Abstract
Background
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been shown to play pivotal role in pathogenesis and prognosis of cancers. Identification of novel clinical biomarkers in advanced stage colorectal cancer (CRC) is warranted.
Aims
To identify potential lncRNAs associated with progression of stage III/IV CRC and illuminate regulatory mechanisms.
Methods
Differentially expressed lncRNAs, mRNAs and miRNAs (DElncRNAs, DEmRNAs, and DEmiRNAs) were extracted between stage III/IV CRC and normal tissues. We used DEGs to construct a ceRNA network and analyzed correlations between key lncRNAs and overall survivals (OS) of stage III/IV CRC patients. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) was applied to a pivotal lncRNA. We conducted functional enrichment analysis on target genes and constructed lncRNA–TF–mRNA network by overlapping mRNAs co-expressed with the key lncRNA and target genes of transcriptional factors (TFs).
Results
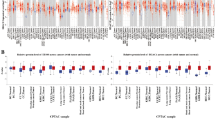
A total of 26 DElncRNAs, 398 DEmiRNAs, 2155 DEmRNAs were identified. A ceRNA network was constructed with 16 lncRNAs, 20 miRNAs, and 59 mRNAs, in which MFI2-AS1 exhibited promising diagnostic efficiency. (AUC was 0.938.) MFI2-AS1 was negatively correlated to OS of stage III/IV CRC patients (P value < 0.05). KEGG analysis showed potential mRNA targets of MFI2-AS1 mainly involved in cell cycle and cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction. We identified 17 potential TFs of MFI2-AS1 and built a lncRNA–TF–mRNA network.
Conclusion
Our study provides novel insights into lncRNAs associated regulatory networks and reveals a promising lncRNA biomarker, MFI2-AS1, as an independent prognostic indicator and potential therapeutic target for CRC.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melina A, Sierra Mónica S, Mathieu L, et al. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut. 2017;66:683–691.
Miller Kimberly D, Siegel Rebecca L, Chieh LC, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:271–289.
Gomes AQ, Nolasco S, Soares H. Non-coding RNAs: multi-tasking molecules in the cell. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:16010–16039.
Ye LC, Zhu X, Qiu JJ, Xu J, Wei Y. Involvement of long non-coding RNA in colorectal cancer: from benchtop to bedside (review). Oncol Lett. 2015;9:1039–1045.
Li J, Wang X, Tang J, et al. HULC and Linc00152 act as novel biomarkers in predicting diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37:687–696.
Xu CZ, Jiang C, Wu Q, Liu L, Yan X, Shi R. A feed-forward regulatory loop between HuR and the long noncoding RNA HOTAIR promotes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression and metastasis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40:1039–1051.
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013;495:384–388.
Tay Y, Rinn J, Pandolfi PP. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature. 2014;505:344–352.
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP. A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell. 2011;146:353–358.
Zhao G, Fu Y, Su Z. How long non-coding RNAs and MicroRNAs mediate the endogenous RNA network of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a comprehensive analysis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50:332–341.
De Jong MC, Pulitano C, Ribero D, et al. Rates and patterns of recurrence following curative intent surgery for colorectal liver metastasis: an international multi-institutional analysis of 1669 patients. Ann Surg. 2009;250:440–448.
Qiao HP, Gao WS, Huo JX, Yang ZS. Long non-coding RNA GAS5 functions as a tumor suppressor in renal cell carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14:1077–1082.
Enfield KS, Pikor LA, Martinez VD, Lam WL. Mechanistic roles of noncoding RNAs in lung cancer biology and their clinical implications. Genet Res Int. 2012;2012:737416.
Tuo YL, Li XM, Luo J. Long noncoding RNA UCA1 modulates breast cancer cell growth and apoptosis through decreasing tumor suppressive miR-143. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19:3403–3411.
Han Y, Yang YN, Yuan HH, et al. UCA1, a long non-coding RNA up-regulated in colorectal cancer influences cell proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle distribution. Pathology. 2014;46:396–401.
Takahashi Y, Sawada G, Kurashige J, et al. Amplification of PVT-1 is involved in poor prognosis via apoptosis inhibition in colorectal cancers. Br J Cancer. 2014;110:164–171.
Flippot R, Mouawad R, Spano JP, et al. Expression of long non-coding RNA MFI2-AS1 is a strong predictor of recurrence in sporadic localized clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. 2017;7:8540.
Jones VS, Huang RY, Chen LP, et al. Cytokines in cancer drug resistance: cues to new therapeutic strategies. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Rev Cancer. 1865;2:255–265.
Tan C, Hu W, He Y, et al. Cytokine-mediated therapeutic resistance in breast cancer. Cytokine. 2018;108:151–159.
Barbagallo C, Brex D, Caponnetto A, et al. LncRNA UCA1, upregulated in CRC biopsies and downregulated in serum exosomes, controls mRNA expression by RNA–RNA interactions. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018;12:229–241.
Wang J, Liu Z, Hu T, et al. Nrf2 promotes progression of non-small cell lung cancer through activating autophagy. Cell Cycle. 2017;16:1053–1062.
Xin X, Aiwen H, Ximao C, et al. Ubiquitin specific peptidase 5 regulates colorectal cancer cell growth by stabilizing Tu translation elongation factor. Theranostics. 2019;9:4208–4220.
Nithyananda T, Petra F-V, Sonja H, et al. Long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 interacts with CDK1 and is involved in p53-dependent cell cycle control and apoptosis in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:622–637.
Xiaoxiang C, Zeng Kaixuan X, et al. SP1-induced lncRNA-ZFAS1 contributes to colorectal cancer progression via the miR-150-5p/VEGFA axis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:982.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to appreciate the GEO and TCGA databases for availability of data.
Funding
Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing in China (Grant no.cstc2018jcyjAX0019 to Longke Ran).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ruihan Luo and Longke Ran conceived of the project; Ruihan Luo and Wangfeng Zhang collected and assembled the data; Ruihan Luo conducted the data analysis, interpretation and manuscript writing; Longke Ran, Jing Song and Ruihan Luo participated in the discussion; Longke Ran and Jing Song performed paper revision. All of the authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, R., Song, J., Zhang, W. et al. Identification of MFI2-AS1, a Novel Pivotal lncRNA for Prognosis of Stage III/IV Colorectal Cancer. Dig Dis Sci 65, 3538–3550 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06064-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06064-1