Abstract
Background
Functional dyspepsia (FD) is characterized with multiple symptoms of indigestion and often accompanied with anxiety. However, there is currently an absence of effective treatment. Tandospirone is commonly used to treat generalized anxiety disorders. Whether tandospirone can improve the clinical symptoms of FD remain unknown.
Aims
The present study was designed to explore the pharmacological effect of tandospirone on FD patient with anxiety, and the potential mechanisms were also elucidated.
Methods
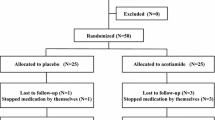
FD patients with anxiety were randomly divided into placebo and tandospirone treatment groups. Healthy volunteers were simultaneously recruited as control group. The gastrointestinal symptom score (GIS) and Hamilton anxiety scale (HAM-A) were performed before and after treatments with placebo or tandospirone. The serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and multiple inflammatory cytokines including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin (IL)-6, IL-4, IL-1β, and IL-10 were determined. Regression analyses relating BDNF levels and gastrointestinal symptoms were performed.
Results
Tandospirone significantly alleviated the gastrointestinal and anxiety symptoms of FD patient, as evidenced by reductions of GIS index and HAM-A scores. Compared with the healthy volunteers, FD patients had lower BDNF and IL-10 levels, but higher levels of IL-6 and TNF-α. Importantly, tandospirone increased serum BDNF and IL-10 and decreased IL-6 levels in FD patients. Relative analysis revealed that BDNF level was negatively associated with gastrointestinal symptoms in FD patients.
Conclusion
Tandospirone effectively improved both anxiety and gastrointestinal symptoms of patients with FD, and these therapeutic effects may be associated with the modulation of BDNF and inflammatory cytokines.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ford AC, Mahadeva S, Carbone MF, Lacy BE, Talley NJ. Functional dyspepsia. Lancet 2020;396:1689–1702.
Mounsey A, Barzin A, Rietz A. Functional Dyspepsia: Evaluation and Management. Am Fam Physician 2020;101:84–88.
Oshima T, Miwa H. Epidemiology of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Japan and in the World. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 2015;21:320–329.
Ly HG, Weltens N, Tack J, Van Oudenhove L. Acute Anxiety and Anxiety Disorders Are Associated With Impaired Gastric Accommodation in Patients With Functional Dyspepsia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;13:1584-1591.e3.
Van Oudenhove L, Aziz Q. The role of psychosocial factors and psychiatric disorders in functional dyspepsia. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;10:158–167.
Aro P, Talley NJ, Johansson SE, Agréus L, Ronkainen J. Anxiety Is Linked to New-Onset Dyspepsia in the Swedish Population: A 10-Year Follow-up Study. Gastroenterology 2015;148:928–937.
Miwa H, Nagahara A, Tominaga K et al. Efficacy of the 5-HT1A agonist tandospirone citrate in improving symptoms of patients with functional dyspepsia: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:2779–2787.
Kinoshita Y, Hashimoto T, Kawamura A et al. Effects of famotidine, mosapride and tandospirone for treatment of functional dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005;21:37–41.
Kindt S, Van Oudenhove L, Broekaert D et al. Immune dysfunction in patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2009;21:389–398.
Powell N, Walker MM, Talley NJ. The mucosal immune system: master regulator of bidirectional gut-brain communications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;14:143–159.
Phillips C. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Depression, and Physical Activity: Making the Neuroplastic Connection. Neural Plast 2017;2017:7260130.
Bus BA, Molendijk ML, Penninx BJ et al. Determinants of serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2011;36:228–239.
Satomura E, Baba H, Nakano Y, Maeshima H, Suzuki T, Arai H. Correlations between brain-derived neurotrophic factor and clinical symptoms in medicated patients with major depression. J Affect Disord 2011;135:332–335.
Cheung C, Lan LL, Kyaw M et al. Up-regulation of transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV) and down-regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression in patients with functional dyspepsia (FD). Neurogastroenterol Motil 2018;30:e13176.
Tack J, Talley NJ. Functional dyspepsia–symptoms, definitions and validity of the Rome III criteria. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;10:134–141.
Adam B, Liebregts T, Saadat-Gilani K, Vinson B, Holtmann G. Validation of the gastrointestinal symptom score for the assessment of symptoms in patients with functional dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005;22:357–363.
von Arnim U, Peitz U, Vinson B, Gundermann KJ, Malfertheiner P. STW 5, a phytopharmacon for patients with functional dyspepsia: results of a multicenter, placebo-controlled double-blind study. Am J Gastroenterol 2007;102:1268–1275.
Forssmann K, Meier L, Uehleke B, Breuer C, Stange R. A non-interventional, observational study of a fixed combination of pepsin and amino acid hydrochloride in patients with functional dyspepsia. BMC Gastroenterol 2017;17:123.
Hu P, Yang Q, Kong L, Hu L, Zeng L. Relationship between the anxiety/depression and care burden of the major caregiver of stroke patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97:e12638.
Tse AW, Lai LH, Lee CC et al. Validation of Self-administrated Questionnaire for Psychiatric Disorders in Patients with Functional Dyspepsia. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 2010;16:52–60.
Koloski N, Holtmann G, Talley NJ. Is there a causal link between psychological disorders and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;14:1047–1059.
Jones MP, Tack J, Van Oudenhove L et al. Mood and Anxiety Disorders Precede Development of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Patients but Not in the Population. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;15:1014-1020.e4.
Black CJ, Houghton LA, Ford AC. Insights into the evaluation and management of dyspepsia: recent developments and new guidelines. Therap Adv Gastroenterol 2018;11:1756284818805597.
Hojo M, Miwa H, Yokoyama T et al. Treatment of functional dyspepsia with antianxiety or antidepressive agents: systematic review. J Gastroenterol 2005;40:1036–1042.
Xiong N, Duan Y, Wei J, Mewes R, Leonhart R. Antidepressants vs. Placebo for the Treatment of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:659.
Cubeddu A, Bucci F, Giannini A et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor plasma variation during the different phases of the menstrual cycle in women with premenstrual syndrome. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2011;36:523–530.
Molendijk ML, Bus BA, Spinhoven P et al. Serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in major depressive disorder: state-trait issues, clinical features and pharmacological treatment. Mol Psychiatry 2011;16:1088–1095.
Bath KG, Chuang J, Spencer-Segal JL et al. Variant brain-derived neurotrophic factor (Valine66Methionine) polymorphism contributes to developmental and estrous stage-specific expression of anxiety-like behavior in female mice. Biol Psychiatry 2012;72:499–504.
Bergami M, Rimondini R, Santi S, Blum R, Götz M, Canossa M. Deletion of TrkB in adult progenitors alters newborn neuron integration into hippocampal circuits and increases anxiety-like behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008;105:15570–15575.
Dutt R, Shankar N, Srivastava S, Yadav A, Ahmed RS. Cardiac autonomic tone, plasma BDNF levels and paroxetine response in newly diagnosed patients of generalised anxiety disorder. Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract 2020;24:135–142.
Wang Y, Zhang H, Li Y et al. BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and plasma levels in Chinese Han population with obsessive-compulsive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder. J Affect Disord 2015;186:7–12.
Molendijk ML, Bus BA, Spinhoven P et al. Gender specific associations of serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in anxiety. World J Biol Psychiatry 2012;13:535–543.
Carlino D, Francavilla R, Baj G et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor serum levels in genetically isolated populations: gender-specific association with anxiety disorder subtypes but not with anxiety levels or Val66Met polymorphism. PeerJ 2015;3:e1252.
Keely S, Walker MM, Marks E, Talley NJ. Immune dysregulation in the functional gastrointestinal disorders. Eur J Clin Invest. 2015;45:1350–1359.
Aro P, Talley NJ, Ronkainen J et al. Anxiety is associated with uninvestigated and functional dyspepsia (Rome III criteria) in a Swedish population-based study. Gastroenterology 2009;137:94–100.
Koloski NA, Jones M, Kalantar J, Weltman M, Zaguirre J, Talley NJ. The brain–gut pathway in functional gastrointestinal disorders is bidirectional: a 12-year prospective population-based study. Gut 2012;61:1284–1290.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by grants from the West China Psychiatric Association (2016-19) and the Training Fund of the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University (PYJJ2019-04).
Funding
This work was supported by Grants from the West China Psychiatric Association (2016-19) and the Training Fund of the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University (PYJJ2019-04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Prof. SG is the guarantor of this work, had full access to all the data, and took full responsibility for the integrity of data and the accuracy of data analysis; LL researched data and edited and revised the manuscript; WY and YL researched data; JW and YZ reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no potential conflicts, including financial interests, activities, relationships, and affiliations.
Ethical approval
The study protocol was approved by the local Ethical Committee of First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University (No.20163101).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from each participant.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Yang, W., Lu, Y. et al. Clinical Efficacy of Tandospirone on Functional Dyspepsia Patients with Anxiety: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. Dig Dis Sci 68, 521–528 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-022-07717-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-022-07717-z