Summary
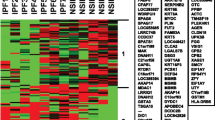
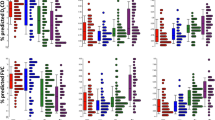
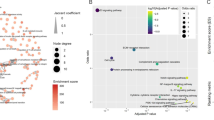
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a rare but lethal adverse effect of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) treatment. The specific mechanism of this disease is not fully understood. To systematically analyze genes associated with EGFR-TKI induced ILD, gene data of EGFR-TKI induced ILD were extracted initially using text mining, and then the intersection between genes from text mining and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) dataset was taken for further protein-protein interaction (PPI) analysis using String-bd database. Go ontology (GO) and pathway enrichment analysis was also conducted based on Database of Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) platform. The PPI network generated by STRING was visualized by Cytoscape, and the topology scores, functional regions and gene annotations were analyzed using plugins of CytoNCA, molecular complex detection (MCODE) and ClueGo. 37 genes were identified as EGFR-TKI induced ILD related. Gene enrichment analysis yield 18 enriched GO terms and 12 associated pathways. A PPI network that included 199 interactions for a total of 35 genes was constructed. Ten genes were selected as hub genes using CytoNCA plugin, and four highly connected clusters were identified using MCODE plugin. GO and pathway annotation analysis for the cluster one revealed that five genes were associated with either response to dexamethasone or with lung fibrosis, including CTGF, CCL2, IGF1, EGFR and ICAM1. Our data might be useful to reveal the pathological mechanisms of EGFR-TKI induced ILD and provide evidence for the diagnosis and treatment in the future.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen W, Zheng R, Zeng H, Zhang S (2015) Epidemiology of lung cancer in China. Thorac cancer 6(2):209–215
Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, Akerley W, Bauman J, Chirieac LR, D'Amico TA, Decamp MM, Dilling TJ, Dobelbower M (2017) Non-small cell lung Cancer, version 5.2017, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 15(4):504–535
Kimura K, Takayanagi R, Fukushima T, Yamada Y (2017) Theoretical method for evaluation of therapeutic effects and adverse effects of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in clinical treatment. Med Oncol 34(10):178
Bagnato G, Harari S (2015) Cellular interactions in the pathogenesis of interstitial lung diseases. European respiratory review : an official journal of the European Respiratory Society 24(135):102–114
Ramos-Casals M, Perez-Alvarez R, Perez-de-Lis M, Xaubet A, Bosch X (2011) Pulmonary disorders induced by monoclonal antibodies in patients with rheumatologic autoimmune diseases. Am J Med 124(5):386–394
Peerzada MM, Spiro TP, Daw HA (2010) Pulmonary toxicities of biologics: a review. Anti-Cancer Drugs 21(2):131–139
Davies EC, Green CF, Taylor S, Williamson PR, Mottram DR, Pirmohamed M (2009) Adverse drug reactions in hospital in-patients: a prospective analysis of 3695 patient-episodes. PLoS One 4(2):e4439
Bast A, Weseler AR, Haenen GR, den Hartog GJ (2010) Oxidative stress and antioxidants in interstitial lung disease. Curr Opin Pulm Med 16(5):516–520
de Boer WI, Hau CM, van Schadewijk A, Stolk J, van Krieken JHJM, Hiemstra PS (2006) Expression of epidermal growth factors and their receptors in the bronchial epithelium of subjects with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Clin Pathol 125(2):184–192
Takeda M, Okamoto I, Nakagawa K (2015) Pooled safety analysis of EGFR-TKI treatment for EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 88(1):74–79
Sakuma K, Nakamura H, Nakamura T, Hoshino Y, Ueda S, Ichikawa M, Tabata C, Fujita S, Masago K, Yodoi J et al (2007) Elevation of serum Thioredoxin in patients with Gefitinib-induced interstitial lung disease. Intern Med 46(23):1905–1909
Inzalkar S, Sharma J (2015) A survey on text mining- techniques and application. Int J Eng Sci 24:1–14
Baran J, Gerner M, Haeussler M, Nenadic G, Bergman CM (2011) pubmed2ensembl: a resource for mining the biological literature on genes. PLoS One 6(9):e24716
Lindahl GE, Stock CJ, Xu SW, Leoni P, Sestini P, Howat SL, Bou-Gharios G, Nicholson AG, Denton CP, Grutters JC (2013) Microarray profiling reveals suppressed interferon stimulated gene program in fibroblasts from scleroderma-associated interstitial lung disease. Respir Res 14(1):1–14
Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M, Wyder S, Simonovic M, Santos A, Doncheva NT, Roth A, Bork P (2017) The STRING database in 2017: quality-controlled protein–protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res 45(Database issue):D362–D368
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13(11):2498–2504
Tang Y, Li M, Wang J, Pan Y (2015) Wu F-X: CytoNCA: a cytoscape plugin for centrality analysis and evaluation of protein interaction networks. Biosystems 127:67–72
Saito R, Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL, Lotia S, Pico AR, Bader GD, Ideker T (2012) A travel guide to Cytoscape plugins. Nat Methods 9(11):1069–1076
Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H, Charoentong P, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Fridman WH, Pagès F, Trajanoski Z, Galon J (2009) ClueGO a Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 25(8):1091–1093
Croft D, Mundo AF, Haw R, Milacic M, Weiser J, Wu G, Caudy M, Garapati P, Gillespie M, Kamdar MR (2014) The Reactome pathway knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res 42(Database issue):472–477
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2008) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4(1):44
Casoni GL, Tomassetti S, Cavazza A, Colby TV, Dubini A, Ryu JH, Carretta E, Tantalocco P, Piciucchi S, Ravaglia C (2014) Transbronchial lung cryobiopsy in the diagnosis of fibrotic interstitial lung diseases. PLoS One 9(2):e86716
Schwaiblmair M, Behr W, Haeckel T, Markl B, Foerg W, Berghaus T (2012) Drug induced interstitial lung disease. Open Respir Med J 6:63–74
Ashiq U, Jamal RA, Mesaik MA, Mahroof-Tahir M, Shahid S, Khan KM (2014) Synthesis, immunomodulation and cytotoxic effects of vanadium (IV) complexes. Med Chem 10(3):287–299
F N, A O, G HC (2011) K N: proteomic biomarkers for acute interstitial lung disease in gefitinib-treated Japanese lung cancer patients. PLoS One 6(7):e22062
Tsuboi M, Le Chevalier T (2006) Interstitial lung disease in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer treated with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Med Oncol 23(2):161–170
Drakopanagiotakis F, Xifteri A, Polychronopoulos V, Bouros D (2008) Apoptosis in lung injury and fibrosis. Eur Respir J 32(6):1631
Costa A, Scholer-Dahirel A, Mechta-Grigoriou F (2014) The role of reactive oxygen species and metabolism on cancer cells and their microenvironment. Semin Cancer Biol 25:23–32
Archontogeorgis K, Steiropoulos P, Tzouvelekis A, Nena E, Bouros D (2012) Lung cancer and interstitial lung diseases: a systematic review. Pulm Med 2012(315918):1–11
Ando M, Okamoto I, Yamamoto N, Takeda K, Tamura K, Seto T, Ariyoshi Y, Fukuoka M (2006) Predictive factors for interstitial lung disease, antitumor response, and survival in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib. J Clin Oncol: Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 24(16):2549–2556
Akamatsu H, Inoue A, Mitsudomi T, Kobayashi K, Nakagawa K, Mori K, Nukiwa T, Nakanishi Y, Yamamoto N (2013) Interstitial lung disease associated with gefitinib in Japanese patients with EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer: combined analysis of two phase III trials (NEJ 002 and WJTOG 3405). Jpn J Clin Oncol 43(6):664–668
Fischer A, West SG, Swigris JJ, Brown KK, Bois RMD (2013) Connective-tissue disease-associated InterstitialLung disease. J Intensive Care Med 84(4):498
Huang SK, Wettlaufer SH, Chung J, Peters-Golden M (2008) Prostaglandin E2 inhibits specific lung fibroblast functions via selective actions of PKA and Epac-1. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 39(4):482–489
Yoshida K, Kuwano K, Hagimoto N, Watanabe K, Matsuba T, Fujita M, Inoshima I, Hara N (2002) MAP kinase activation and apoptosis in lung tissues from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Pathol 198(3):388–396
Goitre L, Trapani E, Trabalzini L, Retta SF (2014) The Ras Superfamily of Small GTPases: The Unlocked Secrets. Ras Signaling 1120:1–18
Hashimoto N, Phan SH, Imaizumi K, Matsuo M, Nakashima H, Kawabe T, Shimokata K, Hasegawa Y (2010) Endothelial-mesenchymal transition in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 43(2):161–172
Fernandez IE, Eickelberg O (2012) The impact of TGF-β on lung fibrosis: from targeting to biomarkers. Proc Am Thorac Soc 9(3):111–116
Kulkarni AA, Thatcher TH, Olsen KC, Maggirwar SB, Phipps RP, Sime PJ (2011) PPAR-γ ligands repress TGFβ-induced myofibroblast differentiation by targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway: implications for therapy of fibrosis. PloS One 6(1):e15909
Andrianifahanana M, Wilkes MC, Gupta SK, Rahimi RA, Repellin CE, Edens M, Wittenberger J, Yin X, Maidl E, Becker J, Leof EB (2013) Profibrotic TGFbeta responses require the cooperative action of PDGF and ErbB receptor tyrosine kinases. FASEB journal 27(11):4444–4454
Hung CF, Rohani MG, Lee SS, Chen P, Schnapp LM (2013) Role of IGF-1 pathway in lung fibroblast activation. Resp Res 14:102
Deshmane SL, Kremlev S, Amini S, Sawaya BE (2009) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): an overview. J Interf Cytok Res 29(6):313–326
Assassi S, Wu M, Tan FK, Chang J, Graham TA, Furst DE, Khanna D, Charles J, Ferguson EC, Feghali-Bostwick C et al (2013) Skin gene expression correlates of severity of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 65(11):2917–2927
Anderssonsjöland A, de Alba CG, Nihlberg K, Becerril C, Ramírez R, Pardo A, Westergrenthorsson G, Selman M (2008) Fibrocytes are a potential source of lung fibroblasts in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40(10):2129
Jiang C, Liu G, Luckhardt T, Antony V, Zhou Y, Carter AB, Thannickal VJ, Liu RM (2017) Serpine 1 induces alveolar type II cell senescence through activating p53-p21-Rb pathway in fibrotic lung disease. Aging Cell 16(5):1114–1124
Harrison NK (2013) Cough, sarcoidosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: raw nerves and bad vibrations. Cough 9(1):9
Kilic A, Sonar SS, Yildirim AO, Fehrenbach H, Nockher WA, Renz H (2011) Nerve growth factor induces type III collagen production in chronic allergic airway inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 128(5):1058–1066 e1051–1054
Richards TJ, Kaminski N, Baribaud F, Flavin S, Brodmerkel C, Horowitz D, Li K, Choi J, Vuga LJ, Lindell KO (2012) Peripheral blood proteins predict mortality in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 185(1):67–76
Ando M, Miyazaki E, Ito T, Hiroshige S, Nureki SI, Ueno T, Takenaka R, Fukami T, Kumamoto T (2010) Significance of serum vascular endothelial growth factor level in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lung 188(3):247–252
Kennedy B, Branagan P, Moloney F, Haroon M, O'Connell OJ, O'Connor TM, O'Regan K, Harney S, Henry MT (2015) Biomarkers to identify ILD and predict lung function decline in scleroderma lung disease or idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sarcoidosis Vasculitis & Diffuse Lung Diseases Official Journal of Wasog 32(3):228
Yamashita M, Mouri T, Niisato M, Nitanai H, Kobayashi H, Ogasawara M, Endo R, Konishi K, Sugai T, Sawai T (2015) Lymphangiogenic factors are associated with the severity of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Bmj Open Respiratory Research 2(1):e000085
Lipson KE, Wong C, Teng Y, Spong S (2012) CTGF is a central mediator of tissue remodeling and fibrosis and its inhibition can reverse the process of fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 20125(Suppl 1):S24
Kono M, Nakamura Y, Suda T, Kato M, Kaida Y, Dai H, Inui N, Hamada E, Miyazaki O, Kurashita S (2011) Plasma CCN2 (connective tissue growth factor; CTGF) is a potential biomarker in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Clin Chim Acta 412(23–24):2211–2215
Campbell P, Morton PE, Takeichi T, Salam A, Roberts N, Proudfoot LE, Mellerio JE, Aminu K, Wellington C, Patil SN et al (2014) Epithelial inflammation resulting from an inherited loss-of-function mutation in EGFR. J Investig Dermatol 134(10):2570–2578
Andrianifahanana M, Wilkes MC, Gupta SK, Rahimi RA, Repellin CE, Edens M, Wittenberger J, Yin X, Maidl E, Becker J (2013) Profibrotic TGFβ responses require the cooperative action of PDGF and ErbB receptor tyrosine kinases. Faseb Journal Official Publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 27(11):4444–4454
Harada C, Kawaguchi T, Ogatasuetsugu S, Yamada M, Hamada N, Maeyama T, Souzaki R, Tajiri T, Taguchi T, Kuwano K (2011) EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition worsens acute lung injury in mice with repairing airway epithelium. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 183(6):743–751
Matsumoto Y, Kawaguchi T, Yamamoto N, Sawa K, Yoshimoto N, Suzumura T, Watanabe T, Mitsuoka S, Asai K, Kimura T (2017) Interstitial lung disease induced by Osimertinib for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M-positive non-small cell lung Cancer. Intern Med 56(17):2325–2328
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yuan Lu, Ang Li, Hu Zhao and Xinling Ren conceived and designed the study. Yuan Lu and Ang Li were responsible for the collection, analysis and interpretation of the data. Yuan Lu, Wen Zhao and Ping Tang were responsible for data visualization. Yuan Lu, Ang Li, XiaoFeng Lai drafted the manuscript, and all authors critically revised it for important intellectual content. Xinling Ren obtained funding, and Hu Zhao was responsible for logistic support. All authors had final approval of the submitted manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81871880), and Director Fund of Shenzhen University General Hospital (No. 0000040546).
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 27 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Li, A., Lai, X. et al. Identification of differentially expressed genes and signaling pathways using bioinformatics in interstitial lung disease due to tyrosine kinase inhibitors targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. Invest New Drugs 37, 384–400 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-018-0664-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-018-0664-z