Summary
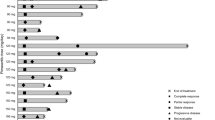
To assess the response rate and toxicity of the kinesin spindle protein (KSP) inhibitor, ispinesib, in malignant melanoma. Seventeen patients were enrolled from April to November 2005. Ispinesib was administered as a 1-hour infusion at a dose of 18 mg/m2 once every 3 weeks until disease progression. No objective responses were seen. Six patients (35%) had a best response of stable disease for a median duration of 2.8 months. Disease progression was documented in 9 (53%) after 1 or 2 cycles. Eighty-eight percent of patients received ≥90% of planned dose intensity. Grade 3 non-hematologic toxicities included dizziness (1) and blurred vision (1). There was one episode of febrile neutropenia, but no grade 3 or 4 biochemical adverse events. Pharmacokinetics was consistent with prior studies. KSP immunoreactivity was seen in 14 of 16 available archival tissue samples (88%). Ispinesib can be safely administered using the dose and schedule employed, with mild hematologic and non-hematologic toxicity. No objective responses were observed, and further development of single-agent ispinesib in malignant melanoma is not recommended. Although KSP expression appears to be common in melanoma, KSP may not be a suitable target for its treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ries LAG, Harkins D, Krapcho M, Mariotto A, Miller BA, Feuer EJ, Clegg L, Eisner MP, Horner MJ, Howlader N, Hayat M, Hankey BF, Edwards BK (eds) (2006) SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2003. National Cancer Institute, Bethesda
Canadian Cancer Society/National Cancer Institute of Canada (2006) Canadian Cancer Statistics 2006. Toronto, Canada
Balch CM, Buzaid AC, Soong SJ, Atkins MB, Cascinelli N, Coit DG, Fleming ID, Gershenwald JE, Houghton A Jr, Kirkwood JM, McMasters KM, Mihm MF, Morton DL, Reintgen DS, Ross MI, Sober A, Thompson JA, Thompson JF (2001) Final version of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system for cutaneous melanoma. J Clin Oncol 19:3635–3648
Eggermont AM, Kirkwood JM (2004) Re-evaluating the role of dacarbazine in metastatic melanoma: what have we learned in 30 years? Eur J Cancer 40:1825–1836
Atkins MB, Lotze MT, Dutcher JP, Fisher RI, Weiss G, Margolin K, Abrams J, Sznol M, Parkinson D, Hawkins M, Paradise C, Kunkel L, Rosenberg SA (1999) High-dose recombinant interleukin-2 therapy for patients with metastatic melanoma: analysis of 270 patients treated between 1985 and 1993. J Clin Oncol 17:2105–2116
Eigentler TK, Caroli UM, Radny P, Garbe C (2003) Palliative therapy of disseminated malignant melanoma: a systematic review of 41 randomised clinical trials. Lancet Oncol 4:748–759
Retsas S, Peat I, Ashford R, Coe M, Maher J, Drury A, Hanham IW, Phillips RH, Newton KA, Westbury G (1980) Update results of vindesine as a single agent in the therapy of advanced malignant melanoma. Cancer Treat Rev 7:87–90
Quagliana JM, Stephens RL, Baker LH, Costanzi JJ (1984) Vindesine in patients with metastatic malignant melanoma: a Southwest Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 2:316–319
Einzig AI, Hochster H, Wiernik PH, Trump DL, Dutcher JP, Garowski E, Sasloff J, Smith TJ (1991) A phase II study of taxol in patients with malignant melanoma. Invest New Drugs 9:59–64
Bedikian AY, Weiss GR, Legha SS, Burris HA 3rd, Eckardt JR, Jenkins J, Eton O, Buzaid AC, Smetzer L, Von Hoff DD, Benjamin RS (1995) Phase II trial of docetaxel in patients with advanced cutaneous malignant melanoma previously untreated with chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 13:2895–2899
Einzig AI, Schuchter LM, Recio A, Coatsworth S, Rodriquez R, Wiernik PH (1996) Phase II trial of docetaxel (Taxotere) in patients with metastatic melanoma previously untreated with cytotoxic chemotherapy. Med Oncol 13:111–117
Hodi FS, Soiffer RJ, Clark J, Finkelstein DM, Haluska FG (2002) Phase II study of paclitaxel and carboplatin for malignant melanoma. Am J Clin Oncol 25:283–286
Rao RD, Holtan SG, Ingle JN, Croghan GA, Kottschade LA, Creagan ET, Kaur JS, Pitot HC, Markovic SN (2006) Combination of paclitaxel and carboplatin as second-line therapy for patients with metastatic melanoma. Cancer 106:375–382
Tao W, South VJ, Zhang Y, Davide JP, Farrell L, Kohl NE, Sepp-Lorenzino L, Lobell RB (2005) Induction of apoptosis by an inhibitor of the mitotic kinesin KSP requires both activation of the spindle assembly checkpoint and mitotic slippage. Cancer Cell 8:49–59
Sakowicz R, Finer JT, Beraud C, Crompton A, Lewis E, Fritsch A, Lee Y, Mak J, Moody R, Turincio R, Chabala JC, Gonzales P, Roth S, Weitman S, Wood KW (2004) Antitumor activity of a kinesin inhibitor. Cancer Res 64:3276–3280
Marcus AI, Peters U, Thomas SL, Garrett S, Zelnak A, Kapoor TM, Giannakakou P (2005) Mitotic kinesin inhibitors induce mitotic arrest and cell death in Taxol-resistant and -sensitive cancer cells. J Biol Chem 280:11569–11577
Burris HA, Lorusso P, Jones S, Guthrie TM, Orr JB, Williams DD, Hodge JP, Bush M, Sabry J (2004) Phase I trial of novel kinesin spindle protein (KSP) inhibitor SB-715992 IV days 1, 8, 15 q 28 days. J Clin Oncol 22:2004
Chu QS, Holen KD, Rowinsky EK, Wilding G, Volkman JL, Orr JB, Williams DD, Hodge JP, Sabry J (2004) Phase I trial of novel kinesin spindle protein (KSP) inhibitor SB-715992 IV Q 21 days. J Clin Oncol 22:2078
Heath EI, Alousi A, Eder JP, Valdivieso M, Vasist LS, Appleman L, Bhargava P, Colevas AD, Lorusso PM, Shapiro G (2006) A phase I dose escalation trial of ispinesib (SB-715992) administered days 1–3 of a 21-day cycle in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 24:2026
Fleming TR (1982) One sample multiple testing procedure for phase II clinical trials. Biometrics 38:143–151
Grossman D, Altieri DC (2001) Drug resistance in melanoma: mechanisms, apoptosis, and new potential therapeutic targets. Cancer Metastasis Rev 20:3–11
Brier S, Lemaire D, DeBonis S, Forest E, Kozielski F (2006) Molecular dissection of the inhibitor binding pocket of mitotic kinesin Eg5 reveals mutants that confer resistance to antimitotic agents. J Mol Biol 360:360–376
Castedo M, Coquelle A, Vivet S, Vitale I, Kauffmann A, Dessen P, Pequignot MO, Casares N, Valent A, Mouhamad S, Schmitt E, Modjtahedi N, Vainchenker W, Zitvogel L, Lazar V, Garrido C, Kroemer G (2006) Apoptosis regulation in tetraploid cancer cells. EMBO J 25:2584–2595
Tao W, South VJ, Diehl RE, Davide JP, Sepp-Lorenzino L, Fraley ME, Arrington KL, Lobell RB (2007) An inhibitor of the kinesin spindle protein activates the intrinsic apoptotic pathway independently of p53 and de novo protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol 27:689–698
Soengas MS, Lowe SW (2003) Apoptosis and melanoma chemoresistance. Oncogene 22:3138–3151
Lens SM, Wolthuis RM, Klompmaker R, Kauw J, Agami R, Brummelkamp T, Kops G, Medema RH (2003) Survivin is required for a sustained spindle checkpoint arrest in response to lack of tension. EMBO J 22:2934–2947
Grossman D, McNiff JM, Li F, Altieri DC (1999) Expression and targeting of the apoptosis inhibitor, survivin, in human melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 113:1076–1081
Miller K, Ng C, Ang P, Brufsky AM, Lee SC, Dees EC, Piccart M, Verrill M, Wardley A, Loftiss J, Bal J, Yeoh S, Hodge J, Williams D, Dar M, Ho PTC (2005) Phase II, open label study of SB-715992 (Ispinesib) in subjects with advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 94(suppl 1):abstr 1089
Tang P, Siu LL, Chen EX, Hotte SJ, Chia S, Schwarz JK, Colevas AD, Johnson C, Pond GR, Winquist E (2006) A phase II study of ispinesib in patients (pts) with recurrent and/or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (RMHNSC). Ann Oncol 17(suppl 9):abstr 600
El-Khoueiry AB, Iqbal S, Singh DA, D’Andre S, Ramanathan RK, Shibata S, Yang DY, Lenz HJ, Synold T, Gandara DR (2006) A randomized phase II non-comparative study of Ispinesib given weekly or every three weeks in metastatic colorectal cancer. A California Cancer Consortium Study (CCC-P). ASCO Annual Meeting Proceedings Part I 24(18S):abstr 3595
Shahin MS, Braly P, Rose P, Malpass T, Bailey H, Alvarez RD, Hodge J, Bowen C, Buller R (2007) A phase II, open-label study of ispinesib (SB-715992) in patients with platinum/taxane refractory or resistant relapsed ovarian cancer. ASCO Annual Meeting Proceedings Part I 25(18S):abstr 5562
Beekman KW, Dunn R, Colevas D, Davis N, Clark J, Agamah E, Thomas S, Nichols K, Redman B, Stadler W (2007) University of Chicago Consortium phase II study of ispinesib (SB-715992) in patients (pts) with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). ASCO Annual Meeting Proceedings Part I 25(18S):abstr 15573
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, C.W., Bélanger, K., Rao, S.C. et al. A phase II study of ispinesib (SB-715992) in patients with metastatic or recurrent malignant melanoma: a National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group trial. Invest New Drugs 26, 249–255 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-007-9097-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-007-9097-9