Summary
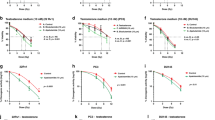
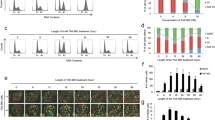
The antiproliferative and cytotoxic potential of the nucleotide analog 8-Cl-cAMP was tested in PC-3 and DU145 metastatic human prostate cancer cells. The drug was examined as the only therapeutic agent and in combination with ionizing irradiation (IR). Highly synergistic effects of IR and 8-Cl-cAMP were observed in both cell lines when examined by the MTT viability and BrdU proliferation assays. The combination of IR and 8-Cl-cAMP at clinically relevant doses exerted substantial growth inhibition. The combination of IR and 8-Cl-cAMP caused a significant disturbance in the distribution of cell cycle phases. Cell cycle arrest in the sub-G0/G1 phase predominated in both cell lines. The most striking observation was a significant increase in apoptotic PC-3 and DU145 cells. The DU145 cells were three times more sensitive to the combined treatment than PC-3 cells. The initial resistance to IR-induced apoptosis in these p53-deficient prostate cancer cell lines was overcome through an alternative proapoptotic pathway induced by 8-Cl-cAMP. Considering the low effective doses of treatments, improved tumor eradication rates and minimal undesirable side effects, the combination of IR and 8-Cl-cAMP could be the therapy of choice in treating prostate cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Denis LJ, Griffiths K (2000) Endocrine treatment of prostate cancer. Semin Surg Oncol 18:52–74
Bubley GJ, Balk GP (1996) Treatment of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Oncologist 1:30–35
Huggins C, Hodges CV (1941) Studies on prostate cancer. I. The effect of castration of estrogen and of androgen injection on serum phosphatases in metastatic carcinoma of the prostate. Cancer Res 1:293–297
Denis LJ, Carneiro de Moura JL, Bono A, Sylvester R, Whelan P, Newling D, Depauw M (1993) Gosrelin acetate and flutamide versus bilateral orchiectomy: a phase III EORTC trial (30853). Urology 42:119–130
Janknegt RA, Abbou CC, Bartoletti R (1993) Orchiectomy and nilutamide or placebo as treatment of metastatic prostatic cancer in a multinational double-blind randomized trial. J Urol 149:77–83
Fornace AJJ, Amundson SA, Bittner M, Myers TG, Meltzer P, Weinsten JN, Trent J (1999) The complexity of radiation stress responses: analysis by informatics and functional genomics approaches. Gene Expr 7:387–400
Dandrea T, Hellmold H, Jonsson C, Zhivotovsky B, Hofer T, Warngard L, Cotgreave I (2004) The transcriptosomal response of human A549 lung cells to a hydrogen peroxide-generating system: relationship to DNA damage, cell cycle arrest, and caspase activation. Free Radic Biol Med 36:881–896
Polyak K, Xia Y, Zweier JL, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1997) A model for p53-induced apoptosis. Nature 389:300–305
Allen RG, Tresisni M (2000) Oxidative stress and gene regulation. Free Radic Biol Med 28:463–499
Lim SD, Sun C, Lambeth JD, Marshall F, Amin M, Chung L, Petros JA, Arnold RS (2005) Increased Nox1 and hydrogen peroxide in prostate cancer. Prostate 62:200–207
Trzeciak AR, Nyaga SG, Jaruga P, Lohani A, Dizdaroglu M, Evans MK (2004) Cellular repair of oxidatively induced DNA base lesions is defective in prostate cancer cell lines, PC-3 and DU-145. Carcinogenesis 25:1359–1370
Oberley TD, Zhong W, Szweda LI, Oberley LW (2000) Localization of antioxidant enzymes and oxidative damage products in normal and malignant prostate epithelium. Prostate 44:144–155
Jung K, Seidel B, Rudolph B, Lein M, Cronauer MV, Henke W, Hampel G, Schnorr D, Loening SA (1997) Antioxidant enzymes in malignant prostate cell lines and in primary cultured prostatic cells. Free Radic Biol Med 23:127–133
Vucic V, Isenovic E, Adzic M, Ruzdijić S, Radojcic MB (2006) Antiproliferative and cytotoxic effects of gamma-radiation on DU-145 human prostate cancer cell line. Braz J Med Biol Res 39:227–236
Das KC, Guo XL, White CW (1998) Protein kinase Cdelta-dependent induction of manganese superoxide dismutase gene expression by microtubule-active anticancer drugs. J Biol Chem 273:34639–34645
Li JJ, Oberley LW, St. Clair DK (1995) Phenotypic changes induced in breast cancer cells by overexpression of manganese-containing superoxide dismutase. Oncogene 10:1989–2000
Denmeade SR, Lin XS, Isaacs JT (1996) Role of programmed (apoptotic) cell death during the progression and therapy for prostate cancer. Prostate 28:251–265
Theyer G, Schirmbock M, Thalhammer T, Sherwood ER, Baumgartner G, Hamilton G (1993) Role of the MDR-1-encoded multiple drug resistance phenotype in prostate cancer cell lines. J Urol 150:1544–1547
Catalona J (1994) Management of cancer of the prostate. N Engl J Med 331:996–1004
Yan SX, Ejima Y, Sasaki R, Zheng SS, Demizu Y, Soejima T, Sugimura K (2004) Combination of genistein with ionizing radiation on androgen-independent prostate cancer cells. Asian J Androl 6:285–290
Cho-Chung YS, Clair T (1993) The regulatory subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase as a target for chemotherapy of cancer and other dysfunctional-related diseases. Pharmacol Ther 60:265–288
Rohlff C, Clair T, Cho-Chung YS (1993) 8-Cl-cAMP induces truncation and down-regulation of the RI α subunits and up-regulation of RII β subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase leading to type II holoenzyme-dependent growth inhibition and differentiationof HL-60 leukemia cells. J Biol Chem 268:5774–5782
Ally S, Clair T, Katsaros D, Tortora G, Yokozaki H, Finch RA, Avery TL, Cho-Chung YS (1989) Inhibition of growth and modulation of gene expression in human lung carcinoma in athymic mice by site-selective 8-Cl-cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Cancer Res 49:5650–5655
McDaid HM, Johnston PG (1999) Synergistic interaction between paclitaxel and 8-chloro-adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate in human ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 5:215–220
Grbovic O, Jovic V, Ruzdijic S, Pejanovic V, Rakic L, Kanazir S (2002) 8-Cl-cAMP affects glioma cell-cycle kinetics and selectively induces apoptosis. Cancer Invest 20:972–982
Juranic Z, Radulovic S, Joksimovic J, Juranic I (1998) The mechanism of 8-Cl-cAMP action. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 17:269–275
Tortora G, Ciardiello F, Pepe S, Tagliaferri P, Ruggiero A, Bianco C, Guarrasi R, Miki K, Bianco AR (1995) Phase I clinical study with 8-chloro-cAMP and evaluation of immunological effects in cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 1:377–384
Schwede F, Maronde E, Genieser HG, Jastorff B (2000) Cyclic nucleotide analogs as biochemical tools and prospective drugs. Pharmacol Ther 87:199–226
Camichael J, de Graf VJ, Gazdar AF, Minna SD, Michell JB (1987) Evaluation of tetrazolium-based semiautomated colorimetric assay: assessment of chemosensitivity testing. Cancer Res 47:936–942
Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC, Grignani F, Riccardi C (1991) A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocite apoptosis by propidium iodate staining and flow-cyometry. J Immunol Methods 139:271–279
Chou TC, Talalay P (1984) Quantitative analysis of dose–effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul 22:27–55
Waldman T, Zhang Y, Dillehay L, Yu J, Kinzler K, Vogelstein B, Williams J (1997) Cell-cycle arrest versus cell death in cancer therapy. Nat Med 3:1034–1036
Tortora G, di Isernia G, Sandomenico C, Bianco R, Pomatico G, Pepe S, Bianco AR, Ciardiello F (1997) Synergistic inhibition of growth and induction of apoptosis by 8-chloro-cAMP and paclitaxel or cisplatin in human cancer cells. Cancer Res 57:5107–5111
Smorenburg CH, Sparreboom A, Bontenbal M, Verweij J (2001) Combination chemotherapy of taxanes and antimetabolites: its use and limitations. Europ J Cancer 37:2310–2323
VanBokhoven A, Varella-Garcia M, Korch C, Hessels D, Miller GJ (2001) Widely used prostate carcinoma cell lines share common origins. Prostate 47:36–51
Srivastava RK, Srivastava AR, Cho-Chung YS (1998) Synergistic effects of 8-chlorocyclic-AMP and retinoic acid on induction of apoptosis in Ewing’s sarcoma CHP-100 cells. Clin Cancer Res 4:755–761
Jankovic D, Pesic M, Markovic J, Kanazir S, Markovic I, Rakic L, Ruzdijic S (2006) The combination of sulfinosine and 8-Cl-cAMP induces synergistic cell growth inhibition of the human neuroblastoma cell line in vitro. Invest New Drugs 24:15–24
Blank KR, Rudolts MS, Kao GD, Muschel RJ, McKenna GW (1997) The molecular regulation of apoptosis and implications for radiation oncology. Int J Radiat Biol 71:455–466
Niciforovic A, Adzic M, Spasic S, Radojcic MB (2007) Antitumor effects of a natural anthracycline analog (Aloin) involve altered activity of antioxidant enzymes in HeLaS3 cells. Cancer Biol Ther 6:8, e1–e6
Yount GL, Hass-Kogan DA, Levine KS, Aldape KD, Israel A (1998) Ionizing radiation inhibits chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in cultured glioma cells: implications for combined modality therapy. Cancer Res 58:3819–3825
Hei TK, Piao CQ, Geard CR, Hall EJ (1994) Taxol and ionizing radiation interaction and mechanisms. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 29:267–271
Dimon-Gadal S, Gerbaud P, Keryer G, Anderson W, Evain-Brion D (1998) In vitro effects of oxygen-derived free radicals on type I and type II cAMP-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem 273:22833–22840
Ahn YH, Jung JM, Hong SH (2005) 8-Chloro-cyclic AMP-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis is mediated by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in HL60 cells. Cancer Res 65:4896–4901
Acknowledgement
This work was funded by the Ministry of Science, Republic of Serbia, projects 143009B and 143042B. Vesna Pesic, PhD is gratefully acknowledged for her help with the statistical analysis of data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vučić, V., Nićiforović, A., Adžić, M. et al. The combination of gamma ionizing radiation and 8-Cl-cAMP induces synergistic cell growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. Invest New Drugs 26, 309–317 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-007-9101-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-007-9101-4