Abstract
Background
The activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) is involved in hepatic fibrogenesis and is regulated by the decreased expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ). Rosiglitazone (RGZ) is a highly potent agonist of PPARγ.
Aims
To clarify molecular regulatory mechanism of RGZ in the activation of HSCs in hepatic fibrosis.
Methods
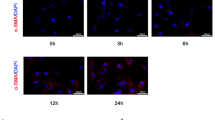
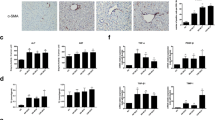
A mouse model of hepatic fibrosis was established by carbon tetrachloride with or without RGZ intervention. A vector carrying pcDNA-HOTAIR was constructed and injected into a mouse model. HSCs were isolated from liver tissue and activated by transforming growth factor-β. The expression of miR-124-3p, HOTAIR, Col1A1, α-SMA, and PPARγ mRNAs was measured by quantitative real-time PCR. The level of PPARγ was measured by Western blotting. The interaction between HOTAIR and PPARγ was assessed by RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) and RNA pull-down. The target gene of miR-124-3p was determined by luciferase reporter assay and RNA interference approaches.
Results
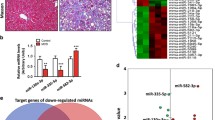
The expression of Col1A1 and α-SMA was reduced after RGZ intervention. Different expressions of HOTAIR and miR-124-3p were observed in liver tissue and HSCs. The luciferase reporter assay and RNA interference approaches indicated that miR-124-3p negatively regulated HOTAIR expression. RIP and RNA pull-down results revealed that PPARγ was interacted by HOTAIR. The therapeutic effect of RGZ on hepatic fibrosis was reversed by overexpression of HOTAIR.
Conclusions
RGZ inhibits the activation of HSCs by up-regulating miR-124-3p. The silencing of HOTAIR by miR-124-3p in HSC activation provided the foundation to understand interactions of ncRNAs and potential treatment target in hepatic fibrosis.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
29 March 2023
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-023-07926-0
References
Trautwein C, Friedman SL, Schuppan D, Pinzani M. Hepatic fibrosis: concept to treatment. J Hepatol. 2015;62:S15–S24.
Mehal WZ, Schuppan D. Antifibrotic therapies in the liver. Semin Liver Dis. 2015;35:184–198.
Hsu W-H, Lee BH, Hsu YW, Pan TM. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activators monascin and rosiglitazone attenuate carboxymethyllysine-induced fibrosis in hepatic stellate cells through regulating the oxidative stress pathway but independent of the receptor for advanced glycation end products signaling. J Agric Food Chem. 2013;61:6873–6879.
Kersten S, Desvergne B, Wahli W. Roles of PPARs in health and disease. Nature. 2000;405:421.
Marra F, Efsen E, Romanelli RG, et al. Ligands of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma modulate profibrogenic and proinflammatory actions in hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology. 2000;119:466–478.
Miyahara T, Schrum L, Rippe R, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and hepatic stellate cell activation. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:35715–35722.
Lu Y, Ma D, Xu W, Shao S, Yu X. Effect and cardiovascular safety of adding rosiglitazone to insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. J Diabetes Investig. 2015;6:78–86.
Zhao C, Chen W, Yang L, Chen L, Stimpson SA, Diehl AM. PPARgamma agonists prevent TGFbeta1/Smad3-signaling in human hepatic stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;350:385–391.
Asano T, Yamazaki H, Kasahara C, et al. Identification, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 6-[(6R)-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-(hydroxymethyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrazolo[1,5-a]pyr imidin-3-yl]-2-(2-methylphenyl)pyridazin-3(2H)-one (AS1940477), a potent p38 MAP kinase inhibitor. J Med Chem. 2012;55:7772–7785.
Yoshihara D, Kurahashi H, Morita M, et al. PPARgamma agonist ameliorates kidney and liver disease in an orthologous rat model of human autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011;300:F465–F474.
Cech TR, Steitz JA. The noncoding RNA revolution-trashing old rules to forge new ones. Cell. 2014;157:77–94.
Zell S, Schmitt R, Witting S, Kreipe HH, Hussein K, Becker JU. Hypoxia induces mesenchymal gene expression in renal tubular epithelial cells: an in vitro model of kidney transplant fibrosis. Nephron Extra. 2013;3:50–58.
Gong M, Liang T, Jin S, et al. Methylation-mediated silencing of miR-124 facilitates chondrogenesis by targeting NFATc1 under hypoxic conditions. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9:4111–4124.
Wang D, Zhang H, Li M, et al. MicroRNA-124 controls the proliferative, migratory, and inflammatory phenotype of pulmonary vascular fibroblasts. Circ Res. 2014;114:67–78.
Jiang J, Gusev Y, Aderca I, et al. Association of microRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with hepatitis infection, cirrhosis, and patient survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:419–427.
Jiang X-P, Ai WB, Wan LY, Zhang YQ, Wu JF. The roles of microRNA families in hepatic fibrosis. Cell Biosci. 2017;7:34.
Wang Y, Hu M. Peroxisome proliferators activated receptor γ protects against acute lung injury alveolar macrophages inflammation by upregulating miR-124 expression. Chin J Lung Dis. 2015;8:160–165.
Carninci P, Kasukawa T, Katayama S, et al. The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. SPJ. 2005;309:1559–1563.
Sun M, Kraus WL. From discovery to function: the expanding roles of long noncoding RNAs in physiology and disease. Endocr Rev. 2015;36:25–64.
Bian EB, Wang YY, Yang Y, et al. Hotair facilitates hepatic stellate cells activation and fibrogenesis in the liver. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2017;1863:674–686.
Rinn JL, Kertesz M, Wang JK, et al. Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by non-coding RNAs. Cell. 2007;129:1311–1323.
Chiyomaru T, Fukuhara S, Saini S, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is targeted and regulated by miR-141 in human cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:12550–12565.
Bennett RG, Simpson RL, Hamel FG. Serelaxin increases the antifibrotic action of rosiglitazone in a model of hepatic fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23:3999–4006.
Zhang K, Han X, Zhang Z, et al. The liver-enriched lnc-LFAR1 promotes liver fibrosis by activating TGFβ and Notch pathways. Nat Commun. 2017;8:144.
Ikeda K, Wakahara T, Wang YQ, Kadoya H, Kawada N, Kaneda K. In vitro migratory potential of rat quiescent hepatic stellate cells and its augmentation by cell activation. Hepatology. 1999;29:1760–1767.
Friedman SL. Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury. J Biol Chem. 2000;28:2247–2250.
Armoni M, Harel C, Karnieli E. PPARγ gene expression is autoregulated in primary adipocytes: ligand, sumoylation, and isoform specificity. Horm Metab Res. 2015;47:89–96.
Zhang Q, Xiang S, Liu Q, et al. PPARγ antagonizes hypoxia-induced activation of hepatic stellate cell through cross mediating PI3K/AKT and cGMP/PKG signaling. PPAR Res. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6970407.
Kweon S-M, Chi F, Higashiyama R, Lai K, Tsukamoto H. Wnt pathway stabilizes MeCP2 protein to repress PPAR-γ in activation of hepatic stellate cells. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0156111.
Troeger JS, Mederacke I, Gwak GY, et al. Deactivation of hepatic stellate cells during liver fibrosis resolution in mice. Gastroenterology. 2012;143:1073. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.036.
Morán-Salvador E, Titos E, Rius B, et al. Cell-specific PPARγ deficiency establishes anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrogenic properties for this nuclear receptor in non-parenchymal liver cells. J Hepatol. 2013;59:1045–1053.
Odegaard JI, Ricardo-Gonzalez RR, Eagle AR, et al. Alternative M2 activation of Kupffer cells by PPARδ ameliorates obesity-induced insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2008;7:496–507.
Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Loomba R, Sanyal AJ, et al. Farnesoid X nuclear receptor ligand obeticholic acid for non-cirrhotic, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (FLINT): a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2015;385:956–965.
Yang J-J, Tao H, Li J. Hedgehog signaling pathway as key player in liver fibrosis: new insights and perspectives. Expert Opin Therap Targets. 2014;18:1011–1021.
Noetel A, Kwiecinski M, Elfimova N, Huang J, Odenthal M. microRNA are central players in anti- and profibrotic gene regulation during liver fibrosis. Front Physiol. 2012;3:49.
Roderburg C, Urban GW, Bettermann K, et al. Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology. 2010;53:209–218.
Lakner AM, Steuerwald NM, Walling TL, et al. Inhibitory effects of microRNA 19b in hepatic stellate cell-mediated fibrogenesis. Hepatology. 2012;56:300–310.
Liang YG, Liu ZT, Guo SX. Ultrasound reverses adriamycin-resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via positive regulation of BRAF-activated non-coding RNA (BANCR) expression. Clin Surg Res Commun. 2017;1:18–23.
Zhang A, Zhao JC, Kim J, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR enhances the androgen-receptor-mediated transcriptional program and drives castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cell Rep. 2015;13:209–221.
Bhan A, Mandal SS. LncRNA HOTAIR: a master regulator of chromatin dynamics and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1856:151–164.
Shenoy A, Blelloch RH. Regulation of microRNA function in somatic stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:565–576.
Song R, Walentek P, Sponer N, et al. miR-34/449 miRNAs are required for motile ciliogenesis by repressing cp110. Nature. 2014;510:115–120.
Sun Q, Csorba T, Skourti-Stathaki K, Proudfoot NJ, Dean C. R-loop stabilization represses antisense transcription at the Arabidopsis FLC locus. Science. 2013;340:619–621.
Ghosal S, Das S, Sen R, Basak P, Chakrabarti J. Circ2Traits: a comprehensive database for circular RNA potentially associated with disease and traits. Front Genet. 2013;4:283.
Wang J, Liu X, Wu H, et al. CREB up-regulates long non-coding RNA, HULC expression through interaction with microRNA-372 in liver cancer. Nucl Acids Res. 2010;38:5366–5383.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Grant Number: LY16H030014) and Zhejiang Provincial Medical Technology Project (Grant Number: 2019KY104) and Zhejiang Provincial Science Technology Project (Grant Number: 2015C37101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University. All of these experiments in the current research were in compliance with the government policies and defined protocols.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Availability of data and material
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Additional information
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-023-07926-0
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhi, Sc., Chen, Sz., Li, Yy. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Rosiglitazone Inhibits Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells via Up-Regulating Micro-RNA-124-3p to Alleviate Hepatic Fibrosis. Dig Dis Sci 64, 1560–1570 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-019-5462-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-019-5462-8