EM, Frost M, Kuperman R, Witt O, Kohrman MH, Flamini JR, Wu JY, Curatolo P, de Vries PJ, Berkowitz N, Anak O, Niolat J, Jozwiak S (2014) Everolimus for subependymal giant cell astrocytoma in patients with tuberous sclerosis complex: 2-year open-label extension of the randomised EXIST-1 study. Lancet Oncol 15:1513–1520
Kirchner GI, Meier-Wiedenbach I, Manns MP (2004) Clinical pharmacokinetics of everolimus. Clin Pharmacokinet 43:83–95
Crowe A, Lemaire M (1998) In vitro and in situ absorption of SDZ-RAD using a human intestinal cell line (Caco-2) and a single pass perfusion model in rats: comparison with rapamycin. Pharm Res 15:1666–1672
Chu C, Abbara C, Noël-Hudson MS, Thomas-Bourgneuf L, Gonin P, Farinotti R, Bonhomme-Faivre L (2009) Disposition of everolimus in mdr1a-/1b- mice and after a pre-treatment of lapatinib in Swiss mice. Biochem Pharmacol 77:1629–1634
Minocha M, Khurana V, Qin B, Pal D, Mitra AK (2012) Co-administration strategy to enhance brain accumulation of vandetanib by modulating P-glycoprotein (P-gp/Abcb1) and breast cancer resistance protein (Bcrp1/Abcg2) mediated efflux with m-TOR inhibitors. Int J Pharm 434:306–314
Lemaitre F, Bezian E, Goldwirt L, Fernandez C, Farinotti R, Varnous S, Urien S, Antignac M (2012) Population pharmacokinetics of everolimus in cardiac recipients: comedications, ABCB1, and CYP3A5 polymorphisms. Ther Drug Monit 34:686–694
Moes DJ, Press RR, den Hartigh J, van der Straaten T, de Fijter JW, Guchelaar HJ (2012) Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenetics of everolimus in renal transplant patients. Clin Pharmacokinet 51:467–480
Schoeppler KE, Aquilante CL, Kiser TH, Fish DN, Zamora MR (2014) The impact of genetic polymorphisms, diltiazem, and demographic variables on everolimus trough concentrations in lung transplant recipients. Clin Transplant 28:590–597
Moes DJ, Swen JJ, den Hartigh J, van der Straaten T, van der Heide JJ, Sanders JS, Bemelman FJ, de Fijter JW, Guchelaar HJ (2014) Effect of CYP3A4*22, CYP3A5*3, and CYP3A combined genotypes on cyclosporine, everolimus, and tacrolimus pharmacokinetics in renal transplantation. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol 3:e100
Picard N, Rouguieg-Malki K, Kamar N, Rostaing L, Marquet P (2011) CYP3A5 genotype does not influence everolimus in vitro metabolism and clinical pharmacokinetics in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation 91:652–656
Schuler W, Sedrani R, Cottens S, Häberlin B, Schulz M, Schuurman HJ, Zenke G, Zerwes HG, Schreier MH (1997) SDZ RAD, a new rapamycin derivative: pharmacological properties in vitro and in vivo. Transplantation 64:36–42
Zou Z, Tao T, Li H, Zhu X (2020) mTOR signaling pathway and mTOR inhibitors in cancer: progress and challenges. Cell Biosci 10:31
Peralba JM, DeGraffenried L, Friedrichs W, Fulcher L, Grünwald V, Weiss G, Hidalgo M (2003) Pharmacodynamic evaluation of CCI-779, an inhibitor of mTOR, in cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 9:2887–2892
Tang SC, Sparidans RW, Cheung KL, Fukami T, Durmus S, Wagenaar E, Yokoi T, van Vlijmen BJ, Beijnen JH, Schinkel AH (2014) P-glycoprotein, CYP3A, and plasma carboxylesterase determine brain and blood disposition of the mTOR Inhibitor everolimus (Afinitor) in mice. Clin Cancer Res 20:3133–3145
Dekter HE, Romijn FP, Temmink WP, van Pelt J, de Fijter JW, Smit NP (2010) A spectrophotometric assay for routine measurement of mammalian target of rapamycin activity in cell lysates. Anal Biochem 403:79–87
Fine JP, Gray RJ (1999) A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk. J Am Stat Assoc 94:496–509
Okamoto I, Doi T, Ohtsu A, Miyazaki M, Tsuya A, Kurei K, Kobayashi K, Nakagawa K (2010) Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of RAD001 (everolimus) administered daily to Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. Jpn J Clin Oncol 40:17–23
Okubo M, Murayama N, Shimizu M, Shimada T, Guengerich FP, Yamazaki H (2013) CYP3A4 intron 6 C > T polymorphism (CYP3A4*22) is associated with reduced CYP3A4 protein level and function in human liver microsomes. J Toxicol Sci 38:349–354
Falkowski S, Woillard JB (2019) Therapeutic drug monitoring of everolimus in oncology: evidences and perspectives. Ther Drug Monit 41:568–574
Deppenweiler M, Falkowski S, Saint-Marcoux F, Monchaud C, Picard N, Laroche ML, Tubiana-Mathieu N, Venat-Bouvet L, Marquet P, Woillard JB (2017) Towards therapeutic drug monitoring of everolimus in cancer? Results of an exploratory study of exposure-effect relationship. Pharmacol Res 121:138–144
Willemsen AECAB, de Geus-Oei LF, de Boer M, Tol J, Kamm Y, de Jong PC, Jonker MA, Vos AH, Grootjans W, de Groot JWB, Mulder SF, Aarntzen EHJG, Gerritsen WR, van Herpen CML, van Erp NP (2018) Everolimus exposure and early metabolic response as predictors of treatment outcomes in breast cancer patients treated with everolimus and exemestane. Target Oncol 13:641–648
de Wit D, Schneider TC, Moes DJ, Roozen CF, den Hartigh J, Gelderblom H, Guchelaar HJ, van der Hoeven JJ, Links TP, Kapiteijn E, van Erp NP (2016) Everolimus pharmacokinetics and its exposure-toxicity relationship in patients with thyroid cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 78:63–71
Willemsen AECAB, Tol J, van Erp NP, Jonker MA, de Boer M, Meek B, de Jong PC, van Moorsel C, Gerritsen WR, Grutters JC, van Herpen CML (2019) Prospective study of drug-induced interstitial lung disease in advanced breast cancer patients receiving everolimus plus exemestane. Target Oncol 14:441–451
Willemsen AE, Grutters JC, Gerritsen WR, van Erp NP, van Herpen CM, Tol J (2016) mTOR inhibitor-induced interstitial lung disease in cancer patients: comprehensive review and a practical management algorithm. Int J Cancer 138:2312–2321
Kovarik JM, Hartmann S, Figueiredo J, Rordorf C, Golor G, Lison A, Budde K, Neumayer HH (2002) Effect of food on everolimus absorption: quantification in healthy subjects and a confirmatory screening in patients with renal transplants. Pharmacotherapy 22:154–159
Kung L, Halloran PF (2000) Immunophilins may limit calcineurin inhibition by cyclosporine and tacrolimus at high drug concentrations. Transplantation 70:327–335
Tabernero J, Rojo F, Calvo E, Burris H, Judson I, Hazell K, Martinelli E, Ramon y Cajal S, Jones S, Vidal L, Shand N, Macarulla T, Ramos FJ, Dimitrijevic S, Zoellner U, Tang P, Stumm M, Lane HA, Lebwohl D, Baselga J (2008) Dose- and schedule-dependent inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway with everolimus: a phase I tumor pharmacodynamic study in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 26:1603–1610
Wright KD, Yao X, London WB, Kao PC, Gore L, Hunger S, Geyer R, Cohen KJ, Allen JC, Katzenstein HM, Smith A, Boklan J, Nazemi K, Trippett T, Karajannis M, Herzog C, Destefano J, Direnzo J, Pietrantonio J, Greenspan L, Cassidy D, Schissel D, Perentesis J, Basu M, Mizuno T, Vinks AA, Prabhu SP, Chi SN, Kieran MW (2021) A POETIC Phase II study of continuous oral everolimus in recurrent, radiographically progressive pediatric low-grade glioma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 68:e28787
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Glen H, Michaelson MD, Molina A, Eisen T, Jassem J, Zolnierek J, Maroto JP, Mellado B, Melichar B, Tomasek J, Kremer A, Kim HJ, Wood K, Dutcus C, Larkin J (2015) Lenvatinib, everolimus, and the combination in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, phase 2, open-label, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol 16:1473–1482
White J, Kearins O, Dodwell D, Horgan K, Hanby AM, Speirs V (2011) Male breast carcinoma: increased awareness needed. Breast Cancer Res 13:219
Sharma M, Duan Z, Zhao H, Giordano SH, Chavez-MacGregor M (2020) Real-world patterns of everolimus use in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Oncologist 25:937–942
Acknowledgements
We thank all patients and medical staff who contributed to this study.
Funding
This work was supported in part by a grant from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI (No. 16K08902) and a grant from the Japan Research Foundation for Clinical Pharmacology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study concept and design: M.F., M.K.; acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: all authors; drafting of the manuscript: M.F.; critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: all authors; statistical analysis: M.F.; acquisition of funding: M.F.; administrative, technical, or material support: K.I., M.K.; supervision: M.F.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The protocol of this study was approved by the institutional ethics committee of Asahikawa Medical University (#14085). The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and its amendments. Written informed consent was obtained from each patient prior to participation in the study.
Consent for publication
All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Research involving human participants
The protocol of this study was approved by the institutional ethics committee of Asahikawa Medical University (#14085). The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and its amendments.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from each patient prior to enrollment.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOC 2798 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukudo, M., Ishibashi, K. & Kitada, M. Real-world pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of everolimus in metastatic breast cancer. Invest New Drugs 39, 1707–1715 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-021-01131-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-021-01131-4