Summary
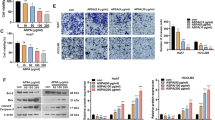
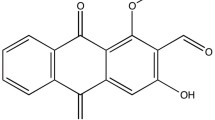
Ent-11-hydroxy-15-oxo-kaur-16-en-19-oic-acid (5F) isolated from Pteris Semipinnata L is known to inhibit certain tumor cells in vitro. The information on the in vivo effect of 5F is limited and its effect on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is unknown. In this study, the anti-tumor effect of 5F was investigated in a diethylnitrosamine (DEN)-induced mouse HCC model. In addition to therapeutic effect, the potential side effect was monitored. A panel of cultured HCC cells was used to confirm the in vivo data and explore the responsible molecular pathway. The result showed that 5F significantly inhibited the DEN-induced HCC tumors by reducing the number of tumor foci and the volume of tumors. Furthermore, 5F induced the death of cultured HCC cells in dose- and time-dependent manners. The cell death was confirmed to be apoptotic by in vivo and in vitro TUNEL assays. 5F inhibited NF-kB by stabilizing its inhibitor IkBα, reducing the nuclear p65 and inhibiting NF-kB activity. Subsequently it affected the NF-kB downstream molecules with a decrease in anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and increase in pro-apoptotic Bax and Bak. During the whole period of the experiment, mice receiving 5F appeared to be healthy, though they suffered from a mild degree of hair loss. 5F did not damage liver and renal functions. In conclusion, 5F is effective against HCC with minimal side effects. It induces apoptosis in HCC cells via inhibiting NF-kB, leading to the decrease of Bcl-2 but the increase of Bax and Bak.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lencioni R, Chen XP, Dagher L, Venook AP (2010) Treatment of intermediate/advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in the clinic: how can outcomes be improved? Oncologist 15(Suppl 4):42–52
Whittaker S, Marais R, Zhu AX (2010) The role of signaling pathways in the development and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 29:4989–5005
Lan L-B, Linag N-C, Mo L-E, Deng Y-F (2003) Purification of 5F from Pteris semipinnata and its enhanced cytotoxicity in vitro. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin 19:804–807
Chen GG, Linag NC, Lee JF, Chan UP, Wang SH, Leung BC et al (2004) Over-expression of Bcl-2 against Pteris semipinnata L-induced apoptosis of human colon cancer cells via a NF-kappa B-related pathway. Apoptosis 9:619–627
He T-P, Mo L-E, Linag N (2005) Effects of 5F from Pteris semipinnata L on expression of NF-kB and FAK protein in HO-8910PM cells. Chin J Cancer Prev Therat 12:565–568
Liu Z, Ng EK, Linag N, Deng YF, Leung BC, Chen GG (2005) Cell death induced by Pteris semipinnata L. is associated with p53 and oxidant stress in gastric cancer cells. FEBS Letters 579:1477–1487
Liu ZM, Chen GG, Vlantis AC, Liang NC, Deng YF, van Hasselt CA (2005) Cell death induced by ent-11alpha-hydroxy-15-oxo-kaur-16-en-19-oic-acid in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells is via a mitochondrial-mediated pathway. Apoptosis 10:1345–1356
Li MY, Leung J, Kong AW, Liang NC, Wu K, Hsin MK et al (2010) Anticancer efficacy of 5F in NNK-induced lung cancer development of A/J mice and human lung cancer cells. J Mol Med 88:1265–1276
Vlantis AC, Lo CS, Chen GG, Liang CN, Lui VW, Wu K et al (2010) Induction of laryngeal cancer cell death by Ent-11-hydroxy-15-oxo-kaur-16-en-19-oic acid. Head Neck 32:1506–1518
Lee GH, Nomura K, Kanda H, Kusakabe M, Yoshiki A, Sakakura T et al (1991) Strain specific sensitivity to diethylnitrosamine-induced carcinogenesis is maintained in hepatocytes of C3H/HeN in equilibrium with C57BL/6N chimeric mice. Cancer Res 51:3257–3260
Teoh NC, Dan YY, Swisshelm K, Lehman S, Wright JH, Haque J et al (2008) Defective DNA strand break repair causes chromosomal instability and accelerates liver carcinogenesis in mice. Hepatology 47:2078–2088
Carlsson G, Gullberg B, Hafstrom L (1983) Estimation of liver tumor volume using different formulas - an experimental study in rats. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 105:20–23
Gee MS, Koch CJ, Evans SM, Jenkins WT, Pletcher CH Jr, Moore JS et al (1999) Hypoxia-mediated apoptosis from angiogenesis inhibition underlies tumor control by recombinant interleukin 12. Cancer Res 59:4882–4889
Jacobs DS, Oxley DK, DeMott WR (2002) Laboratory test handbook, 2nd edn. Lexi-Comp, Hudson
Chen GG, Lai PBS, Chak ECW, Lau WY (2001) Immunohistochemical analysis of pro-apoptotic Bid level in chronic hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinoma and liver metastases. Cancer Lett 172:75–82
Chen GG, Chan UPF, Bai L, Fung KY, Tessier A, To AKY et al (2009) ZBP-89 reduces the cell death threshold by increasing caspase-6 and S phase arrest in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Letters 283:52–58
Miao J, Chen GG, Chun SY, Yun JP, Chak ECW, Ho RLK et al (2006) Adenovirus-mediated tBid overexpression results in therapeutic effects on p53-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma. International Journal of Cancer 119:1985–1993
Gramantieri L, Trerè D, Chieco P, Lacchini M, Giovannini C, Piscaglia F et al (2003) In human hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is involved in cell proliferation and cooperates with P21 in DNA repair. J Hepatol 39:997–1003
Loeppky RN (1999) The mechanism of bioactivation of N-nitrosodiethanolamine. Drug Metab Rev 31:175–193
Van Waes C (2007) Nuclear factor-kappaB in development, prevention, and therapy of cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13:1076–1082
Ghashghaeinia M, Toulany M, Saki M, Bobbala D, Fehrenbacher B, Rupec R et al (2011) The NFĸB pathway inhibitors Bay 11-7082 and parthenolide induce programmed cell death in anucleated Erythrocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem 27:45–54
Fahy BN, Schlieman MG, Mortenson MM, Virudachalam S, Bold RJ (2005) Targeting BCL-2 overexpression in various human malignancies through NF-kappaB inhibition by the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 56:46–54
Cianfrocca R, Muscolini M, Marzano V, Annibaldi A, Marinari B, Levrero M et al (2008) RelA/NF-kappaB recruitment on the Bax gene promoter antagonizes p73-dependent apoptosis in costimulated T cells. Cell Death Differ 15:354–363
Simmons MJ, Fan G, Zong WX, Degenhardt K, White E, Gélinas C (2008) Bfl-1/A1 functions, similar to Mcl-1, as a selective tBid and Bak antagonist. Oncogene 27:1421–1428
Wu MH, Ma WL, Hsu CL, Chen YL, Ou JH, Ryan CK et al (2010) Androgen receptor promotes hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocarcinogenesis through modulation of hepatitis B virus RNA transcription. Sci Transl Med 2: 32ra35
Bishayee A, Mbimba T, Thoppil RJ, Háznagy-Radnai E, Sipos P, Darvesh AS et al (2011) Anthocyanin-rich black currant (Ribes nigrum L.) extract affords chemoprevention against diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinogenesis in rats. J Nutr Biochem 2011 (In press)
Naugler WE, Sakurai T, Kim S, Maeda S, Kim K, Elsharkawy AM et al (2007) Gender disparity in liver cancer due to sex differences in MyD88-dependent IL-6 production. Science 317:121–124
García A, Zeng Y, Muthupalani S, Ge Z, Potter A, Mobley MW et al (2011) Helicobacter hepaticus–induced liver tumor promotion is associated with increased serum bile acid and a persistent microbial-induced immune response. Cancer Res 71:2529–2540
Park O, Wang H, Weng H, Feigenbaum L, Li H, Yin S et al (2011) In vivo consequences of liver-specific interleukin-22 expression in mice: Implications for human liver disease progression. Hepatology 54:252–261
Amin A, Hamza AA, Bajbouj K, Ashraf SS, Daoud S (2011) Saffron: A potential candidate for a novel anticancer drug against hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 54:857–867
Khan MS, Devaraj H, Devaraj N (2011) Chrysin abrogates early hepatocarcinogenesis and induces apoptosis in N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced preneoplastic nodules in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 251:85–94
Ramadori G, Cameron S (2010) Effects of systemic chemotherapy on the liver. Ann Hepatol 9:133–143
Gracias VH, McGonigal MD (2000) Monitoring organ function. Heart, liver, and kidney. Surg Clin North Am 80:911–919, x
Yao Y, Chen F, Wang M, Wang J, Ren G (2008) Antidiabetic activity of Mung bean extracts in diabetic KK-Ay mice. J Agric Food Chem 56:8869–8873
de Vries B, Köhl J, Leclercq WK, Wolfs TG, van Bijnen AA, Heeringa P et al (2003) Complement factor C5a mediates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury independent from neutrophils. J Immunol 170:3883–3889
Goldenberg I, Moss AJ, McNitt S, Barsheshet A, Gray D, Andrews ML et al (2010) Relation between renal function and response to cardiac resynchronization therapy in Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation Trial–Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (MADIT-CRT). Heart Rhythm 7:1777–1782
Chiu CT, Yeh TS, Hsu JC, Chen MF (2003) Expression of Bcl-2 family modulated through p53-dependent pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 48:670–676
Qiao L, Zhang H, Yu J, Francisco R, Dent P, Ebert MP et al (2006) Constitutive activation of NF-kappaB in human hepatocellular carcinoma: evidence of a cytoprotective role. Human Gene Therapy 17:280–290
Omar HA, Sargeant AM, Weng JR, Wang D, Kulp SK, Patel T et al (2009) Targeting of the Akt-nuclear factor-kappa B signaling network by [1-(4-chloro-3-nitrobenzenesulfonyl)-1H-indol-3-yl]-methanol (OSU-A9), a novel indole-3-carbinol derivative, in a mouse model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Pharmacol 76:957–968
Pizem J, Marolt VF, Luzar B, Cör A (2001) Proliferative and apoptotic activity in hepatocellular carcinoma and surrounding non-neoplastic liver tissue. Pflugers Arch 442:R174–176
Luo D, Cheng SC, Xie H, Xie Y (1999) Chemosensitivity of human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line QGY-7703 is related to bcl-2 protein levels. Tumour Biol 20:331–340
Guo XZ, Shao XD, Liu MP, Xu JH, Ren LN, Zhao JJ et al (2002) Effect of bax, bcl-2 and bcl-xL on regulating apoptosis in tissues of normal liver and hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 8:1059–1062
Liu LX, Jiang HC, Liu ZH, Zhu AL, Zhou J, Zhang WH et al (2003) Gene expression profiles of hepatoma cell line BEL-7402. Hepatogastroenterology 50:1496–1501
Rousseau B, Menard L, Haurie V, Taras D, Blanc JF, Moreau-Gaudry F et al (2007) Overexpression and role of the ATPase and putative DNA helicase RuvB-like 2 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 46:1108–1118
To AK, Chen GG, Chan UP, Ye C, Yun JP, Ho RL et al (2011) ZBP-89 enhances Bak expression and causes apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:222–230
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from Innovation and Technology Fund of Innovation and Technology Commission, the government of the Hong Kong Special Administration Region, Project No: GHP/022/06.
Conflict of Interest
All authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G.G., Leung, J., Liang, N.C. et al. Ent-11α-hydroxy-15-oxo-kaur-16-en-19-oic-acid inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo via stabilizing IkBα. Invest New Drugs 30, 2210–2218 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-011-9791-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-011-9791-5