Abstract
Background and Aim
Previous reports have suggested IFI16 as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma (HC). Nonetheless, the biological significance of IFI16 and its mechanism concerning resistance to cisplatin (DDP) in HC requires further exploration.
Methods
Samples of tumor and corresponding para-carcinoma tissues were acquired from patients with HC. Furthermore, DDP-resistant cell lines of HC, specifically HCC, Huh7 and Hepatoblastoma, HepG3, were generated by gradually increasing the concentration of DDP. Cell apoptosis and DNA damage were evaluated by utilizing flow cytometry assay and TUNEL staining. The interaction between IFI16 and interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) proteins were analyzed using Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assay. In vivo assays were conducted by establishing HC subcutaneous xenograft tumor models.
Results
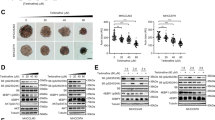
The study found a reduction in IFI16 expression in both HC tissues and DDP-resistant HC cell lines. The binding of IFI16 to IRF3 regulated DNA damage-associated markers in vitro. Overexpression of IFI16 heightened the susceptibility of DDP-induced apoptosis and DNA damage, which was counteracted by IRF3 knockdown, while strengthened by IRF3 overexpression. Moreover, overexpression of IFI16 diminished in vivo DDP-resistant HC tumorigenicity.
Conclusion
In summary, our findings suggest that IFI16 serves as a tumor suppressor in HC by promoting DNA damage via its interaction with IRF3, thereby reversing DDP resistance.
Graphical Abstract
Cisplatin-induced damage in tumor cells, with the involvement of DNA repair, leads to survival of tumor cells, manifesting as drug resistance of the tumor. However, the binding of IRF3 and IFI16 inhibits DNA repair, resulting in the ultimate fate of cell death.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rumgay H, Ferlay J, de Martel C et al. Global, regional and national burden of primary liver cancer by subtype. Eur J Cancer 2022;161:108–118.
Singal AG, Zhang E, Narasimman M et al. HCC surveillance improves early detection, curative treatment receipt, and survival in patients with cirrhosis: A meta-analysis. J Hepatol 2022;77:128–139.
Zhu AX, Abbas AR, de Galarreta MR et al. Molecular correlates of clinical response and resistance to atezolizumab in combination with bevacizumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Med 2022;28:1599–1611.
Li P, Song R, Yin F et al. circMRPS35 promotes malignant progression and cisplatin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Ther 2022;30:431–447.
Gao Z, Xu J, Fan Y et al. ARPC1B promotes mesenchymal phenotype maintenance and radiotherapy resistance by blocking TRIM21-mediated degradation of IFI16 and HuR in glioma stem cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2022;41:323.
Justice JL, Kennedy MA, Hutton JE et al. Systematic profiling of protein complex dynamics reveals DNA-PK phosphorylation of IFI16 en route to herpesvirus immunity. Sci Adv 2021;7:6680.
Orzalli MH, DeLuca NA, Knipe DM. Nuclear IFI16 induction of IRF-3 signaling during herpesviral infection and degradation of IFI16 by the viral ICP0 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012;109:E3008–E3017.
Aglipay JA, Lee SW, Okada S et al. A member of the Pyrin family, IFI16, is a novel BRCA1-associated protein involved in the p53-mediated apoptosis pathway. Oncogene 2003;22:8931–8938.
Veeranki S, Choubey D. Interferon-inducible p200-family protein IFI16, an innate immune sensor for cytosolic and nuclear double-stranded DNA: regulation of subcellular localization. Mol Immunol 2012;49:567–571.
Alimirah F, Chen J, Davis FJ, Choubey D. IFI16 in human prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Res 2007;5:251–259.
Piccaluga PP, Agostinelli C, Righi S et al. IFI16 reduced expression is correlated with unfavorable outcome in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. APMIS 2017;125:511–522.
Azzimonti B, Pagano M, Mondini M et al. Altered patterns of the interferon-inducible gene IFI16 expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: immunohistochemical study including correlation with retinoblastoma protein, human papillomavirus infection and proliferation index. Histopathology 2004;45:560–572.
Ka NL, Lim GY, Hwang S, Kim SS, Lee MO. IFI16 inhibits DNA repair that potentiates type-I interferon-induced antitumor effects in triple negative breast cancer. Cell Rep 2021;37:110138.
Januchowski R, Sterzynska K, Zawierucha P et al. Microarray-based detection and expression analysis of new genes associated with drug resistance in ovarian cancer cell lines. Oncotarget 2017;8:49944–49958.
Borucka J, Sterzynska K, Kazmierczak D et al. The significance of interferon gamma inducible protein 16 (IFI16) expression in drug resistant ovarian cancer cell lines. Biomed Pharmacother 2022;150:113036.
Kikuchi M, Yamashita K, Waraya M et al. Epigenetic regulation of ZEB1-RAB25/ESRP1 axis plays a critical role in phenylbutyrate treatment-resistant breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016;7:1741–1753.
Ma H, Li L, Dou G et al. Z-ligustilide restores tamoxifen sensitivity of ERa negative breast cancer cells by reversing MTA1/IFI16/HDACs complex mediated epigenetic repression of ERa. Oncotarget 2017;8:29328–29345.
Lin W, Zhao Z, Ni Z, Zhao Y, Du W, Chen S. IFI16 restoration in hepatocellular carcinoma induces tumour inhibition via activation of p53 signals and inflammasome. Cell Prolif 2017;50:e12392.
Li XY, Luo DH, Guo L et al. Deintensified Chemoradiotherapy for Pretreatment Epstein-Barr Virus DNA-Selected Low-Risk Locoregionally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Phase II Randomized Noninferiority Trial. J Clin Oncol 2022;40:1163–1173.
Housman G, Byler S, Heerboth S et al. Drug resistance in cancer: an overview. Cancers (Basel) 2014;6:1769–1792.
Piccaluga PP, Navari M, Visani A et al. Interferon gamma inducible protein 16 (IFI16) expression is reduced in mantle cell lymphoma. Heliyon 2019;5:e02643.
Li D, Xie L, Qiao Z et al. STING-mediated degradation of IFI16 negatively regulates apoptosis by inhibiting p53 phosphorylation at serine 392. J Biol Chem 2021;297:100930.
Kim EJ, Park JI, Nelkin BD. IFI16 is an essential mediator of growth inhibition, but not differentiation, induced by the leukemia inhibitory factor/JAK/STAT pathway in medullary thyroid carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 2005;280:4913–4920.
Wang Y, Yang L, Mao L et al. SGLT2 inhibition restrains thyroid cancer growth via G1/S phase transition arrest and apoptosis mediated by DNA damage response signaling pathways. Cancer Cell Int 2022;22:74.
Berthel E, Foray N, Ferlazzo ML. The Nucleoshuttling of the ATM Protein: A Unified Model to Describe the Individual Response to High- and Low-Dose of Radiation? Cancers (Basel) 2019;11:905.
Kinner A, Wu W, Staudt C, Iliakis G. Gamma-H2AX in recognition and signaling of DNA double-strand breaks in the context of chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res 2008;36:5678–5694.
Bourton EC, Plowman PN, Smith D, Arlett CF, Parris CN. Prolonged expression of the γ-H2AX DNA repair biomarker correlates with excess acute and chronic toxicity from radiotherapy treatment. Int J Cancer 2011;129:2928–2934.
Ko JJ, Klimowicz AC, Jagdis A et al. ATM, THMS, and RRM1 protein expression in nasopharyngeal carcinomas treated with curative intent. Head Neck 2016;38(1):E384–E391.
Romano FJ, Guadagno E, Solari D et al. ATM and p53 combined analysis predicts survival in glioblastoma multiforme patients: A clinicopathologic study. J Cell Biochem 2018;119:4867–4877.
Koch U, Höhne K, von Neubeck C et al. Residual γH2AX foci predict local tumour control after radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 2013;108:434–439.
Shi X, Li S, Wang L et al. RalB degradation by dihydroartemisinin induces autophagy and IFI16/caspase-1 inflammasome depression in the human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Chin Med 2020;15:64.
De Andrea M, Gioia D, Mondini M et al. Effects of IFI16 overexpression on the growth and doxorubicin sensitivity of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma-derived cell lines. Head Neck 2007;29:835–844.
Ong LT, Lee WC, Ma S et al. IFI16-dependent STING signaling is a crucial regulator of anti-HER2 immune response in HER2+ breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2022;119:e2201376119.
Jiao S, Guan J, Chen M et al. Targeting IRF3 as a YAP agonist therapy against gastric cancer. J Exp Med 2018;215:699–718.
Qi Z, Yan F, Chen D et al. Identification of prognostic biomarkers and correlations with immune infiltrates among cGAS-STING in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biosci Rep 2020;40:BSR20202603.
Funding
This study was supported by Wenzhou Medical University Affiliated Second Hospital, Yuying Children's Hospital Doctoral Research Startup Fund Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, W., Zhao, Z., Du, W. et al. Interferon-Gamma-Inducible Protein 16 Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 on Chemosensitivity. Dig Dis Sci 69, 491–501 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-023-08175-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-023-08175-x