Summary
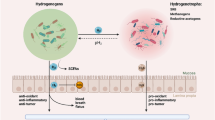
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the most frequently encountered malignancy associated with the rectum or colon, and accumulating evidences have implicated intestinal dysbacteriosis (IDB, disruption of gut microbiome) and exosomes in the pathology of CRC. We aimed to investigate the effect of IDB on exosome secretion in a CRC xenograft mouse model. An IDB mouse model was established and was inoculated with the CRC cell line SW480 as a xenograft tumor. Tumor growth was monitored for 15 days in sham and IDB mice, after which blood was collected to assess serum exosome secretion. A novel exosome secretion inhibitor, neticonazole, was administered to IDB mice bearing CRC xenograft tumors, followed by monitoring of tumor growth and mouse survival. Western blot analysis was performed in xenograft tumors to investigate the underlying molecular mechanism. IDB promoted CRC xenograft tumor growth and exosome secretion, which could be inhibited by the exosome secretion inhibitor neticonazole. Moreover, neticonazole treatment significantly improved the survival of IDB mice with CRC xenograft tumors, likely through increasing apoptosis of CRC xenograft tumor cells. The exosome secretion inhibitor neticonazole may serve as a promising therapeutic candidate against CRC by suppressing IDB-induced CRC tumorigenesis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- IDB:
-
Intestinal dysbacteriosis
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2016) Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 66(1):7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21332
Brenner H, Kloor M, Pox CP (2014) Colorectal cancer. Lancet 383(9927):1490–1502. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61649-9
Movahedi M, Bishop DT, Macrae F, Mecklin JP, Moeslein G, Olschwang S, Eccles D, Evans DG, Maher ER, Bertario L, Bisgaard ML, Dunlop MG, Ho JW, Hodgson SV, Lindblom A, Lubinski J, Morrison PJ, Murday V, Ramesar RS, Side L, Scott RJ, Thomas HJ, Vasen HF, Burn J, Mathers JC (2015) Obesity, aspirin, and risk of colorectal Cancer in carriers of hereditary colorectal Cancer: a prospective investigation in the CAPP2 study. J Clin Oncol 33(31):3591–3597. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.58.9952
Grivennikov SI (2013) Inflammation and colorectal cancer: colitis-associated neoplasia. Semin Immunopathol 35(2):229–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-012-0352-6
De Rosa M, Pace U, Rega D, Costabile V, Duraturo F, Izzo P, Delrio P (2015) Genetics, diagnosis and management of colorectal cancer (review). Oncol Rep 34(3):1087–1096. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.4108
Van Raay T, Allen-Vercoe E (2017) Microbial interactions and interventions in colorectal Cancer. Microbiol Spectr 5(3). https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.BAD-0004-2016
Sears CL, Pardoll DM (2011) Perspective: alpha-bugs, their microbial partners, and the link to colon cancer. J Infect Dis 203(3):306–311. https://doi.org/10.1093/jinfdis/jiq061
Tjalsma H, Boleij A, Marchesi JR, Dutilh BE (2012) A bacterial driver-passenger model for colorectal cancer: beyond the usual suspects. Nat Rev Microbiol 10(8):575–582. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2819
Demory Beckler M, Higginbotham JN, Franklin JL, Ham AJ, Halvey PJ, Imasuen IE, Whitwell C, Li M, Liebler DC, Coffey RJ (2013) Proteomic analysis of exosomes from mutant KRAS colon cancer cells identifies intercellular transfer of mutant KRAS. Mol Cell Proteomics 12(2):343–355. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M112.022806
Ji H, Chen M, Greening DW, He W, Rai A, Zhang W, Simpson RJ (2014) Deep sequencing of RNA from three different extracellular vesicle (EV) subtypes released from the human LIM1863 colon cancer cell line uncovers distinct miRNA-enrichment signatures. PLoS One 9(10):e110314. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110314
Bigagli E, Luceri C, Guasti D, Cinci L (2016) Exosomes secreted from human colon cancer cells influence the adhesion of neighboring metastatic cells: role of microRNA-210. Cancer Biol Ther:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2016.1219815
Lugini L, Valtieri M, Federici C, Cecchetti S, Meschini S, Condello M, Signore M, Fais S (2016) Exosomes from human colorectal cancer induce a tumor-like behavior in colonic mesenchymal stromal cells. Oncotarget 7(31):50086–50098. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10574
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S, Allgayer H (2008) MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 27(15):2128–2136. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210856
Helwa I, Cai J, Drewry MD, Zimmerman A, Dinkins MB, Khaled ML, Seremwe M, Dismuke WM, Bieberich E, Stamer WD, Hamrick MW, Liu Y (2017) A comparative study of serum exosome isolation using differential ultracentrifugation and three commercial reagents. PLoS One 12(1):e0170628. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0170628
Riches A, Campbell E, Borger E, Powis S (2014) Regulation of exosome release from mammary epithelial and breast cancer cells – a new regulatory pathway. Eur J Cancer 50(5):1025–1034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2013.12.019
Longhi MS, Moss A, Jiang ZG, Robson SC (2017) Purinergic signaling during intestinal inflammation. J Mol Med (Berl) 95(9):915–925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-017-1545-1
Datta A, Kim H, McGee L, Johnson AE, Talwar S, Marugan J, Southall N, Hu X, Lal M, Mondal D, Ferrer M, Abdel-Mageed AB (2018) High-throughput screening identified selective inhibitors of exosome biogenesis and secretion: a drug repurposing strategy for advanced cancer. Sci Rep 8(1):8161. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-26411-7
Petersen C, Round JL (2014) Defining dysbiosis and its influence on host immunity and disease. Cell Microbiol 16(7):1024–1033. https://doi.org/10.1111/cmi.12308
Butto LF, Haller D (2016) Dysbiosis in intestinal inflammation: cause or consequence. Int J Med Microbiol 306(5):302–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2016.02.010
Chiba M, Kimura M, Asari S (2012) Exosomes secreted from human colorectal cancer cell lines contain mRNAs, microRNAs and natural antisense RNAs, that can transfer into the human hepatoma HepG2 and lung cancer A549 cell lines. Oncol Rep 28(5):1551–1558. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2012.1967
Yu JL, May L, Lhotak V, Shahrzad S, Shirasawa S, Weitz JI, Coomber BL, Mackman N, Rak JW (2005) Oncogenic events regulate tissue factor expression in colorectal cancer cells: implications for tumor progression and angiogenesis. Blood 105(4):1734
Huang Z, Feng Y (2017) Exosomes Derived From Hypoxic Colorectal Cancer Cells Promote Angiogenesis Through Wnt4-Induced β-Catenin Signaling in Endothelial Cells. Oncology Research Featuring Preclinical and Clinical Cancer Therapeutics 25 (5):651–661. https://doi.org/10.3727/096504016X14752792816791
Lim JWE, Mathias RA, Kapp EA, Layton MJ, Faux MC, Burgess AW, Ji H, Simpson RJ (2012) Restoration of full-length APC protein in SW480 colon cancer cells induces exosome-mediated secretion of DKK-4. Electrophoresis 33(12):1873–1880. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201100687
Green DR, Reed JC (1998) Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281(5381):1309–1312
Bratton SB, Walker G, Srinivasula SM, Sun XM, Butterworth M, Alnemri ES, Cohen GM (2001) Recruitment, activation and retention of caspases-9 and -3 by Apaf-1 apoptosome and associated XIAP complexes. Embo J 20(5):998–1009. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.5.998
Huber V, Fais S, Iero M, Lugini L, Canese P, Squarcina P, Zaccheddu A, Colone M, Arancia G, Gentile M, Seregni E, Valenti R, Ballabio G, Belli F, Leo E, Parmiani G, Rivoltini L (2005) Human colorectal Cancer cells induce T-cell death through release of Proapoptotic microvesicles: role in immune escape. Gastroenterology 128(7):1796–1804. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2005.03.045
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81272720).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 120 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, L., Xu, Y., Xu, W. et al. The exosome secretion inhibitor neticonazole suppresses intestinal dysbacteriosis-induced tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer. Invest New Drugs 38, 221–228 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-019-00759-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-019-00759-7