Summary
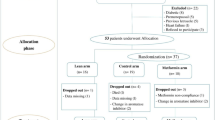
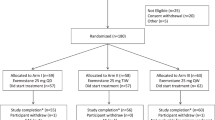
Background Increased adiposity is thought to result in worse clinical outcomes in patients with breast cancer through increased estrogen production, hyperinsulinemia, insulin resistance, and activation of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway. Thus, we hypothesized that the addition of metformin to everolimus and exemestane, could lead to better outcomes in overweight and obese patients with metastatic, hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer. We conducted a phase II trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the combination of metformin, everolimus and exemestane in overweight and obese postmenopausal women with metastatic, hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer. Methods Twenty-two patients with a body mass index ≥25 kg/m2 were treated with metformin 1000 mg twice daily, everolimus 10 mg daily and exemestane 25 mg daily. Median progression-free (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method. Results Median PFS and OS were 6.3 months (95% confidence interval [CI]: 3.8–11.3 months) and 28.8 months (95% CI: 17.5–59.7 months), respectively. Five patients had a partial response and 7 had stable disease for ≥24 weeks yielding a clinical benefit rate of 54.5%. Compared with overweight patients, obese patients had an improved PFS on univariable (p = 0.015) but not multivariable analysis (p = 0.215). Thirty-two percent of patients experienced a grade 3 treatment-related adverse event (TRAE). There were no grade 4 TRAEs and 7 patients experienced a grade 3 TRAE. Conclusion The combination of metformin, everolimus and exemestane was safe and had moderate clinical benefit in overweight and obese with patients metastatic, hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neuhouser ML, Aragaki AK, Prentice RL, Manson JE, Chlebowski R, Carty CL, Ochs-Balcom HM, Thomson CA, Caan BJ, Tinker LF, Urrutia RP, Knudtson J, Anderson GL (2015) Overweight, obesity, and postmenopausal invasive breast Cancer risk: a secondary analysis of the Women's Health Initiative randomized clinical trials. JAMA Oncol 1(5):611–621. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.1546
Carmichael AR (2006) Obesity and prognosis of breast cancer. Obes Rev 7(4):333–340. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2006.00261.x
Whiteman MK, Hillis SD, Curtis KM, McDonald JA, Wingo PA, Marchbanks PA (2005) Body mass and mortality after breast cancer diagnosis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 14(8):2009–2014. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-05-0106
Demirkan B, Alacacioglu A, Yilmaz U (2007) Relation of body mass index (BMI) to disease free (DFS) and distant disease free survivals (DDFS) among Turkish women with operable breast carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol 37(4):256–265. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hym023
Rose DP, Komninou D, Stephenson GD (2004) Obesity, adipocytokines, and insulin resistance in breast cancer. Obes Rev 5(3):153–165. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2004.00142.x
Grodin JM, Siiteri PK, MacDonald PC (1973) Source of estrogen production in postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 36(2):207–214. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem-36-2-207
Mawson A, Lai A, Carroll JS, Sergio CM, Mitchell CJ, Sarcevic B (2005) Estrogen and insulin/IGF-1 cooperatively stimulate cell cycle progression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells through differential regulation of c-Myc and cyclin D1. Mol Cell Endocrinol 229(1–2):161–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2004.08.002
Dupont J, Le Roith D (2001) Insulin-like growth factor 1 and oestradiol promote cell proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells: new insights into their synergistic effects. Mol Pathol 54(3):149–154
Bernard L, Legay C, Adriaenssens E, Mougel A, Ricort JM (2006) Estradiol regulates the insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) signalling pathway: a crucial role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase) in estrogens requirement for growth of MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 350(4):916–921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.09.116
Fuentes-Mattei E, Velazquez-Torres G, Phan L, Zhang F, Chou PC, Shin JH, Choi HH, Chen JS, Zhao R, Chen J, Gully C, Carlock C, Qi Y, Zhang Y, Wu Y, Esteva FJ, Luo Y, McKeehan WL, Ensor J, Hortobagyi GN, Pusztai L, Fraser Symmans W, Lee MH, Yeung SC (2014) Effects of obesity on transcriptomic changes and cancer hallmarks in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 106(7). https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/dju158
Wysocki PJ, Wierusz-Wysocka B (2010) Obesity, hyperinsulinemia and breast cancer: novel targets and a novel role for metformin. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 10(4):509–519. https://doi.org/10.1586/erm.10.22
Alimova IN, Liu B, Fan Z, Edgerton SM, Dillon T, Lind SE, Thor AD (2009) Metformin inhibits breast cancer cell growth, colony formation and induces cell cycle arrest in vitro. Cell Cycle 8(6):909–915. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.8.6.7933
Sonnenblick A, Agbor-Tarh D, Bradbury I, Di Cosimo S, Azim HA Jr, Fumagalli D, Sarp S, Wolff AC, Andersson M, Kroep J, Cufer T, Simon SD, Salman P, Toi M, Harris L, Gralow J, Keane M, Moreno-Aspitia A, Piccart-Gebhart M, de Azambuja E (2017) Impact of diabetes, insulin, and metformin use on the outcome of patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive primary breast Cancer: analysis from the ALTTO phase III randomized trial. J Clin Oncol 35(13):1421–1429. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.69.7722
Jiralerspong S, Palla SL, Giordano SH, Meric-Bernstam F, Liedtke C, Barnett CM, Hsu L, Hung MC, Hortobagyi GN, Gonzalez-Angulo AM (2009) Metformin and pathologic complete responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in diabetic patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 27(20):3297–3302. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.19.6410
Baselga J, Campone M, Piccart M, Burris HA 3rd, Rugo HS, Sahmoud T, Noguchi S, Gnant M, Pritchard KI, Lebrun F, Beck JT, Ito Y, Yardley D, Deleu I, Perez A, Bachelot T, Vittori L, Xu Z, Mukhopadhyay P, Lebwohl D, Hortobagyi GN (2012) Everolimus in postmenopausal hormone-receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 366(6):520–529. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1109653
Esteva FJ, Moulder SL, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Ensor J, Murray JL, Green MC, Koenig KB, Lee MH, Hortobagyi GN, Yeung SC (2013) Phase I trial of exemestane in combination with metformin and rosiglitazone in nondiabetic obese postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 71(1):63–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-012-1977-9
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45(2):228–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Piccart M, Hortobagyi GN, Campone M, Pritchard KI, Lebrun F, Ito Y, Noguchi S, Perez A, Rugo HS, Deleu I, Burris HA 3rd, Provencher L, Neven P, Gnant M, Shtivelband M, Wu C, Fan J, Feng W, Taran T, Baselga J (2014) Everolimus plus exemestane for hormone-receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative advanced breast cancer: overall survival results from BOLERO-2dagger. Ann Oncol 25(12):2357–2362. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdu456
Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ (2003) Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med 348(17):1625–1638. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa021423
Lee A, Morley JE (1998) Metformin decreases food consumption and induces weight loss in subjects with obesity with type II non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Obes Res 6(1):47–53
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a PROMISE grant from Susan G. Komen for the Cure (to FJE, SCJY and VV), the Breast Cancer Research Foundation (to FJE), the National Institutes of Health through MD Anderson’s Cancer Center Support Grant (NCI P30 CA016672). Dr. Yam is supported by the Allison and Brian Grove Endowed Fellowship for Breast Medical Oncology, the Susan Papizan Dolan Fellowship in Breast Oncology, and the 2018 Gianni Bonadonna Breast Cancer Research Fellowship. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect those of the sponsors. The authors thank Jeanie F. Woodruff, BS. ELS, for editorial support.
Funding
This work was supported by a PROMISE grant from Susan G. Komen for the Cure (to FJE, SCJY and VV), the Breast Cancer Research Foundation (to FJE), the National Institutes of Health through MD Anderson’s Cancer Center Support Grant (NCI P30 CA016672). Dr. Yam is supported by the Allison and Brian Grove Endowed Fellowship for Breast Medical Oncology, the Susan Papizan Dolan Fellowship in Breast Oncology, and the 2018 Gianni Bonadonna Breast Cancer Research Fellowship. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect those of the sponsors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
FJE has received honoraria from Novartis and Pfizer for consultancy. MCM has received honoraria for serving on the advisory boards of Roche and Pfizer and has received institutional research funding from Novartis. SCJY has received research funding and grant support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and DepoMed. GNH was the principal investigator of the BOLERO-2 trial and received research funding from Norvatis for conducting the trial and honoraria for chairing the protocol steering committee. VV has received honoraria from Novartis for consultancy. All other authors declare no relevant potential conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yam, C., Esteva, F.J., Patel, M.M. et al. Efficacy and safety of the combination of metformin, everolimus and exemestane in overweight and obese postmenopausal patients with metastatic, hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer: a phase II study. Invest New Drugs 37, 345–351 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-018-0700-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-018-0700-z