Abstract
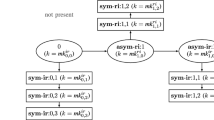
The subset difference (SD) method proposed by Naor, Naor and Lotspiech is the most popular broadcast encryption (BE) scheme. It is suitable for real-time applications like Pay-TV and has been suggested for use by the AACS standard for digital rights management in Blu-Ray and HD-DVD discs. The SD method assumes the number of users to be a power of two. We propose the complete tree subset difference (CTSD) method that allows the system to support an arbitrary number of users. In particular, it subsumes the SD method and all results proved for the CTSD method also hold for the SD method. Recurrences are obtained for the CTSD scheme to count the number, N(n, r, h), of possible ways r users in the system of n users can be revoked to result in a transmission overhead or header length of h. The recurrences lead to a polynomial time dynamic programming algorithm for computing N(n, r, h). Further, they provide bounds on the maximum possible header length. A probabilistic analysis is performed to obtain an O(r log n) time algorithm to compute the expected header length in the CTSD scheme. Further, for the SD scheme we obtain an explicit limiting upper bound on the expected header length.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACS: Advanced Access Content System, http://www.aacsla.com .
Asano T.: A revocation scheme with minimal storage at receivers. In: Zheng Y. (ed.) ASIACRYPT. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 2501, pp. 433–450. Springer, New York (2002).
Attrapadung N., Kobara K., Imai H.: Sequential key derivation patterns for broadcast encryption and key predistribution schemes. In: Laih, C.-S. (ed.) ASIACRYPT. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 2894, pp. 374–391. Springer, New York (2003)
Austrin P., Kreitz G.: Lower bounds for subset cover based broadcast encryption. In: Vaudenay, S. (ed) AFRICACRYPT. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 5023, pp. 343–356. Springer, New York (2008)
Berkovits S.: How to broadcast a secret. In: Davies, D.W. (ed) EUROCRYPT. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 547, pp. 535–541. Springer, New York (1991)
Boneh D., Franklin M.K.: An efficient public key traitor tracing scheme. In: Wiener, M.J. (eds.) CRYPTO. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 1666, pp. 338–353. Springer, New York (1999)
Boneh D., Gentry C., Waters B.: Collusion resistant broadcast encryption with short ciphertexts and private keys. In: Shoup, V. (ed) CRYPTO. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 3621, pp. 258–275. Springer, New York (2005)
Bhattacherjee S., Sarkar P.: An analysis of the Naor-Naor-Lotspiech subset difference algorithm (for possibly incomplete binary trees). In: Augot D., Canteaut A. (eds.) Workshop on Coding and Cryptography, April 11–15, 2011, Workshop on Coding and Cryptography, pp. 483–492. INRIA (2011).
Chor B., Fiat A., Naor M.: Tracing traitors. In: Desmedt, Y. (ed.) CRYPTO Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 839, pp. 257–270. Springer, New York (1994)
Dodis Y., Fazio N.: Public key trace and revoke scheme secure against adaptive chosen ciphertext attack. In: Desmedt, Y. (ed.) Public Key Cryptography. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 2567, pp. 100–115. Springer, New York (2003)
Eagle C., Omar M., Panario D., Richmond B.: Distribution of the number of encryptions in revocation schemes for stateless receivers. In: Roesler U., Spitzmann J., Ceulemans M.-C. (eds.) Fifth Colloquium on Mathematics and Computer Science. DMTCS Proceedings, vol. AI, pp. 195–206. Discrete Mathematics and Theoretical Computer Science (2008).
Fiat A., Naor M.: Broadcast encryption. In: Stinson, D.R. (ed) CRYPTO Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 773., pp. 480–491. Springer, New York (1993)
Fiat A., Tassa T.: Dynamic traitor tracing. J. Cryptol. 14(3), 211–223 (2001)
Gentry C., Waters B.: Adaptive security in broadcast encryption systems (with short ciphertexts). In: Joux, A. (ed) EUROCRYPT. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 5479, pp. 171–188. Springer, New York (2009)
Goodrich M.T., Sun J.Z., Tamassia R.: Efficient tree-based revocation in groups of low-state devices. In: Franklin, M.K. (ed) CRYPTO. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 3152, pp. 511–527. Springer, New York (2004)
Halevy D., Shamir A.: The LSD broadcast encryption scheme. In: Yung, M. (ed.) CRYPTO. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 2442, pp. 47–60. Springer, New York (2002)
Jho N.-S., Hwang J.Y., Cheon J.H., Kim M.-H., Lee D.H., Yoo E.S.: One-way chain based broadcast encryption schemes. In: Cramer, R. (ed.) EUROCRYPT. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 3494, pp. 559–574. Springer, New York (2005)
Jiang S., Gong G.: Multi-service oriented broadcast encryption. In: Wang, H., Pieprzyk, J., Varadharajan, V. (ed.) ACISP. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 3108, pp. 1–11. Springer, New York (2004)
Kiayias A., Yung M.: Self protecting pirates and black-box traitor tracing. In: Kilian, J. (ed.) CRYPTO. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 2139, pp. 63–79. Springer, New York (2001)
Liu Y.-R., Tzeng W.-G.: Public key broadcast encryption with low number of keys and constant decryption time. In: Cramer, R. (ed.) Public Key Cryptography. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 4939, pp. 380–396. Springer, New York (2008)
Luby M., Staddon J.: Combinatorial bounds for broadcast encryption. In: Nyberg, K. (ed.) EUROCRYPT. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 1403, pp. 512–526. Springer, New York (1998)
Martin T., Martin K.M., Wild P.R.: Establishing the broadcast efficiency of the subset difference revocation scheme. Des. Codes Cryptogr. 51(3), 315–334 (2009)
Naor M., Pinkas B.: Threshold traitor tracing. In: Krawczyk, H. (ed.) CRYPTO. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 1462, pp. 502–517. Springer, New York (1998)
Naor D., Naor M., Lotspiech J.: Revocation and tracing schemes for stateless receivers. In: Kilian, J. (ed.) CRYPTO.Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 2139, pp. 41–62. Springer, New York (2001)
Park E.C., Blake I.F.: On the mean number of encryptions for tree-based broadcast encryption schemes. J. Discret. Algorithms 4(2), 215–238 (2006)
Padró C., Gracia I., Molleví S.M., Morillo P.: Linear key predistribution schemes. Des. Codes Cryptogr. 25(3), 281–298 (2002)
Padró C.: Gracia I., Molleví S.M., Morillo P.: Linear broadcast encryption schemes. Discret. Appl. Math. 128(1), 223–238 (2003)
Padró C., Gracia I., Molleví S.M.: Improving the trade-off between storage and communication in broadcast encryption schemes. Discret. Appl. Math. 143(1–3), 213–220 (2004)
Phan D.H., Pointcheval D., Strefler M.: Security notions for broadcast encryption. In: Lopez, J., Tsudik, G. (ed.) ACNS. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 6715, pp. 377–394. Springer, New York (2011)
Silverberg A., Staddon J., Walker J.L.: Efficient traitor tracing algorithms using list decoding. In: Boyd, C. (ed.) ASIACRYPT Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 2248., pp. 175–192. Springer, New York (2001)
Stinson D.R.: On some methods for unconditionally secure key distribution and broadcast encryption. Des. Codes Cryptogr. 12(3), 215–243 (1997)
Stinson D.R., Wei R.: Combinatorial properties and constructions of traceability schemes and frameproof codes. SIAM J. Discret. Math. 11(1), 41–53 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This is one of several papers published in Designs, Codes and Cryptography comprising the “Special Issue on Coding and Cryptography”.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacherjee, S., Sarkar, P. Complete tree subset difference broadcast encryption scheme and its analysis. Des. Codes Cryptogr. 66, 335–362 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10623-012-9702-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10623-012-9702-6
Keywords
- Broadcast encryption
- Subset difference
- Combinatorial analysis
- Recurrence
- Probabilistic analysis
- Expected header length
- Transmission overhead
- Asymptotic analysis