Abstract
Background
Development of bowel preparation products has been based upon colon cleansing rating by a local endoscopist. It is unclear how bowel preparation scales perform when centrally evaluated.
Aims
To evaluate the reliability of bowel preparation quality scales when assessed by central readers.
Methods
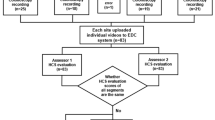
Four central readers evaluated 52 videos in triplicate, 2 weeks apart, during the entire endoscopic procedure (insertion/withdrawal of the colonoscope) and exclusively on colonoscope withdrawal using the Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS), Chicago Bowel Preparation scale, Harefield Cleansing Scale, Ottawa Bowel Preparation Quality Scale (OBPQS), Aronchick score, a visual analogue scale, and additional items proposed in a modified Research and Development/University of California Los Angeles appropriateness process. Reliability was assessed with intraclass correlation coefficients.
Results
Intraclass correlation coefficients (95% confidence interval) for inter-rater reliability of the quality scales ranged from 0.51 to 0.65 (consistent with moderate to substantial inter-rater reliability) during the entire procedure. Corresponding intraclass correlation coefficients for intra-rater reliability ranged from 0.69 to 0.77 (consistent with substantial intra-rater reliability). Reliability was highest in the right colon and lowest in the left colon. No differences were observed in reliability when assessed for the procedure overall (insertion/withdrawal) relative to assessment on withdrawal alone.
Conclusion
All five bowel preparation quality scales had moderate to substantial inter-rater reliability. Panelists considered the Aronchick score too simplistic for clinical trials and recognized that assessment of residual fluid in the Ottawa Bowel Preparation Quality Scale was not amenable to central assessment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All de-identified data from this analysis is available upon request.
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- BBPS:
-
Boston Bowel Preparation Scale
- B-Clear:
-
Boston Classification of Excrement and Residue
- BP:
-
Bowel preparation
- CBPS:
-
Chicago Bowel Preparation Scale
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- FDA:
-
United States Food and Drug Administration
- HCS:
-
Harefield Cleansing Scale
- ICC:
-
Intraclass correlation coefficients
- MBPC:
-
Marden Bowel Preparation Classification
- OBPQS:
-
Ottawa Bowel Preparation Quality Scale
- RAND/UCLA:
-
Research and Development University of California Los Angeles
- RCT:
-
Randomized controlled trial
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SES:
-
Standardized effect size
- VAS:
-
Visual analogue scale
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 2020;70:7–30.
Baxter NN, Goldwasser MA, Paszat LF et al. Association of colonoscopy and death from colorectal cancer. Ann Intern Med 2009;150:1–8.
Nishihara R, Wu K, Lochhead P et al. Long-term colorectal-cancer incidence and mortality after lower endoscopy. N Engl J Med 2013;369:1095–1105.
Løberg M, Kalager M, Holme Ø et al. Long-Term Colorectal-Cancer Mortality after Adenoma Removal. N Engl J Med 2014;371:799–807.
Adler A, Wegscheider K, Lieberman D et al. Factors determining the quality of screening colonoscopy: a prospective study on adenoma detection rates, from 12,134 examinations (Berlin colonoscopy project 3, BECOP-3). Gut 2013;62:236–241.
Froehlich F, Wietlisbach V, Gonvers JJ et al. Impact of colonic cleansing on quality and diagnostic yield of colonoscopy: the European Panel of Appropriateness of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy European multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc 2005;61:378–384.
Harewood GC, Sharma VK, de Garmo P. Impact of colonoscopy preparation quality on detection of suspected colonic neoplasia. Gastrointest Endosc 2003;58:76–79.
Sherer EA, Imler TD, Imperiale TF. The effect of colonoscopy preparation quality on adenoma detection rates. Gastrointest Endosc 2012;75:545–553.
Rex DK, Imperiale TF, Latinovich DR et al. Impact of bowel preparation on efficiency and cost of colonoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol 2002;97:1696–1700.
Lebwohl B, Kastrinos F, Glick M et al. The impact of suboptimal bowel preparation on adenoma miss rates and the factors associated with early repeat colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 2011;73:1207–1214.
Johnson DA, Barkun AN, Cohen LB et al. Optimizing adequacy of bowel cleansing for colonoscopy: recommendations from the U.S. multi-society task force on colorectal cancer. Gastrointest Endosc 2014;80:543–562.
Kaminski MF, Thomas-Gibson S, Bugajski M et al. Performance measures for lower gastrointestinal endoscopy: a European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Quality Improvement Initiative. Endoscopy 2017;49:378–397.
Parmar R, Martel M, Rostom A et al. Validated Scales for Colon Cleansing: A Systematic Review. Am J Gastroenterol 2016;111:197–204.
DeMicco MP, Clayton LB, Pilot J et al. Novel 1 L polyethylene glycol-based bowel preparation NER1006 for overall and right-sided colon cleansing: a randomized controlled phase 3 trial versus trisulfate. Gastrointest Endosc 2018;87:e673.
Schreiber S, Baumgart DC, Drenth JPH et al. Colon cleansing efficacy and safety with 1 L NER1006 versus sodium picosulfate with magnesium citrate: a randomized phase 3 trial. Endoscopy 2019;51:73–84.
Bisschops R, Manning J, Clayton LB et al. Colon cleansing efficacy and safety with 1 L NER1006 versus 2 L polyethylene glycol + ascorbate: a randomized phase 3 trial. Endoscopy 2019;51:60–72.
Feagan BG, Sandborn WJ, D’Haens G et al. The role of centralized reading of endoscopy in a randomized controlled trial of mesalamine for ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 2013;145:e142.
Division of Gastroenterology and Inborn Errors Products Bowel cleansing for colonoscopy: efficacy and safety considerations for developing new products guidance for industry. City: U.S. Food and Drug Administration; 2021.
Fitch K, Bernstein S, Aguilar M, et al The RAND/UCLA Appropriateness Method User’s Manual. City: RAND Corporation; 2001.
Lai EJ, Calderwood AH, Doros G et al. The Boston bowel preparation scale: a valid and reliable instrument for colonoscopy-oriented research. Gastrointest Endosc 2009;69:620–625.
Gerard DP, Foster DB, Raiser MW et al. Validation of a new bowel preparation scale for measuring colon cleansing for colonoscopy: the chicago bowel preparation scale. Clinical and translational gastroenterology 2013;4:e43.
Halphen M, Heresbach D, Gruss HJ et al. Validation of the Harefield Cleansing Scale: a tool for the evaluation of bowel cleansing quality in both research and clinical practice. Gastrointest Endosc 2013;78:121–131.
Rostom A, Jolicoeur E. Validation of a new scale for the assessment of bowel preparation quality. Gastrointest Endosc 2004;59:482–486.
Aronchick CA, Lipshutz WH, Wright SH et al. A novel tableted purgative for colonoscopic preparation: efficacy and safety comparisons with Colyte and Fleet Phospho-Soda. Gastrointest Endosc 2000;52:346–352.
Aronchick CA, Lipshutz WH, Wright SH. Validation of an instrument to assess colon cleansing [abstract]. Am J Gastroenterol 1999;94:2667.
Fleiss JL, Cohen J. Equivalence of weighted kappa and intraclass correlation coefficient as measures of reliability. Educ Psychol Meas 1973;33:613–619.
Gilder K, Ting N, Tian LL et al. Confidence intervals on intraclass correlation coefficients in a balanced two-factor random design. J Stat Plan Infer 2007;137:1199–1212.
Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977;33:159–174.
Zou GY. Sample size formulas for estimating intraclass correlation coefficients with precision and assurance. Statistics in Medicine 2012;31:3972–3981.
Cohen J, Grunwald D, Grossberg LB et al. The Effect of Right Colon Retroflexion on Adenoma Detection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Clin Gastroenterol 2016;51:818–824.
Tang S, Dong X, Liu W et al. Compare risk factors associated with postoperative infectious complication in Crohn’s disease with and without preoperative infliximab therapy: a cohort study. Int J Colorectal Dis 2020;35:727–737.
Rodrigues-Pinto E, Ferreira-Silva J, Macedo G et al. (Technically) Difficult colonoscope insertion—Tips and tricks. Dig Endosc 2019;31:583–587.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Norgine Ltd who provided images used in the assessment of reliability.
Funding
JEE is funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Oxford Biomedical Research Centre. The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the National Health Service, the NIHR or the Department of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guarantor of the article: Dr. Vipul Jairath is acting as the article guarantor. VJ, GYZ, LC, RN: conception and design, GYZ, VJ: analysis and interpretation of the data, VJ, JH, LMS: Drafting of the article, all authors: critical revision of the article for important intellectual content, final approval of the article, GYZ: statistical methods. All authors have reviewed and approved the final version of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
JH has received speaker's fees from Abbvie, Janssen, and Takeda; consulting fees from Alimentiv, Inc. MS has received research grants and speaker’s fees from Pendopharm Inc.; consulting fees from Medtronic Inc. (consultant). CM has received consulting fees from AbbVie, Alimentiv, Amgen, AVIR Pharma Inc, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ferring, Fresenius Kabi, Janssen, McKesson, Mylan, Takeda, Pendopharm, Pfizer, Roche; speaker's fees from AbbVie, Amgen, AVIR Pharma Inc, Alimentiv, Ferring, Janssen, Takeda, and Pfizer; research support from Pfizer. GYZ has received consulting fees from Alimentiv, Inc. JEE has served on clinical advisory boards for Lumendi, Boston Scientific, and Paion; has served on the clinical advisory board and owns share options in Satisfai Health; and reports speaker fees from Falk and Janssen. CAS has received consulting fees from Abbvie, BMS, Lilly, Janssen, Napo Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Prometheus, Takeda, Tellus Health; speaker fees for CME activities for Abbvie, Janssen, Pfizer, Takeda; grant support from Abbvie, Janssen, Pfizer and Takeda. Dr. Corey Siegel and Dr. Lori Siegel are co-founders of MiTest Health, LLC (software company). Technology developed by MiTest Health, LLC has been licensed to Takeda. Dr. Corey Siegel is a co-founder of ColonaryConcepts, LLC and has United States Patents on “Dietary Purgatives” and “Foods, Systems, Methods, and Kits for Providing Electrolyte Replacement.” MM has received speaker’s fees from Abbvie, Takeda, Janssen, Pfizer, Amgen, Novartis, Hikma, Ferring; grant/research support from Takeda, Pfizer, and Janssen. WR is a speaker for Abbott Laboratories, Abbvie, Aesca, Aptalis, Astellas, Centocor, Celltrion, Danone Austria, Elan, Falk Pharma GmbH, Ferring, Immundiagnostik, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, MSD, Otsuka, PDL, Pharmacosmos, PLS Education, Schering-Plough, Shire, Takeda, Therakos, Vifor, Yakult; consultant for Abbott Laboratories, Abbvie, Aesca, Algernon, Amgen, AM Pharma, AMT, AOP Orphan, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Astellas, Astra Zeneca, Avaxia, Roland Berger GmBH, Bioclinica, Biogen IDEC, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cellerix, Chemocentryx, Celgene, Centocor, Celltrion, Covance, Danone Austria, DSM, Elan, Eli Lilly, Ernest & Young, Falk Pharma GmbH, Ferring, Galapagos, Genentech, Gilead, Grünenthal, ICON, Index Pharma, Inova, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, Kyowa Hakko Kirin Pharma, Lipid Therapeutics, LivaNova, Mallinckrodt, Medahead, MedImmune, Millenium, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, MSD, Nash Pharmaceuticals, Nestle, Nippon Kayaku, Novartis, Ocera, OMass, Otsuka, Parexel, PDL, Periconsulting, Pharmacosmos, Philip Morris Institute, Pfizer, Procter & Gamble, Prometheus, Protagonist, Provention, Alimentiv Inc, Sandoz, Schering-Plough, Second Genome, Seres Therapeutics, Setpointmedical, Sigmoid, Sublimity, Takeda, Therakos, Theravance, Tigenix, UCB, Vifor, Zealand, Zyngenia, and 4SC; and advisory board member for Abbott Laboratories, Abbvie, Aesca, Amgen, AM Pharma, Astellas, Astra Zeneca, Avaxia, Biogen IDEC, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cellerix, Chemocentryx, Celgene, Centocor, Celltrion, Danone Austria, DSM, Elan, Ferring, Galapagos, Genentech, Grünenthal, Inova, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, Kyowa Hakko, Kirin Pharma, Lipid Therapeutics, MedImmune, Millenium, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, MSD, Nestle, Novartis, Ocera, Otsuka, PDL, Pharmacosmos, Pfizer, Procter & Gamble, Prometheus, Sandoz, Schering-Plough, Second Genome, Setpointmedical, Takeda, Therakos, Tigenix, UCB, Zealand, Zyngenia, and 4SC. JWDM has received consulting fees from Alimentiv, Inc. MSS has nothing relevant to disclose. TvV is an employee of Alimentiv, Inc. LMS has received consulting fees from Alimentiv, Inc. LC is an employee of Norgine Ltd. RE has nothing relevant to disclose. IE has received consulting fees from AbbVie. RJH has received grant support and advisory board fees from Exact Sciences, Inc. LH has received consulting fees from Pendopharm. DCM has nothing relevant to disclose. RN is an employee of Norgine Ltd. JJT has received consulting fees from Pendopharm. DvR has received research funding from Arm’s length, ERBE, Boston Scientific, Pendopharm, Pentax, Fuji; consulting fees from Boston Scientific, Pendopharm; and speaker’s honoraria from Boston Scientific, Pendopharm, ERBE. BGF has received grant/research support from AbbVie Inc., Amgen Inc., AstraZeneca/MedImmune Ltd., Atlantic Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene Corporation, Celltech, Genentech Inc/Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Gilead Sciences Inc., GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Janssen Research & Development LLC., Pfizer Inc., Receptos Inc./Celgene International, Sanofi, Santarus Inc., Takeda Development Center Americas Inc., Tillotts Pharma AG, and UCB; consulting fees from Abbott/AbbVie, Akebia Therapeutics, Allergan, Amgen, Applied Molecular Transport Inc., Aptevo Therapeutics, Astra Zeneca, Atlantic Pharma, Avir Pharma, Biogen Idec, BioMx Israel, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Calypso Biotech, Celgene, Elan/Biogen, EnGene, Ferring Pharma, Roche/Genentech, Galapagos, GiCare Pharma, Gilead, Gossamer Pharma, GSK, Inception IBD Inc, JnJ/Janssen, Kyowa Kakko Kirin Co Ltd., Lexicon, Lilly, Lycera BioTech, Merck, Mesoblast Pharma, Millennium, Nestle, Nextbiotix, Novonordisk, Pfizer, Prometheus Therapeutics and Diagnostics, Progenity, Protagonist, Receptos, Salix Pharma, Shire, Sienna Biologics, Sigmoid Pharma, Sterna Biologicals, Synergy Pharma Inc., Takeda, Teva Pharma, TiGenix, Tillotts, UCB Pharma, Vertex Pharma, Vivelix Pharma, VHsquared Ltd., and Zyngenia; speakers bureau fees from Abbott/AbbVie, JnJ/Janssen, Lilly, Takeda, Tillotts, and UCB Pharma; is a scientific advisory board member for Abbott/AbbVie, Allergan, Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Atlantic Pharma, Avaxia Biologics Inc., Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Centocor Inc., Elan/Biogen, Galapagos, Genentech/Roche, JnJ/Janssen, Merck, Nestle, Novartis, Novonordisk, Pfizer, Prometheus Laboratories, Protagonist, Salix Pharma, Sterna Biologicals, Takeda, Teva, TiGenix, Tillotts Pharma AG, and UCB Pharma; and is the Senior Scientific Officer of Alimentiv Inc. AB has received speaking and consulting fees from Pendopharm, Inc (Canada). VJ has received consulting fees from AbbVie, Alimentiv Inc (formerly Robarts Clinical Trials), Arena pharmaceuticals, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Ferring, Fresenius Kabi, GlaxoSmithKline, Genentech, Gilead, Janssen, Merck, Mylan, Pendopharm, Pfizer, Roche, Sandoz, Takeda, Topivert; speaker’s fees from, Abbvie, Ferring, Janssen, Pfizer, Shire, Takeda. Alimentiv Inc is an academic gastrointestinal contract research organization (CRO), operating under the Alimentiv Health Trust. Alimentiv Inc. provides comprehensive clinical trial services, precision medicine offerings, and centralized imaging solutions for endoscopy, histopathology, and other imaging modalities. The beneficiaries of the Alimentiv Health Trust are the employees of the enterprises it holds. CM, GYZ, LMS, BGF, and VJ are consultants to Alimentiv Inc.; they do not hold equity positions or shares in Alimentiv Inc. and CM, GYZ, BGF, and VJ have a primary academic appointment.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Western University Health Science Research Ethics Board (File Number: 108879).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hanzel, J., Sey, M., Ma, C. et al. Existing Bowel Preparation Quality Scales Are Reliable in the Setting of Centralized Endoscopy Reading. Dig Dis Sci 68, 1195–1207 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-022-07729-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-022-07729-9