Abstract
Background
Receptor tyrosine kinases of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family such as human epidermal receptor-2 (HER2) are involved in the development and progression of esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC). Prior studies have demonstrated that group IIa secretory phospholipase A2 (sPLA2 IIa) can function as a ligand for the EGFR family of receptors and lead to an increase in receptor signaling.
Aims
We hypothesized that sPLA2 IIa inhibition downregulates the expression of EGFR and HER-2 in EAC and through this mechanism decreases proliferation in EAC.
Methods
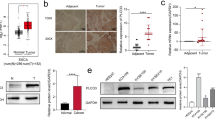
Normal human esophageal epithelium, Barrett’s esophagus (BE), and EAC tissue samples were assayed for baseline expression of EGFR, HER-2, and sPLA2 IIa. sPLA2 IIa was attenuated via inhibitor or lentiviral knockdown in esophageal cell lines, and cells were assayed for EGFR and HER2 expression as well as proliferation. FLO1 EAC cells were injected into the flank of nude mice. After randomization, mice received daily group IIA sPLA2 inhibitor or a control solution, and tumor volume was measured with calipers.
Results
sPLA2 IIa, EGFR, and HER2 expression increased across the spectrum of normal esophageal epithelium to EAC. sPLA2 IIa inhibition and knockdown decreased the expression of HER-2 and EGFR and proliferation. Mice treated with sPLA2 IIa inhibitor had smaller tumors than controls.
Conclusions
sPLA2 IIa inhibition decreases EGFR and HER2 expression and lowers proliferation of human EAC. The discovery of sPLA2 IIa inhibition’s ability to attenuate growth factor receptor signaling underscores the exciting potential of sPLA2 IIa inhibitors as therapeutics in the treatment of EAC.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BE:
-
Barrett’s esophagus
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- EAC:
-
Esophageal adenocarcinoma
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- HER2:
-
Human epidermal receptor-2
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry]
- IP:
-
Intraperitoneal
- MTS:
-
(3-(4,5-dimethylithiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium)
- RPMI:
-
Roswell Park Memorial Institute Media
- SCC:
-
Squamous cell carcinoma
- shRNA:
-
Short hairpin ribonucleic acid
- sPLA2 IIa:
-
Group IIa secretory phospholipase A2
References
Noone A-M, Cronin KA, Altekruse SF, et al. Cancer incidence and survival trends by subtype using data from the surveillance epidemiology and end results program, 1992–2013. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2017;26:632.
Dong Z, Meller J, Succop P, et al. Secretory phospholipase A2-IIa upregulates HER/HER2-elicited signaling in lung cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2014;45:978–984.
Lu S, Dong Z. Overexpression of secretory phospholipase A2-IIa supports cancer stem cell phenotype via HER/ERBB-elicited signaling in lung and prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2017;50:2113–2122.
Sadaria MR, Meng X, Fullerton DA, et al. Secretory phospholipase A2 inhibition attenuates intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in human esophageal adenocarcinoma cells. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;91:1539–1545.
Sadaria MR, Yu JA, Meng X, et al. Secretory phospholipase A2 mediates human esophageal adenocarcinoma cell growth and proliferation via ERK 1/2 pathway. Anticancer Res. 2013;33:1337–1342.
Mauchley D, Meng X, Johnson T, et al. Modulation of growth in human esophageal adenocarcinoma cells by group IIa secretory phospholipase A(2). J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;139:591–599. (discussion 599).
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:127–137.
Arteaga CL, Engelman JA. ERBB receptors: from oncogene discovery to basic science to mechanism-based cancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell. 2014;25:282–303.
Cronin J, McAdam E, Danikas A, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is overexpressed in high-grade dysplasia and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and may represent a biomarker of histological progression in Barrett’s esophagus (BE). Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106:46–56.
Goltsov AA, Fang B, Pandita TK, et al. HER2 confers resistance to foretinib inhibition of MET-amplified esophageal adenocarcinoma cells. Ann Thorac Surg. 2018;105:363–370.
Hanawa M, Suzuki S, Dobashi Y, et al. EGFR protein overexpression and gene amplification in squamous cell carcinomas of the esophagus. Int J Cancer. 2006;118:1173–1180.
Reichelt U, Duesedau P, Tsourlakis M, et al. Frequent homogeneous HER-2 amplification in primary and metastatic adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Mod Pathol. 2007;20:120–129.
Yamamoto Y, Yamai H, Seike J, et al. Prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in patients positive for human epidermal growth factor receptor family can be improved by initial chemotherapy with docetaxel, fluorouracil, and cisplatin. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:757–765.
Yoon HH, Shi Q, Sukov WR, et al. Association of HER2/ErbB2 expression and gene amplification with pathologic features and prognosis in esophageal adenocarcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:546–554.
Fichter CD, Przypadlo CM, Buck A, et al. A new model system identifies epidermal growth factor receptor-human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) and HER2-human epidermal growth factor receptor 3 heterodimers as potent inducers of oesophageal epithelial cell invasion. J Pathol. 2017;243:481–495.
Walch A, Bink K, Hutzler P, et al. HER-2/neu gene amplification by FISH predicts poor survival in Barrett’s esophagus-associated adenocarcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2000;31:1332–1334.
Oleksowicz L, Liu Y, Bracken RB, et al. Secretory phospholipase A2-IIa is a target gene of the HER/HER2-elicited pathway and a potential plasma biomarker for poor prognosis of prostate cancer. Prostate. 2012;72:1140–1149.
Bennett DT, Reece TB, Foley LS, et al. C-terminal tensin-like protein mediates invasion of human lung cancer cells and is regulated by signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;149:369–375.
Yu JA, Li H, Meng X, et al. Group IIa secretory phospholipase expression correlates with group IIa secretory phospholipase inhibition-mediated cell death in K-ras mutant lung cancer cells. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012;144:1479–1485.
Fichter CD, Timme S, Braun JA, et al. EGFR, HER2 and HER3 dimerization patterns guide targeted inhibition in two histotypes of esophageal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2014;135:1517–1530.
Guo K, Wang WP, Jiang T, et al. Assessment of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation/copy number and K-ras mutation in esophageal cancer. J Thorac Dis. 2016;8:1753–1763.
Fassan M, Mastracci L, Grillo F, et al. Early HER2 dysregulation in gastric and oesophageal carcinogenesis. Histopathology. 2012;61:769–776.
Bradley JD, Dmitrienko AA, Kivitz AJ, et al. A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial of LY333013, a selective inhibitor of group II secretory phospholipase A2, in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2005;32:417–423.
Rosenson RS, Hislop C, Elliott M, et al. Effects of varespladib methyl on biomarkers and major cardiovascular events in acute coronary syndrome patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56:1079–1088.
Rosenson RS, Hislop C, McConnell D, et al. Effects of 1-H-indole-3-glyoxamide (A-002) on concentration of secretory phospholipase A2 (PLASMA study): a phase II double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;373:649–658.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the University of Colorado Research Histology Core Laboratory for assistance with immunohistochemistry and Dr. Jeffrey Kaplan, MD, for the pathologic interpretation of the immunohistochemistry.
Funding
This work was funded by the Department of Surgery, Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery, and American Cancer Society Institutional Research Grant #16-184-56.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halpern, A.L., Kohtz, P.D., White, A.M. et al. Secretory Phospholipase A2 IIa Mediates Expression of Growth Factor Receptors in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 66, 784–795 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06241-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06241-2