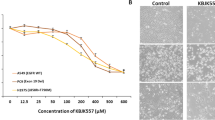
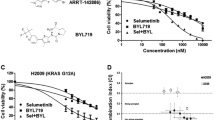
Summary
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been the major cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Targeted therapy has been available as an additive strategy for NSCLC patients, but the inevitable resistance to mono-targeted agents has largely hampered its usage in the clinic. We have previously designed and synthesized a novel small molecule compound S1, 2-methoxy-3-phenylsulfonamino-5-(quinazolin-6-yl) benzamides and demonstrated its inhibition of PI3K and mTOR as well as the anti-tumor potential. In the present study, we have identified that S1 alone or combined with the multi-kinase inhibitor sorafenib can inhibit the in vitro cell proliferation of NSCLC cells (A549, NCI-H157 and 95D cells) and tumor growth in the A549 xenograft model. S1 alone produced inhibitory effects on the colony formation, cell migration and invasion and angiogenesis, with more pronounced inhibition when used with sorafenib. We further revealed that S1 mainly inhibited the Akt/S6 phosphorylation while sorafenib mostly decreased the phosphorylation of ERK. Together, the novel PI3K/mTOR inhibitor S1 per se exhibits strong anti-tumor effects in NSCLC cells and A549 xenograft, effects possibly via its inhibition of cell proliferation, invasion and migration and angiogenesis. The combination of S1 and sorafenib exerts potentiated anti-tumor effects, in which the underlying mechanisms may involve their differential modulation of the phosphorylation of Akt and S6 in the PI3K/Akt/mTOR cascades and ERK phosphorylation in the Raf/MEK/ERK pathways. The combination of S1 and sorafenib could be used as an additive approach in treating NSCLC in the clinic.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirsch FR, Scagliotti GV, Mulshine JL, Kwon R, Curran WJ Jr, Wu YL, Paz-Ares L (2017) Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet 389(10066):299–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30958-8
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65(2):87–108. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21262
Ray MR, Jablons D, He B (2010) Lung cancer therapeutics that target signaling pathways: an update. Expert Rev Respir Med 4(5):631–645. https://doi.org/10.1586/ers.10.64
Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, Langer C, Sandler A, Krook J, Zhu J, Johnson DH, Eastern Cooperative Oncology G (2002) Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 346(2):92–98. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa011954
J E, Xing J, Gong H, He J, Zhang W (2015) Combine MEK inhibition with PI3K/mTOR inhibition exert inhibitory tumor growth effect on KRAS and PIK3CA mutation CRC xenografts due to reduced expression of VEGF and matrix metallopeptidase-9. Tumor Biol 36(2):1091–1097. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2667-5
Gadgeel SM, Wozniak A (2013) Preclinical rationale for PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitors as therapy for epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 14(4):322–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2012.12.001
Rusconi P, Caiola E, Broggini M (2012) RAS/RAF/MEK inhibitors in oncology. Curr Med Chem 19(8):1164–1176
Forde PM, Ettinger DS (2013) Targeted therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer: past, present and future. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 13(6):745–758. https://doi.org/10.1586/era.13.47
Heavey S, O'Byrne KJ, Gately K (2014) Strategies for co-targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in NSCLC. Cancer Treat Rev 40(3):445–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2013.08.006
Xu CX, Li Y, Yue P, Owonikoko TK, Ramalingam SS, Khuri FR, Sun SY (2011) The combination of RAD001 and NVP-BEZ235 exerts synergistic anticancer activity against non-small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One 6(6):e20899. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0020899
Maira SM, Stauffer F, Brueggen J, Furet P, Schnell C, Fritsch C, Brachmann S, Chene P, De Pover A, Schoemaker K, Fabbro D, Gabriel D, Simonen M, Murphy L, Finan P, Sellers W, Garcia-Echeverria C (2008) Identification and characterization of NVP-BEZ235, a new orally available dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor with potent in vivo antitumor activity. Mol Cancer Ther 7(7):1851–1863. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0017
Knight SD, Adams ND, Burgess JL, Chaudhari AM, Darcy MG, Donatelli CA, Luengo JI, Newlander KA, Parrish CA, Ridgers LH, Sarpong MA, Schmidt SJ, Van Aller GS, Carson JD, Diamond MA, Elkins PA, Gardiner CM, Garver E, Gilbert SA, Gontarek RR, Jackson JR, Kershner KL, Luo L, Raha K, Sherk CS, Sung CM, Sutton D, Tummino PJ, Wegrzyn RJ, Auger KR, Dhanak D (2010) Discovery of GSK2126458, a highly potent inhibitor of PI3K and the mammalian target of rapamycin. ACS Med Chem Lett 1(1):39–43. https://doi.org/10.1021/ml900028r
Shao T, Wang J, Chen JG, Wang XM, Li H, Li YP, Li Y, Yang GD, Mei QB, Zhang SQ (2014) Discovery of 2-methoxy-3-phenylsulfonamino-5-(quinazolin-6-yl or quinolin-6-yl)benzamides as novel PI3K inhibitors and anticancer agents by bioisostere. Eur J Med Chem 75:96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.01.053
Wilhelm S, Carter C, Lynch M, Lowinger T, Dumas J, Smith RA, Schwartz B, Simantov R, Kelley S (2006) Discovery and development of sorafenib: a multikinase inhibitor for treating cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5(10):835–844. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2130
Gridelli C, Maione P, Del Gaizo F, Colantuoni G, Guerriero C, Ferrara C, Nicolella D, Comunale D, De Vita A, Rossi A (2007) Sorafenib and sunitinib in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Oncologist 12(2):191–200. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.12-2-191
Blumenschein G Jr (2008) Sorafenib in lung cancer: clinical developments and future directions. J Thorac Oncol 3(6 Suppl 2):S124–S127. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e318174e085
Smit EF, Dingemans AM, Thunnissen FB, Hochstenbach MM, van Suylen RJ, Postmus PE (2010) Sorafenib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer that harbor K-ras mutations: a brief report. J Thorac Oncol 5(5):719–720. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181d86ebf
Paz-Ares L, Hirsh V, Zhang L, de Marinis F, Yang JC, Wakelee HA, Seto T, Wu YL, Novello S, Juhasz E, Aren O, Sun Y, Schmelter T, Ong TJ, Pena C, Smit EF, Mok TS (2015) Monotherapy Administration of Sorafenib in patients with non-small cell lung Cancer (MISSION) trial: a phase III, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial of Sorafenib in patients with relapsed or refractory predominantly nonsquamous non-small-cell lung Cancer after 2 or 3 previous treatment regimens. J Thorac Oncol 10(12):1745–1753. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0000000000000693
Kim ES, Herbst RS, Wistuba II, Lee JJ, Blumenschein GR Jr, Tsao A, Stewart DJ, Hicks ME, Erasmus J Jr, Gupta S, Alden CM, Liu S, Tang X, Khuri FR, Tran HT, Johnson BE, Heymach JV, Mao L, Fossella F, Kies MS, Papadimitrakopoulou V, Davis SE, Lippman SM, Hong WK (2011) The BATTLE trial: personalizing therapy for lung cancer. Cancer Discov 1(1):44–53. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8274.CD-10-0010
O'Brien PJ, Prevost N, Molino M, Hollinger MK, Woolkalis MJ, Woulfe DS, Brass LF (2000) Thrombin responses in human endothelial cells. Contributions from receptors other than PAR1 include the transactivation of PAR2 by thrombin-cleaved PAR1. J Biol Chem 275(18):13502–13509
Chou TC, Talalay P (1984) Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzym Regul 22:27–55
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144(5):646–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
Carracedo A, Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Rojo F, Salmena L, Alimonti A, Egia A, Sasaki AT, Thomas G, Kozma SC, Papa A, Nardella C, Cantley LC, Baselga J, Pandolfi PP (2008) Inhibition of mTORC1 leads to MAPK pathway activation through a PI3K-dependent feedback loop in human cancer. J Clin Invest 118(9):3065–3074. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI34739
Wan X, Harkavy B, Shen N, Grohar P, Helman LJ (2007) Rapamycin induces feedback activation of Akt signaling through an IGF-1R-dependent mechanism. Oncogene 26(13):1932–1940. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209990
Sosman JA, Puzanov I, Atkins MB (2007) Opportunities and obstacles to combination targeted therapy in renal cell cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13(2 Pt 2):764s–769s. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1975
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2000) Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 407(6801):249–257. https://doi.org/10.1038/35025220
Zhan P, Wang J, Lv XJ, Wang Q, Qiu LX, Lin XQ, Yu LK, Song Y (2009) Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in patients with lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis. J Thorac Oncol 4(9):1094–1103. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181a97e31
Newell P, Toffanin S, Villanueva A, Chiang DY, Minguez B, Cabellos L, Savic R, Hoshida Y, Lim KH, Melgar-Lesmes P, Yea S, Peix J, Deniz K, Fiel MI, Thung S, Alsinet C, Tovar V, Mazzaferro V, Bruix J, Roayaie S, Schwartz M, Friedman SL, Llovet JM (2009) Ras pathway activation in hepatocellular carcinoma and anti-tumoral effect of combined sorafenib and rapamycin in vivo. J Hepatol 51(4):725–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2009.03.028
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (No.18DZ2290900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Juan Wang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Shumei Ma declares that she has no conflict of interest. Xiuhua Chen declares that she has no conflict of interest. Sanqi Zhang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Zhiyong Wang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Qibing Mei declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed consent
Informed constent was obtained from all individual participants included in this study.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 21 kb)
Supplemental Figure 1
(PNG 270 kb)
Supplemental Figure 2
(PNG 175 kb)
Supplemental Figure 3
(PNG 301 kb)
Supplemental Figure 4
(PNG 265 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Ma, S., Chen, X. et al. The novel PI3K inhibitor S1 synergizes with sorafenib in non-small cell lung cancer cells involving the Akt-S6 signaling. Invest New Drugs 37, 828–836 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-018-0698-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-018-0698-2