Summary
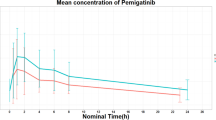
Introduction This phase 1, open-label, multicenter, single-arm, dose-escalation study aimed to evaluate safety, pharmacokinetics (PK), and pharmacodynamics of erdafitinib (JNJ-42756493), an oral selective pan-fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and to determine the recommended phase 2 dose in Japanese patients with advanced or refractory solid tumors. Methods Three to 6 patients were enrolled into sequentially escalating dose cohorts (erdafitinib 2, 4, or 6 mg) with a daily dosing schedule of 21-day cycles or a 7 days-on/7 days-off intermittent schedule (erdafitinib 10 mg or 12 mg) of 28-day cycles. Results Nineteen patients received escalating doses of erdafitinib with a daily or intermittent schedule. The most common treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were hyperphosphatemia (73.7%), nausea (36.8%), stomatitis (26.3%), dysgeusia (26.3%) and dry mouth (21.1%). The maximum tolerated dose was not reached in this study. No Grade 3 or higher TEAEs, or serious TEAEs were noted and no clinically significant changes in vital signs, laboratory parameters, and electrocardiogram readings were observed. However, one case of dose-limiting toxicity in the 12 mg intermittent dosing group was observed: Grade 2 detachment of retinal pigment epithelium (bilateral) with treatment discontinuation. The maximum plasma concentrations of erdafitinib exhibited a dose-dependent increase. The median tmax ranged from 2 to 3 h after the initial dose to 2–6 h following multiple daily dosing. Based on the safety and PK data, the 10 mg 7 days-on/7 days-off regimen was determined as the recommended phase 2 dose in this study. Conclusions Erdafitinib was well tolerated in Japanese patients with advanced or refractory solid tumors. Trial Registration: NCT01962532.



Similar content being viewed by others

References
Wesche J, Haglund K, Haugsten EM (2011) Fibroblast growth factors and their receptors in cancer. Biochem J 437(2):199–213. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20101603
Wohrle S, Bonny O, Beluch N, Gaulis S, Stamm C, Scheibler M, Muller M, Kinzel B, Thuery A, Brueggen J, Hynes NE, Sellers WR, Hofmann F, Graus-Porta D (2011) FGF receptors control vitamin D and phosphate homeostasis by mediating renal FGF-23 signaling and regulating FGF-23 expression in bone. J Bone Miner Res 26(10):2486–2497. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.478
Razzaque MS (2009) The FGF23-Klotho axis: endocrine regulation of phosphate homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol 5(11):611–619. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2009.196
Eswarakumar VP, Lax I, Schlessinger J (2005) Cellular signaling by fibroblast growth factor receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16(2):139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2005.01.001
Beenken A, Mohammadi M (2009) The FGF family: biology, pathophysiology and therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8(3):235–253. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2792
Li F, Huynh H, Li X, Ruddy DA, Wang Y, Ong R, Chow P, Qiu S, Tam A, Rakiec DP, Schlegel R, Monahan JE, Huang A (2015) FGFR-Mediated Reactivation of MAPK Signaling Attenuates Antitumor Effects of Imatinib in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. Cancer Discov 5(4):438–451. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0763
Tomlinson DC, Lamont FR, Shnyder SD, Knowles MA (2009) Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 promotes proliferation and survival via activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in bladder cancer. Cancer Res 69(11):4613–4620. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2816
Baselga J (2011) Targeting the phosphoinositide-3 (PI3) kinase pathway in breast cancer. Oncologist 16(Suppl 1):12–19. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2011-S1-12
Chen Y, Li X, Eswarakumar VP, Seger R, Lonai P (2000) Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling through PI 3-kinase and Akt/PKB is required for embryoid body differentiation. Oncogene 19(33):3750–3756. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203726
Ahmad I, Iwata T, Leung HY (2012) Mechanisms of FGFR-mediated carcinogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1823(4):850–860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.01.004
Singh D, Chan JM, Zoppoli P, Niola F, Sullivan R, Castano A, Liu EM, Reichel J, Porrati P, Pellegatta S, Qiu K, Gao Z, Ceccarelli M, Riccardi R, Brat DJ, Guha A, Aldape K, Golfinos JG, Zagzag D, Mikkelsen T, Finocchiaro G, Lasorella A, Rabadan R, Iavarone A (2012) Transforming fusions of FGFR and TACC genes in human glioblastoma. Science 337(6099):1231–1235. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1220834
Weiss J, Sos ML, Seidel D, Peifer M, Zander T, Heuckmann JM, Ullrich RT, Menon R, Maier S, Soltermann A, Moch H, Wagener P, Fischer F, Heynck S, Koker M, Schottle J, Leenders F, Gabler F, Dabow I, Querings S, Heukamp LC, Balke-Want H, Ansen S, Rauh D, Baessmann I, Altmuller J, Wainer Z, Conron M, Wright G, Russell P, Solomon B, Brambilla E, Brambilla C, Lorimier P, Sollberg S, Brustugun OT, Engel-Riedel W, Ludwig C, Petersen I, Sanger J, Clement J, Groen H, Timens W, Sietsma H, Thunnissen E, Smit E, Heideman D, Cappuzzo F, Ligorio C, Damiani S, Hallek M, Beroukhim R, Pao W, Klebl B, Baumann M, Buettner R, Ernestus K, Stoelben E, Wolf J, Nurnberg P, Perner S, Thomas RK (2010) Frequent and focal FGFR1 amplification associates with therapeutically tractable FGFR1 dependency in squamous cell lung cancer. Sci Transl Med 2(62):62ra93. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3001451
Weeden CE, Solomon B, Asselin-Labat ML (2015) FGFR1 inhibition in lung squamous cell carcinoma: questions and controversies. Cell Death Dis 1:15049. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddiscovery.2015.49
Jang JH, Shin KH, Park JG (2001) Mutations in fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 and fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 genes associated with human gastric and colorectal cancers. Cancer Res 61(9):3541–3543
Desnoyers LR, Pai R, Ferrando RE, Hotzel K, Le T, Ross J, Carano R, D'Souza A, Qing J, Mohtashemi I, Ashkenazi A, French DM (2008) Targeting FGF19 inhibits tumor growth in colon cancer xenograft and FGF19 transgenic hepatocellular carcinoma models. Oncogene 27(1):85–97. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210623
Gatius S, Velasco A, Azueta A, Santacana M, Pallares J, Valls J, Dolcet X, Prat J, Matias-Guiu X (2011) FGFR2 alterations in endometrial carcinoma. Mod Pathol 24(11):1500–1510. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2011.110
Haugsten EM, Wiedlocha A, Olsnes S, Wesche J (2010) Roles of fibroblast growth factor receptors in carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer Res 8(11):1439–1452. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0168
Guancial EA, Werner L, Bellmunt J, Bamias A, Choueiri TK, Ross R, Schutz FA, Park RS, O'Brien RJ, Hirsch MS, Barletta JA, Berman DM, Lis R, Loda M, Stack EC, Garraway LA, Riester M, Michor F, Kantoff PW, Rosenberg JE (2014) FGFR3 expression in primary and metastatic urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Cancer Med 3(4):835–844. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.262
Touat M, Ileana E, Postel-Vinay S, Andre F, Soria JC (2015) Targeting FGFR Signaling in Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 21(12):2684–2694. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2329
Katoh M (2016) FGFR inhibitors: Effects on cancer cells, tumor microenvironment and whole-body homeostasis (Review). Int J Mol Med 38(1):3–15. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2016.2620
Gavine PR, Mooney L, Kilgour E, Thomas AP, Al-Kadhimi K, Beck S, Rooney C, Coleman T, Baker D, Mellor MJ, Brooks AN, Klinowska T (2012) AZD4547: an orally bioavailable, potent, and selective inhibitor of the fibroblast growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase family. Cancer Res 72(8):2045–2056. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3034
Jonker DJ, Rosen LS, Sawyer MB, de Braud F, Wilding G, Sweeney CJ, Jayson GC, McArthur GA, Rustin G, Goss G, Kantor J, Velasquez L, Syed S, Mokliatchouk O, Feltquate DM, Kollia G, Nuyten DS, Galbraith S (2011) A phase I study to determine the safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a dual VEGFR and FGFR inhibitor, brivanib, in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors. Ann Oncol 22(6):1413–1419. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdq599
Goke A, Goke R, Ofner A, Herbst A, Lankat-Buttgereit B (2015) The FGFR Inhibitor NVP-BGJ398 Induces NSCLC Cell Death by Activating Caspase-dependent Pathways as well as Caspase-independent Apoptosis. Anticancer Res 35(11):5873–5879
Goke F, Franzen A, Hinz TK, Marek LA, Yoon P, Sharma R, Bode M, von Maessenhausen A, Lankat-Buttgereit B, Goke A, Golletz C, Kirsten R, Boehm D, Vogel W, Kleczko EK, Eagles JR, Hirsch FR, Van Bremen T, Bootz F, Schroeck A, Kim J, Tan AC, Jimeno A, Heasley LE, Perner S (2015) FGFR1 Expression Levels Predict BGJ398 Sensitivity of FGFR1-Dependent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancers. Clin Cancer Res 21(19):4356–4364. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-3357
Cheng AL, Thongprasert S, Lim HY, Sukeepaisarnjaroen W, Yang TS, Wu CC, Chao Y, Chan SL, Kudo M, Ikeda M, Kang YK, Pan H, Numata K, Han G, Balsara B, Zhang Y, Rodriguez AM, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Poon RT (2016) Randomized, open-label phase 2 study comparing frontline dovitinib versus sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 64(3):774–784. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.28600
Lim SH, Sun JM, Choi YL, Kim HR, Ahn S, Lee JY, Lee SH, Ahn JS, Park K, Kim JH, Cho BC, Ahn MJ (2016) Efficacy and safety of dovitinib in pretreated patients with advanced squamous non-small cell lung cancer with FGFR1 amplification: A single-arm, phase 2 study. Cancer 122(19):3024–3031. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.30135
Milowsky MI, Dittrich C, Duran I, Jagdev S, Millard FE, Sweeney CJ, Bajorin D, Cerbone L, Quinn DI, Stadler WM, Rosenberg JE, Lochheed M, Sen P, Squires M, Shi M, Sternberg CN (2014) Phase 2 trial of dovitinib in patients with progressive FGFR3-mutated or FGFR3 wild-type advanced urothelial carcinoma. Eur J Cancer 50(18):3145–3152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2014.10.013
Ledermann JA, Embleton AC, Raja F, Perren TJ, Jayson GC, Rustin GJ, Kaye SB, Hirte H, Eisenhauer E, Vaughan M, Friedlander M, Gonzalez-Martin A, Stark D, Clark E, Farrelly L, Swart AM, Cook A, Kaplan RS, Parmar MK, collaborators I (2016) Cediranib in patients with relapsed platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer (ICON6): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 387(10023):1066–1074. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01167-8
Symonds RP, Gourley C, Davidson S, Carty K, McCartney E, Rai D, Banerjee S, Jackson D, Lord R, McCormack M, Hudson E, Reed N, Flubacher M, Jankowska P, Powell M, Dive C, West CM, Paul J (2015) Cediranib combined with carboplatin and paclitaxel in patients with metastatic or recurrent cervical cancer (CIRCCa): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 16(15):1515–1524. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00220-X
Powell MA, Sill MW, Goodfellow PJ, Benbrook DM, Lankes HA, Leslie KK, Jeske Y, Mannel RS, Spillman MA, Lee PS, Hoffman JS, McMeekin DS, Pollock PM (2014) A phase II trial of brivanib in recurrent or persistent endometrial cancer: an NRG Oncology/Gynecologic Oncology Group Study. Gynecol Oncol 135(1):38–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2014.07.083
Tabernero J, Bahleda R, Dienstmann R, Infante JR, Mita A, Italiano A, Calvo E, Moreno V, Adamo B, Gazzah A, Zhong B, Platero SJ, Smit JW, Stuyckens K, Chatterjee-Kishore M, Rodon J, Peddareddigari V, Luo FR, Soria JC (2015) Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of JNJ-42756493, an Oral Pan-Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor, in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors. J Clin Oncol 33(30):3401–3408. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.60.7341
Soria JIA, Cervantes A, Tabernero J, Infante J, Lara PN, Spira A, Calvo E, Moreno V, Blay J, Lauer R, Chan N, Zhong B, Santiago-Walker A, Bussolari J, Luo FR, Xie H, Hammerman P (2016) Safety and activity of the pan–fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) inhibitor erdafitinib in phase 1 study patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma. Ann Oncol 27(Suppl_6):781PD
Dienstmann R, Rodon J, Prat A, Perez-Garcia J, Adamo B, Felip E, Cortes J, Iafrate AJ, Nuciforo P, Tabernero J (2014) Genomic aberrations in the FGFR pathway: opportunities for targeted therapies in solid tumors. Ann Oncol 25(3):552–563. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdt419
Crawford Y, Ferrara N (2009) Tumor and stromal pathways mediating refractoriness/resistance to anti-angiogenic therapies. Trends Pharmacol Sci 30(12):624–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2009.09.004
Brooks AN, Kilgour E, Smith PD (2012) Molecular pathways: fibroblast growth factor signaling: a new therapeutic opportunity in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 18(7):1855–1862. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0699
van der Noll R, Leijen S, Neuteboom GH, Beijnen JH, Schellens JH (2013) Effect of inhibition of the FGFR-MAPK signaling pathway on the development of ocular toxicities. Cancer Treat Rev 39(6):664–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2013.01.003
Acknowledgments
Investigational compound erdafitinib (JNJ-42756493) was discovered in collaboration with Astex Pharmaceuticals. This study was supported by Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K. The authors thank all the patients for their participation in this study and acknowledge the collaboration and commitment of all investigators and their staff. The authors thank the safety monitoring committee members (Dr. I. Hyodo from the University of Tsukuba and Dr. F. Nagashima from Kyorin University). The authors thank Dr. Shivangi Gupta and Dr. Himabindu Gutha (both, SIRO Clinpharm Pvt. Ltd.) for providing writing assistance and Dr. Harry Ma (Janssen Research & Development, LLC.) for providing additional editorial support for this manuscript.
Funding
The study is sponsored by Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Drs. Nishina, Takahashi, and Doi were involved in study design, data interpretation, and involved as investigators. Ryota Iwasawa and Dr. Aoki had primary role in the study design, analysis, and data interpretation. Hidehisa Noguchi was responsible for the statistical analyses and design/interpretation of study results. All authors had full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. All authors meet ICMJE criteria and all those who fulfilled those criteria are listed as authors. All authors provided direction and comments on the manuscript, made the final decision about where to publish these data, and approved submission to this journal.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
Ryota Iwasawa, Hidehisa Noguchi, and Mayasuki Aoki are employees of Janssen Pharmaceutical K. K. (JPKK). Drs. Takahashi, Nishina and Doi received research grants from JPKK.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishina, T., Takahashi, S., Iwasawa, R. et al. Safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamics of erdafitinib, a pan-fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced or refractory solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 36, 424–434 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-017-0514-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-017-0514-4