Summary
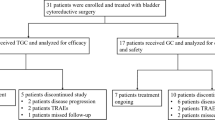
Purpose Sunitinib is a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) inhibitor with antitumor activity against bladder cancer. We hypothesized that treatment with sunitinib may decrease progression or recurrence in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) refractory to intra-vesical BCG. Patients and Methods This is a single-arm phase II study of sunitinib in patients (pts) with NMIBC who progressed after BCG. Treatment included sunitinib 37.5 g daily for 12 weeks followed by 12± 2-week cystoscopy and surveillance for one year. The primary endpoint was the complete response rate at 12 months. Secondary endpoints included recurrence free survival (RFS), progression free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and safety of sunitinib. Correlative studies on effects of sunitinib on myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSC) and humoral immune responses were also performed. This trial was registered on ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT01118351. Results Between June 2011 and September 2011, 15/19 pts. completed 12 weeks of therapy. The remaining 4 pts. had treatment related adverse events leading to discontinuation of sunitinib with one patient withdrawing consent. On the 12-week cystoscopy, 44% (8/18) of the pts. showed remission, 50% (9/18) progression and 1/18 recurrence. Overall, 22% (4/18) of pts. remained free of progression for >12 months. Grade (G) 4 toxicities were noted in 2 pts. (anemia and thrombocytopenia) while G3 were noted in 58%. Sunitinib resulted in reversal of MDSC mediated immunosuppression. Conclusions In NMIBC refractory to BCG, treatment with sunitinib was safe but not associated with improved clinical outcomes. The immune effects of sunitinib deserve further investigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2018) Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin 68:7–30
Pasin E, Josephson DY, Mitra AP, Cote RJ, Stein JP (2008) Superficial bladder cancer: an update on etiology, molecular development, classification, and natural history. Rev Urol 10:31–43
Spiess PE, Agarwal N, Bangs R, Boorjian SA, Buyyounouski MK, Clark PE, Downs TM, Efstathiou JA, Flaig TW, Friedlander T, Greenberg RE, Guru KA, Hahn N, Herr HW, Hoimes C, Inman BA, Jimbo M, Kader AK, Lele SM, Meeks JJ, Michalski J, Montgomery JS, Pagliaro LC, Pal SK, Patterson A, Plimack ER, Pohar KS, Porter MP, Preston MA, Sexton WJ, Siefker-Radtke AO, Sonpavde G, Tward J, Wile G, Dwyer MA, Gurski LA (2017) Bladder Cancer, version 5.2017, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 15:1240–1267
Smith JA Jr, Labasky RF, Cockett AT et al (1999) Bladder cancer clinical guidelines panel summary report on the management of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer (stages ta, T1 and TIS). The American Urological Association. J Urol 162:1697–1701
Soloway MS, Sofer M, Vaidya A (2002) Contemporary management of stage T1 transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Urol 167:1573–1583
Thalmann GN, Markwalder R, Shahin O et al (2004) Primary T1G3 bladder cancer: organ preserving approach or immediate cystectomy? J Urol 172:70–75
Lamm DL, Griffith JG (1992) Intravesical therapy: does it affect the natural history of superficial bladder cancer? Semin Urol 10:39–44
Herr HW, Sogani PC (2001) Does early cystectomy improve the survival of patients with high risk superficial bladder tumors? J Urol 166:1296–1299
Shabsigh A, Korets R, Vora KC, Brooks CM, Cronin AM, Savage C, Raj G, Bochner BH, Dalbagni G, Herr HW, Donat SM (2009) Defining early morbidity of radical cystectomy for patients with bladder cancer using a standardized reporting methodology. Eur Urol 55:164–174
Bradley DA, Dunn R, Nanus D, Stadler W, Dreicer R, Rosenberg J, Smith DC, Hussain M (2007) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II trial of maintenance sunitinib versus placebo after chemotherapy for patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma: scientific rationale and study design. Clin Genitourin Cancer 5:460–463
Brown LF, Berse B, Jackman RW, Tognazzi K, Manseau EJ, Dvorak HF, Senger DR (1993) Increased expression of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) and its receptors in kidney and bladder carcinomas. Am J Pathol 143:1255–1262
Sonpavde G, Jian W, Liu H, Wu MF, Shen SS, Lerner SP (2009) Sunitinib malate is active against human urothelial carcinoma and enhances the activity of cisplatin in a preclinical model. Urol Oncol 27:391–399
Gallagher DJ, Milowsky MI, Gerst SR, Ishill N, Riches J, Regazzi A, Boyle MG, Trout A, Flaherty AM, Bajorin DF (2010) Phase II study of sunitinib in patients with metastatic urothelial cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:1373–1379
Bellmunt J, Gonzalez-Larriba JL, Prior C, Maroto P, Carles J, Castellano D, Mellado B, Gallardo E, Perez-Gracia JL, Aguilar G, Villanueva X, Albanell J, Calvo A (2011) Phase II study of sunitinib as first-line treatment of urothelial cancer patients ineligible to receive cisplatin-based chemotherapy: baseline interleukin-8 and tumor contrast enhancement as potential predictive factors of activity. Ann Oncol 22:2646–2653
Harshman L, Srinivas S (2008) Continuous daily dosing of sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer. Onkologie 31:432–433
Escudier B, Roigas J, Gillessen S, Harmenberg U, Srinivas S, Mulder SF, Fountzilas G, Peschel C, Flodgren P, Maneval EC, Chen I, Vogelzang NJ (2009) Phase II study of sunitinib administered in a continuous once-daily dosing regimen in patients with cytokine-refractory metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 27:4068–4075
Chen F, Zhuang X, Lin L, Yu P, Wang Y, Shi Y, Hu G, Sun Y (2015) New horizons in tumor microenvironment biology: challenges and opportunities. BMC Med 13:45
Ko JS, Zea AH, Rini BI, Ireland JL, Elson P, Cohen P, Golshayan A, Rayman PA, Wood L, Garcia J, Dreicer R, Bukowski R, Finke JH (2009) Sunitinib mediates reversal of myeloid-derived suppressor cell accumulation in renal cell carcinoma patients. Clin Cancer Res 15:2148–2157
Demetri GD, van Oosterom AT, Garrett CR, Blackstein ME, Shah MH, Verweij J, McArthur G, Judson IR, Heinrich MC, Morgan JA, Desai J, Fletcher CD, George S, Bello CL, Huang X, Baum CM, Casali PG (2006) Efficacy and safety of sunitinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumour after failure of imatinib: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 368:1329–1338
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik C, Kim ST, Chen I, Bycott PW, Baum CM, Figlin RA (2007) Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356:115–124
Raymond E, Dahan L, Raoul JL, Bang YJ, Borbath I, Lombard-Bohas C, Valle J, Metrakos P, Smith D, Vinik A, Chen JS, Hörsch D, Hammel P, Wiedenmann B, van Cutsem E, Patyna S, Lu DR, Blanckmeister C, Chao R, Ruszniewski P (2011) Sunitinib malate for the treatment of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. N Engl J Med 364:501–513
Motzer RJ, Jonasch E, Agarwal N, Bhayani S, Bro WP, Chang SS, Choueiri TK, Costello BA, Derweesh IH, Fishman M, Gallagher TH, Gore JL, Hancock SL, Harrison MR, Kim W, Kyriakopoulos C, LaGrange C, Lam ET, Lau C, Michaelson MD, Olencki T, Pierorazio PM, Plimack ER, Redman BG, Shuch B, Somer B, Sonpavde G, Sosman J, Dwyer M, Kumar R (2016) Clinical practice guidelines in oncology: kidney cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 15(6):804-834. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2017.0100
Grivas PD, Daignault S, Tagawa ST, Nanus DM, Stadler WM, Dreicer R, Kohli M, Petrylak DP, Vaughn DJ, Bylow KA, Wong SG, Sottnik JL, Keller ET, al-Hawary M, Smith DC, Hussain M (2014) Double-blind, randomized, phase 2 trial of maintenance sunitinib versus placebo after response to chemotherapy in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma. Cancer 120:692–701
Izawa JI, Slaton JW, Kedar D, Karashima T, Perrotte P, Czerniak B, Grossman HB, Dinney CP (2001) Differential expression of progression-related genes in the evolution of superficial to invasive transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Oncol Rep 8:9–15
Bochner BH, Cote RJ, Weidner N, Groshen S, Chen SC, Skinner DG, Nichols PW (1995) Angiogenesis in bladder cancer: relationship between microvessel density and tumor prognosis. J Natl Cancer Inst 87:1603–1612
Canoglu A, Gogus C, Beduk Y et al (2004) Microvessel density as a prognostic marker in bladder carcinoma: correlation with tumor grade, stage and prognosis. Int Urol Nephrol 36:401–405
Dickinson AJ, Fox SB, Persad RA et al (1994) Quantification of angiogenesis as an independent predictor of prognosis in invasive bladder carcinomas. Br J Urol 74:762–766
Donmez G, Sullu Y, Baris S, Yildiz L, Aydin O, Karagoz F, Kandemir B (2009) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), and thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) expression in urothelial carcinomas. Pathol Res Pract 205:854–857
Goddard JC, Sutton CD, Furness PN, O'Byrne KJ, Kockelbergh RC (2003) Microvessel density at presentation predicts subsequent muscle invasion in superficial bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res 9:2583–2586
Hurwitz HI, Fehrenbacher L, Hainsworth JD, Heim W, Berlin J, Holmgren E, Hambleton J, Novotny WF, Kabbinavar F (2005) Bevacizumab in combination with fluorouracil and leucovorin: an active regimen for first-line metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:3502–3508
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J, Schiller JH, Dowlati A, Lilenbaum R, Johnson DH (2006) Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 355:2542–2550
Miller K, Wang M, Gralow J, Dickler M, Cobleigh M, Perez EA, Shenkier T, Cella D, Davidson NE (2007) Paclitaxel plus bevacizumab versus paclitaxel alone for metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med 357:2666–2676
Goel S, Duda DG, Xu L, Munn LL, Boucher Y, Fukumura D, Jain RK (2011) Normalization of the vasculature for treatment of cancer and other diseases. Physiol Rev 91:1071–1121
Gemcitabine Hydrochloride and Cisplatin With or Without Bevacizumab in Treating Patients With Advanced Urinary Tract Cancer. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00942331. [Last accessed August 25, 2018]
Gopalakrishnan D, Koshkin VS, Ornstein MC, Papatsoris A, Grivas P (2018) Immune checkpoint inhibitors in urothelial cancer: recent updates and future outlook. Ther Clin Risk Manag 14:1019–1040
Motzer RJ, Bander NH, Nanus DM (1996) Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 335:865–875
Lamiell JM, Salazar FG, von Hsia YE (1989) Hippel-Lindau disease affecting 43 members of a single kindred. Medicine (Baltimore) 68:1–29
Latif F, Tory K, Gnarra J, Yao M, Duh F, Orcutt M, Stackhouse T, Kuzmin I, Modi W, Geil L et al (1993) Identification of the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene. Science 260:1317–1320
Ohki S, Shibata M, Gonda K et al (2012) Circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells are increased and correlate to immune suppression, inflammation and hypoproteinemia in patients with cancer. Oncol Rep 28:453–458
Kusmartsev S, Gabrilovich DI (2006) Role of immature myeloid cells in mechanisms of immune evasion in cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 55:237–245
George DJ, Kaelin WG Jr (2003) The von Hippel-Lindau protein, vascular endothelial growth factor, and kidney cancer. N Engl J Med 349:419–421
Rini BI, Campbell SC, Escudier B (2009) Renal cell carcinoma. Lancet 373:1119–1132
Ping SY, Wu CL, Yu DS (2010) Sunitinib can enhance BCG mediated cytotoxicity to transitional cell carcinoma through apoptosis pathway. Urol Oncol
Alexander M, Helfand CTL, Hafez K, Hussain M, Liebert M, Daignault S, Montgomery JS, Miller DC, Drnek L, Hollenbeck BK, Weizer AZ (2015) Phase II clinical trial of intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) followed by sunitinib for the treatment of high-risk nonmuscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC). J Clin Oncol 33(suppl 7; abstr 293):2015
Funding
The work was supported by the Pfizer Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HZ contributed to the data acquisition, drafting and final revision of the manuscript. MCM participated in data acquisition and final revision of the manuscript. PCB participated in data acquisition and final revision of the manuscript. AJS participated in data acquisition and final revision of the manuscript. SCC participated in data acquisition and final revision of the manuscript. RD participated in data acquisition and final revision of the manuscript. JAG contributed to the conception and coordination of the study, data acquisition, drafting and final revision of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
HZ declares that he has no conflict of interest. MCM declares that he has no conflict of interest. PCB declares that he has no conflict of interest. AJS declares that he has no conflict of interest. SCC declares that he has no conflict of interest. AF declares that he has no conflict of interest. RD has served as a consultant for Astra Zeneca, Janssen, Pfizer, Lilly and Astellas. The other authors declare no competing interests directly related to this manuscript. JAG has honoraria from Bayer, Sanofi, Pfizer, Genentech, Janssen, Eisai and Exelixis.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zahoor, H., Mir, M.C., Barata, P.C. et al. Phase II trial of continuous treatment with sunitinib in patients with high-risk (BCG-refractory) non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Invest New Drugs 37, 1231–1238 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-018-00716-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-018-00716-w