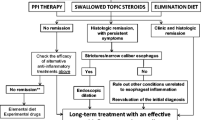
Abstract
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an immune-mediated disease triggered by food antigens for which dietary elimination treatment can induce and sustain histologic remission. Our review aims to describe the state of the art regarding dietary treatment of EoE, highlighting a number of areas of controversy related to dietary therapy in EoE, including novel modalities for determining food triggers, making the empiric dietary elimination process more efficient, issues of cross-contamination and “dosing” of how much food to avoid or add back, costs and effects on quality of life, long-term efficacy, and the risk of developing immediate IgE-type reactions after initial dietary elimination. Elemental formulas, empiric elimination diets, and targeted allergy test-directed elimination diets are well-described treatments for EoE. Although elemental diets are most efficacious, their clinical use is limited by cost and the palatability of an exclusively liquid diet. While empiric elimination is less effective than elemental formula-based diets, they are more easily implemented and often sustainable. Since the comparative effectiveness of elimination diets with proton-pump inhibitors and swallowed topical steroids remains unknown, there are multiple areas to address with future research.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dellon ES, Hirano I. Epidemiology and natural history of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:319–332.
Dellon ES, Jensen ET, Martin CF, Shaheen NJ, Kappelman MD. Prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;12:589–596.
Dellon ES, Kim HP, Sperry SLW, Rybnicek DA, Woosley JT, Shaheen NJ. A phenotypic analysis shows that eosinophilic esophagitis is a progressive fibrostenotic disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;79:577–585.
Jensen ET, Kappelman MD, Martin CF, Dellon ES. Health-care utilization, costs and the burden of disease related to eosinophilic esophagitis in the United States. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015;110:626–632.
Dougherty M, Runge TM, Eluri S, Dellon ES. Esophageal dilation with either bougie or balloon technique as a treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;86:581–591.
Straumann A, Katzka DA. Diagnosis and treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:346–359.
Dellon ES, Liacouras CA. Advances in clinical management of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2014;147:1238–1254.
Richter JE. Endoscopic treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2018;28:97–110.
Reed CC, Dellon ES. Eosinophilic esophagitis. Med Clin N Am. 2019;103:29–42.
Cheng E, Zhang X, Huo X, et al. Omeprazole blocks eotaxin-3 expression by oesophageal squamous cells from patients with eosinophilic oesophagitis and GORD. Gut. 2013;62:824–832.
van Rhijn BD, Weijenborg PW, Verheij J, et al. Proton pump inhibitors partially restore mucosal integrity in patients with proton pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia but not eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;12:1815–1823.
Zhang X, Cheng E, Huo X, et al. Omeprazole blocks STAT6 binding to the eotaxin-3 promoter in eosinophilic esophagitis cells. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:9–70. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0050037.
Lucendo AJ, Arias Á, Molina-Infante J. Efficacy of proton pump inhibitor drugs for inducing clinical and histologic remission in patients with symptomatic esophageal eosinophilia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14:13–22.
Sawas T, Dhalla S, Sayyar M, Pasricha PJ, Hernaez R. Systematic review with meta-analysis: pharmacological interventions for eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;41:797–806.
Cotton CC, Eluri S, Wolf WA, Dellon ES. Six-food elimination diet and topical steroids are effective for eosinophilic esophagitis: a meta-regression. Dig Dis Sci. 2017;62:2408–2420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4642-7.
Straumann A, Conus S, Grzonka P, et al. Anti-interleukin-5 antibody treatment (mepolizumab) in active eosinophilic oesophagitis: a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Gut. 2010;59:21–30.
Assa’ad AH, Gupta SK, Collins MH, et al. An antibody against IL-5 reduces numbers of esophageal intraepithelial eosinophils in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:1593–1604.
Rothenberg ME, Wen T, Greenberg A, et al. Intravenous anti-IL-13 mAb QAX576 for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;135:500–507.
Hirano I, Collins MH, Assouline-Dayan Y, et al. RPC4046, a monoclonal antibody against IL13, reduces histologic and endoscopic activity in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:592–603.
Hirano I, Dellon ES, Hamilton JD, et al. Dupilumab efficacy and safety in adult patients with active eosinophilic oesophagitis: a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. United Eur Gastroenterol J. 2017;5:1146–1147.
Kelly KJ, Lazenby AJ, Rowe PC, Yardley JH, Perman JA, Sampson HA. Eosinophilic esophagitis attributed to gastroesophageal reflux: improvement with an amino acid-based formula. Gastroenterology. 1995;109:1503–1512.
O’Shea KM, Aceves SS, Dellon ES, et al. Pathophysiology of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:333–345.
Liacouras CA, Spergel JM, Ruchelli E, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: a 10-year experience in 381 children. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;3:1198–1206.
Assa’ad AH, Putnam PE, Collins MH, et al. Pediatric patients with eosinophilic esophagitis: an 8-year follow-up. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:731–738.
Markowitz JE, Spergel JM, Ruchelli E, Liacouras CA. Elemental diet is an effective treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adolescents. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:777–782.
Kagalwalla AF, Sentongo TA, Ritz S, et al. Effect of six-food elimination diet on clinical and histologic outcomes in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:1097–1102.
Gonsalves N, Yang G, Doerfler B, Ritz S, Ditto AM, Hirano I. Elimination diet effectively treats eosinophilic esophagitis in adults; food reintroduction identifies causative factors. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:1451–1459.
Lucendo AJ, Arias Á, González-Cervera J, et al. Empiric 6-food elimination diet induced and maintained prolonged remission in patients with adult eosinophilic esophagitis: a prospective study on the food cause of the disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131:797–804.
Philpott H, Nandurkar S, Royce SG, Thien F, Gibson PR. A prospective open clinical trial of a proton pump inhibitor, elimination diet and/or budesonide for eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;43:985–993.
Wolf WA, Jerath MR, Sperry SLW, Shaheen NJ, Dellon ES. Dietary elimination therapy is an effective option for adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;12:1272–1279.
Simon D, Cianferoni A, Spergel JM, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis is characterized by a non-IgE-mediated food hypersensitivity. Allergy. 2016;71:611–620.
Mishra A, Hogan SP, Brandt EB, Rothenberg ME. An etiological role for aeroallergens and eosinophils in experimental esophagitis. J Clin Investig. 2001;107:83–90.
Henderson CJ, Abonia JP, King EC, et al. Comparative dietary therapy effectiveness in remission of pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129:1570–1578.
Colson D, Kalach N, Soulaines P, et al. The impact of dietary therapy on clinical and biologic parameters of pediatric patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2014;2:587–593.
Rodríguez-Sánchez J, Gómez Torrijos E, López Viedma B, et al. Efficacy of IgE-targeted vs empiric six-food elimination diets for adult eosinophilic oesophagitis. Allergy. 2014;69:936–942.
Arias Á, Lucendo AJ, Martínez-Fernández P, et al. Dietary treatment modulates mast cell phenotype, density, and activity in adult eosinophilic oesophagitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2016;46:78–91.
Lieberman JA, Morotti RA, Konstantinou GN, Yershov O, Chehade M. Dietary therapy can reverse esophageal subepithelial fibrosis in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis: a historical cohort. Allergy. 2012;67:1299–1307.
Leung J, Mehrzad R, Hundal NV, et al. Longitudinal perspective on managing refractory eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015;3:951–956.
Spergel JM, Brown-Whitehorn TF, Cianferoni A, et al. Identification of causative foods in children with eosinophilic esophagitis treated with an elimination diet. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:461–467.
Groetch M, Venter C, Skypala I, et al. Dietary therapy and nutrition management of eosinophilic esophagitis: a work group report of the American Academy of allergy, asthma, and immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2017;5:312–324.
Philpott H, Dellon ES. The role of maintenance therapy in eosinophilic esophagitis: Who, why, and how? J Gastroenterol. 2018;53:165–171.
Borschel MW, Antonson DL, Murray ND, et al. Two single group, prospective, baseline-controlled feeding studies in infants and children with chronic diarrhea fed a hypoallergenic free amino acid-based formula. BMC Pediatr. 2014;14:136. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2431-14-136.
Sicherer SH, Noone SA, Koerner CB, Christie L, Burks AW, Sampson HA. Hypoallergenicity and efficacy of an amino acid-based formula in children with cow’s milk and multiple food hypersensitivities. J Pediatr. 2001;138:688–693.
Warners MJ, Vlieg-Boerstra BJ, Verheij J, et al. Elemental diet decreases inflammation and improves symptoms in adult eosinophilic oesophagitis patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;45:777–787.
Peterson KA, Byrne KR, Vinson LA, et al. Elemental diet induces histologic response in adult eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:759–766.
Al-Hussaini A, Al-Idressi E, Al-Zahrani M. The role of allergy evaluation in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. J Gastroenterol. 2013;48:1205–1212.
Kagalwalla AF, Amsden K, Shah A, et al. Cowʼs milk elimination: a novel dietary approach to treat eosinophilic esophagitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012;55:711–716.
Arias Á, González-Cervera J, Tenias JM, Lucendo AJ. Efficacy of dietary interventions for inducing histologic remission in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:1639–1648.
Syrigou E, Angelakopoulou A, Zande M, Panagiotou I, Roma E, Pitsios C. Allergy-test-driven elimination diet is useful in children with eosinophilic esophagitis, regardless of the severity of symptoms. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2015;26:323–329.
Spergel JM, Andrews T, Brown-Whitehorn TF, Beausoleil JL, Liacouras CA. Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis with specific food elimination diet directed by a combination of skin prick and patch tests. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005;95:336–343.
Clayton F, Fang JC, Gleich GJ, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults is associated with IgG4 and not mediated by IgE. Gastroenterology. 2014;147:602–609.
Doerfler B, Bryce P, Hirano I, Gonsalves N. Practical approach to implementing dietary therapy in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis: the Chicago experience: dietary therapy in adult EoE. Dis Esophagus. 2015;28:42–58.
Reed CC, Fan C, Koutlas NT, Shaheen NJ, Dellon ES. Food elimination diets are effective for long-term treatment of adults with eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46:836–844.
Asher Wolf W, Huang KZ, Durban R, et al. The six-food elimination diet for eosinophilic esophagitis increases grocery shopping cost and complexity. Dysphagia. 2016;31:765–770.
Philpott H, Nandurkar S, Royce SG, Thien F, Gibson PR. Allergy tests do not predict food triggers in adult patients with eosinophilic oesophagitis. A comprehensive prospective study using five modalities. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;44:223–233.
Spergel JM, Brown-Whitehorn T, Beausoleil JL, Shuker M, Liacouras CA. Predictive values for skin prick test and atopy patch test for eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:509–511.
Armentia A, Martín-Armentia S, Martín-Armentia B, et al. Is eosinophilic esophagitis an equivalent of pollen allergic asthma? Analysis of biopsies and therapy guided by component resolved diagnosis. Allergol Immunopathol. 2018;46:181–189.
Armentia A, Martín S, Barrio J, et al. Value of microarray allergen assay in the management of eosinophilic oesophagitis. Allergol Immunopathol. 2015;43:73–80.
Erwin EA, Tripathi A, Ogbogu PU, et al. IgE antibody detection and component analysis in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015;3:896–904.
Wright BL, Kulis M, Guo R, et al. Food-specific IgG 4 is associated with eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;138:1190–1192.
Dellon ES, Guo R, McGee SJ, et al. An allergen-specific immune signature identifies food triggers in eosinophilic esophagitis with high accuracy. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:S260.
Warners MJ, Terreehorst I, van den Wijngaard RM, et al. Abnormal responses to local esophageal food allergen injections in adult patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:57–60.
Molina-Infante J, Arias A, Barrio J, Rodríguez-Sánchez J, Sanchez-Cazalilla M, Lucendo AJ. Four-food group elimination diet for adult eosinophilic esophagitis: a prospective multicenter study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:1093–1099.
Kagalwalla AF, Wechsler JB, Amsden K, et al. Efficacy of a 4-food elimination diet for children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15:1698–1707.
Gonsalves N, Doerfler B, Schwartz S, et al. Prospective trial of four food elimination diet demonstrates comparable effectiveness in the treatment of adult and pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:S154.
Molina-Infante J, Arias Á, Alcedo J, et al. Step-up empiric elimination diet for pediatric and adult eosinophilic esophagitis: The 2-4-6 study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141:1365–1372.
Kruszewski PG, Russo JM, Franciosi JP, Varni JW, Platts-Mills TAE, Erwin EA. Prospective, comparative effectiveness trial of cow’s milk elimination and swallowed fluticasone for pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis: pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis therapy. Dis Esophagus. 2016;29:377–384.
Zhan T, Ali A, Choi JG, et al. Model to determine the optimal dietary elimination strategy for treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16:1730–1737.
Kliewer KL, Venter C, Cassin AM, et al. Should wheat, barley, rye, and/or gluten be avoided in a 6-food elimination diet? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;137:1011–1014.
Hernando A, Mujico JR, Mena MC, Lombardía M, Méndez E. Measurement of wheat gluten and barley hordeins in contaminated oats from Europe, the United States and Canada by Sandwich R5 ELISA. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;20:545–554.
Philpott H, Dellon E. Histologic improvement after 6 weeks of dietary elimination for eosinophilic esophagitis may be insufficient to determine efficacy. Asia Pac Allergy. 2018;8:e20.
Cotton CC, Erim D, Eluri S, et al. Cost utility analysis of topical steroids compared with dietary elimination for treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15:841–849.
Friedlander JA, DeBoer EM, Soden JS, et al. Unsedated transnasal esophagoscopy for monitoring therapy in pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;83:299–306.
Philpott H, Nandurkar S, Royce SG, Gibson PR. Ultrathin unsedated transnasal gastroscopy in monitoring eosinophilic esophagitis: transnasal gastroscopy for EoE. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;31:590–594.
Januszewicz W, Tan WK, Lehovsky K, et al. Safety and acceptability of esophageal cytosponge cell collection device in a pooled analysis of data from individual patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17:647.e1–656.e1.
Katzka DA, Smyrk TC, Alexander JA, et al. Accuracy and safety of the cytosponge for assessing histologic activity in eosinophilic esophagitis: a two-center study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112:1538–1544.
Alexander JA, Katzka DA, Ravi K, et al. Efficacy of cytosponge directed food elimination diet in eosinophilic esophagitis. A pilot trial. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:S76.
Gottlieb SJ, Markowitz JE, Dellon ES. New IgE immediate hypersensitivity reactions upon reintroduction of food restricted for treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019; Epub ahead of print.
Alsalamah M, Makhajia M, Somers G, Marcon M, Hummel D, Upton J. Anaphylaxis to milk after elimination diet for eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111:752–753.
Hill DA, Shuker M, Cianferoni A, et al. The development of IgE-mediated immediate hypersensitivity after the diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis to the same food. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015;3:123–124.
Acknowledgments
This paper was supported by NIH R01 DK101856, NIH T32 DK007634, and CEGIR (U54 AI117804) which is part of the Rare Disease Clinical Research Network (RDCRN), an initiative of the Office of Rare Diseases Research (ORDR), NCATS, and is funded through collaboration between NIAID, NIDDK, and NCATS. CEGIR is also supported by patient advocacy groups including APFED, CURED, and EFC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Dellon has received research funding from Adare, Allakos, GSK, Meritage, Miraca, Nutricia, Celgene/Receptos, Regeneron, and Shire; has received consulting fees from Adare, Alivio, Allakos, AstraZeneca, Banner, Calypso, Enumeral, EsoCap, Celgene/Receptos, GSK, Gossamer Bio, Regeneron, Robarts, Shire, and educational grants from Allakos, Banner, and Holoclara. The other authors have no potential conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cotton, C.C., Durban, R. & Dellon, E.S. Illuminating Elimination Diets: Controversies Regarding Dietary Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci 64, 1401–1408 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-019-05602-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-019-05602-w