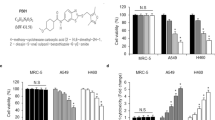
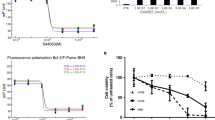
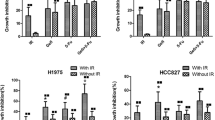
Summary
Chemotherapy is usually the subsequent treatment for non-small cell lung cancer patients with acquired radioresistance after long-term fractionated radiotherapy. However, few studies have focused on the selection of chemotherapeutic drugs to treat lung adenocarcinoma patients with radioresistance. Our study compared the sensitivity changes of lung adenocarcinoma cells to conventional chemotherapeutic drugs under radioresistant circumstances by using three lung adenocarcinoma cell models, which were irradiated with fractionated X-rays at a total dose of 60 Gy. The results showed that the toxicities of paclitaxel, docetaxel and SN-38 were increased in radioresistant cells. The IC50 values of docetaxel and SN-38 decreased 0 ~ 3 times and 3 ~ 36 times in radioresistant cells, respectively. Notably, the A549 radioresistant cells were approximately 36 times more sensitive to SN-38 than the parental cells. Further results revealed that the downregulation of the efflux transporter BCRP by long-term fractionated irradiation was an important factor contributing to the increased cytotoxicity of SN-38. In addition, the reported miRNAs and transcriptional factors that regulate BCRP did not participate in the downregulation. In conclusion, these results presented important data on the sensitivity changes of lung adenocarcinoma cells to chemotherapeutic drugs after acquiring radioresistance and suggested that irinotecan (the prodrug of SN-38) might be a promising drug candidate for lung adenocarcinoma patients with acquired radioresistance.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Zappa C, Mousa SA (2016) Non-small cell lung cancer: current treatment and future advances. Transl Lung Cancer Res 5(3):288–300. https://doi.org/10.21037/tlcr.2016.06.07
Skvortsova I, Debbage P, Kumar V, Slwortsov S (2015) Radiation resistance: Cancer stem cells (CSCs) and their enigmatic pro-survival signaling. Semin Cancer Biol 35:39–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.09.009
Curtin N (2007) Therapeutic potential of drugs to modulate DNA repair in cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 11(6):783–799. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728222.11.6.783
Morgan MA, Lawrence TS (2015) Molecular pathways: overcoming radiation resistance by targeting DNA damage response pathways. Clin Cancer Res 21(13):2898–2904. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3229
Tang L, Wei F, Wu Y, He Y, Shi L, Xiong F, Gong Z, Guo C, Li X, Deng H, Cao K, Zhou M, Xiang B, Li X, Li Y, Li G, Xiong W, Zeng Z (2018) Role of metabolism in cancer cell radioresistance and radiosensitization methods. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37(1):87. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0758-7
Schulz A, Meyer F, Dubrovska A, Borgmann K (2019) Cancer stem cells and Radioresistance: DNA repair and beyond. Cancers 11(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11060862
Lee DH (2017) Treatments for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): the road to a success, paved with failures. Pharmacol Ther 174:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.02.001
Yoneda K, Imanishi N, Ichiki Y, Tanaka F (2019) Treatment of non-small cell lung Cancer with EGFR-mutations. J UOEH 41(2):153–163. https://doi.org/10.7888/juoeh.41.153
Zhang YL, Yuan JQ, Wang KF, Fu XH, Han XR, Threapleton D, Yang ZY, Mao C, Tang JL (2016) The prevalence of EGFR mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 7(48):78985–78993. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12587
Han B, Tjulandin S, Hagiwara K, Normanno N, Wulandari L, Laktionov K, Hudoyo A, He Y, Zhang YP, Wang MZ, Liu CY, Ratcliffe M, McCormack R, Reck M (2017) EGFR mutation prevalence in Asia-Pacific and Russian patients with advanced NSCLC of adenocarcinoma and non-adenocarcinoma histology: the IGNITE study. Lung Cancer 113:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.08.021
Santivasi WL, Xia F (2014) Ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage, response, and repair. Antioxid Redox Signal 21(2):251–259. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2013.5668
Perez-Tomas R (2006) Multidrug resistance: retrospect and prospects in anti-cancer drug treatment. Curr Med Chem 13(16):1859–1876. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986706777585077
Amawi H, Sim HM, Tiwari AK, Ambudkar SV, Shukla S (2019) ABC transporter-mediated multidrug-resistant Cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 1141:549–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7647-4_12
Mao Q, Unadkat JD (2015) Role of the breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) in drug transport--an update. AAPS J 17(1):65–82. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-014-9668-6
Azimi R, Alaei P, Spezi E, Hui SK (2015) Characterization of an orthovoltage biological irradiator used for radiobiological research. J Radiat Res 56(3):485–492. https://doi.org/10.1093/jrr/rru129
Lin TY, Chang JT, Wang HM, Chan SH, Chiu CC, Lin CY, Fan KH, Liao CT, Chen IH, Liu TZ, Li HF, Cheng AJ (2010) Proteomics of the radioresistant phenotype in head-and-neck cancer: Gp96 as a novel prediction marker and sensitizing target for radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78(1):246–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.03.002
Sato K, Shimokawa T, Imai T (2019) Difference in acquired Radioresistance induction between repeated photon and particle irradiation. Front Oncol 9:1213. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.01213
Zhao YY, Wu Q, Wu ZB, Zhang JJ, Zhu LC, Yang Y, Ma SL, Zhang SR (2018) Microwave hyperthermia promotes caspase3-dependent apoptosis and induces G2/M checkpoint arrest via the ATM pathway in nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. Int J Oncol 53(2):539–550. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2018.4439
Wang Y, Sun D, Song F, Hu Y, Smith DE, Jiang H (2014) Expression and regulation of the proton-coupled oligopeptide transporter PhT2 by LPS in macrophages and mouse spleen. Mol Pharm 11(6):1880–1888. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp500014r
Wang YQ, Hu YJ, Li P, Weng YY, Kamada N, Jiang HD, Smith DE (2018) Expression and regulation of proton-coupled oligopeptide transporters in colonic tissue and immune cells of mice. Biochem Pharmacol 148:163–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2017.12.025
Durm G, Hanna N (2017) Second-line chemotherapy and beyond for non-small cell lung Cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 31(1):71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hoc.2016.08.002
Arunachalam A, Li HJ, Biutoni MA, Camacho R, Cao XT, Zhong YC, Lubiniecki GM, Carbone DP (2018) Real-world treatment patterns, overall survival, and occurrence and costs of adverse events associated with second-line therapies for Medicare patients with advanced non-small-cell lung Cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 19(5):E783–E799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2018.05.016
Toth EL, Li H, Dzierlenga AL, Clarke JD, Vildhede A, Goedken M, Cherrington NJ (2018) Gene-by-environment interaction of Bcrp(−/−) and methionine- and choline-deficient diet-induced nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis alters SN-38 disposition. Drug Metab Dispos 46(11):1478–1486. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.118.082081
Li X, Pan YZ, Seigel GM, Hu ZH, Huang M, Yu AM (2011) Breast cancer resistance protein BCRP/ABCG2 regulatory microRNAs (hsa-miR-328, −519c and -520h) and their differential expression in stem-like ABCG2+ cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol 81(6):783–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2010.12.018
Haenisch S, Werk AN, Cascorbi I (2014) MicroRNAs and their relevance to ABC transporters. Brit J Clin Pharmaco 77(4):587–596. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.12251
Jia M, Wei Z, Liu P, Zhao X (2016) Silencing of ABCG2 by MicroRNA-3163 inhibits multidrug resistance in retinoblastoma Cancer stem cells. J Korean Med Sci 31(6):836–842. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.6.836
Bircsak KM, Moscovitz JE, Wen X, Archer F, Yuen PYS, Mohammed M, Memon N, Weinberger BI, Saba LM, Vetrano AM, Aleksunes LM (2018) Interindividual regulation of the breast Cancer resistance protein/ABCG2 transporter in term human placentas. Drug Metab Dispos 46(5):619–627. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.117.079228
Ota S, Ishii G, Goto K, Kubota K, Kim YH, Kojika M, Murata Y, Yamazaki M, Nishiwaki Y, Eguchi K, Ochiai A (2009) Immunohistochemical expression of BCRP and ERCC1 in biopsy specimen predicts survival in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Lung Cancer 64(1):98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2008.07.014
Lee SH, Kim H, Hwang JH, Lee HS, Cho JY, Yoon YS, Han HS (2012) Breast cancer resistance protein expression is associated with early recurrence and decreased survival in resectable pancreatic cancer patients. Pathol Int 62(3):167–175. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1827.2011.02772.x
Xie L, Song X, Yu J, Wei L, Song B, Wang X, Lv L (2009) Fractionated irradiation induced radio-resistant esophageal cancer EC109 cells seem to be more sensitive to chemotherapeutic drugs. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 28:68. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-9966-28-68
Wang Y, Chen Q, Jin S, Deng W, Li S, Tong Q, Chen Y (2012) Up-regulation of P-glycoprotein is involved in the increased paclitaxel resistance in human esophageal cancer radioresistant cells. Scand J Gastroenterol 47(7):802–808. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365521.2012.683042
Kuwahara Y, Roudkenar MH, Suzuki M, Urushihara Y, Fukumoto M, Saito Y, Fukumoto M (2016) The involvement of mitochondrial membrane potential in cross-resistance between radiation and Docetaxel. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 96(3):556–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.07.002
de Man FM, Goey AKL, van Schaik RHN, Mathijssen RHJ, Bins S (2018) Individualization of Irinotecan treatment: a review of pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and Pharmacogenetics. Clin Pharmacokinet 57(10):1229–1254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-018-0644-7
Fujita D, Saito Y, Nakanishi T, Tamai I (2016) Organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP)2B1 contributes to gastrointestinal toxicity of anticancer drug SN-38, active metabolite of Irinotecan hydrochloride. Drug Metab Dispos 44(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.115.066712
Messersmith WA (2019) NCCN guidelines updates: Management of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 17(5.5):599–601. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2019.5014
Kalemkerian GP, Loo BW, Akerley W, Attia A, Bassetti M, Boumber Y, Decker R, Dobelbower MC, Dowlati A, Downey RJ, Florsheim C, Ganti AKP, Grecula JC, Gubens MA, Hann CL, Hayman JA, Heist RS, Koczywas M, Merritt RE, Mohindra N, Molina J, Moran CA, Morgensztern D, Pokharel S, Portnoy DC, Rhodes D, Rusthoven C, Sands J, Santana-Davila R, Williams CC, Hoffmann KG, Hughes M (2018) NCCN guidelines insights: small cell lung Cancer, version 2.2018. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 16(10):1171–1182. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2018.0079
Yang XQ, Li CY, Xu MF, Zhao H, Wang D (2015) Comparison of first-line chemotherapy based on irinotecan or other drugs to treat non-small cell lung cancer in stage IIIB/IV: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 15:949. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-015-1978-2
Matsubara N, Maemondo M, Inoue A, Ishimoto O, Watanabe K, Sakakibara T, Fukuhara T, Morikawa N, Tanaka M, Sugawara S, Nukiwa T (2013) Phase II study of irinotecan as a third- or fourth-line treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: NJLCG0703. Respir Investig 51(1):28–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resinv.2012.09.004
Ohe Y, Ohashi Y, Kubota K, Tamura T, Nakagawa K, Negoro S, Nishiwaki Y, Saijo N, Ariyoshi Y, Fukuoka M (2007) Randomized phase III study of cisplatin plus irinotecan versus carboplatin plus paclitaxel, cisplatin plus gemcitabine, and cisplatin plus vinorelbine for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: four-arm cooperative study in Japan. Ann Oncol 18(2):317–323. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdl377
Yamamoto N, Fukuoka M, Negoro SI, Nakagawa K, Saito H, Matsui K, Kawahara M, Senba H, Takada Y, Kudoh S, Nakano T, Katakami N, Sugiura T, Hoso T, Ariyoshi Y (2004) Randomised phase II study of docetaxel/cisplatin vs docetaxel/irinotecan in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a West Japan thoracic oncology group study (WJTOG9803). Br J Cancer 90(1):87–92. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6601462
Han JY, Lee DH, Song JE, Lee SY, Kim HY, Kim HT, Lee JS (2008) Randomized phase 2 study of irinotecan plus cisplatin versus gemcitabine plus vinorelbine as first-line chemotherapy with second-line crossover in patients with advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer 113(2):388–395. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.23582
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Prof. Huidi Jiang and Prof. Su Zeng from the College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhejiang University, for their kind advice and help.
Availability of data and material
We declared that materials described in the manuscript, including all relevant raw data, will be freely available to any scientist wishing to use them for non-commercial purposes, without breaching participant confidentiality.
Funding
The work was supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. LQ19H310001, Zhejiang Provincial Medicine and Health Science Foundation (grant No. 2020RC027) and National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (81803631, 81773242).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shirong Zhang, Shenglin Ma and Yuqing Wang conceived and designed the study. Yuqing Wang, Jie Huang, Qiong Wu and Jingjing Zhang performed the experiments. Yuqing Wang wrote the paper. Shirong Zhang, Shenglin Ma and Zhiyuan Ma reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yuqing Wang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Jie Huang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Qiong Wu declares that she has no conflict of interest. Jingjing Zhang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Zhiyuan Ma declares that she has no conflict of interest. Shenglin Ma declares that he has no conflict of interest. Shirong Zhang declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 20.3 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Huang, J., Wu, Q. et al. Downregulation of breast cancer resistance protein by long-term fractionated radiotherapy sensitizes lung adenocarcinoma to SN-38. Invest New Drugs 39, 458–468 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-020-01003-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-020-01003-3