Abstract
Background
Liver metastasis is a major cause of mortality in colorectal cancer (CRC). Epigenetic alternations could serve as biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. In this study, we analyzed microarray data in order to identify core genes and pathways which contribute to liver metastasis in CRC under epigenetic regulations.
Materials and Methods
Data of miRNAs (GSE35834, GSE81582), DNA methylation (GSE90709, GSE77955), and mRNA microarrays (GSE68468, GSE81558) were downloaded from GEO database. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs), differentially expressed miRNAs (DEMs), and differentially methylated genes (DMGs) were obtained by GEO2R. The target genes of DEMs were predicted by miRWalk. Functional and enrichment analyses were conducted by DAVID database. Protein–protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed in STRING and visualized using Cytoscape.
Results
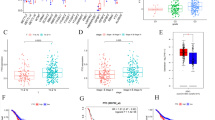
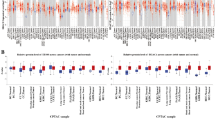
In liver metastasis, miR-143-3p, miR-10b-5p, miR-21-5p, and miR-518f-5p were down-regulated, while miR-122-5p, miR-885-5p, miR-210-3p, miR-130b-5p, miR-1275, miR-139-5p, miR-139-3p, and miR-1290 were up-regulated compared with primary CRC. DEGs targeted by altered miRNAs were enriched in pathways including complement, PPAR signaling, ECM–receptor interaction, spliceosome, and focal adhesion. In addition, aberrant DNA methylation-regulated genes showed enrichment in pathways of amino acid metabolism, calcium signaling, TGF-beta signaling, cell cycle, spliceosome, and Wnt signaling.
Conclusion
Our study identified a series of differentially expressed genes which are associated with epigenetic alternations of miRNAs and DNA methylation in colorectal liver metastasis. Up-regulated genes of SLC10A1, MAPT, SHANK2, PTH1R, and C2, as well as down-regulated genes of CAB39, CFLAR, CTSC, THBS1, and TRAPPC3 were associated with both miRNA and DNA methylation, which might become promising biomarker of colorectal liver metastasis in future.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- DEG:
-
Differentially expressed gene
- DMG:
-
Differentially methylated gene
- DEMs:
-
Differentially expressed miRNAs
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
- GEO:
-
Gene Expression Omnibus
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
- PPI:
-
Protein–protein interaction
- STRING:
-
Search tool for the retrieval of interacting genes
- NCBI:
-
The National Center for Biotechnology Information
- BP:
-
Biological processes
- MF:
-
Molecular function
- CC:
-
Cell component
- CLM:
-
Colorectal liver metastasis
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29.
Siegel R, DeSantis C, Virgo K, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:220–241.
Donadon M, Ribero D, Morris-Stiff G, Abdalla EK, Vauthey JN. New paradigm in the management of liver-only metastases from colorectal cancer. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 2007;1:20–27.
Garden OJ, Rees M, Poston GJ, et al. Guidelines for resection of colorectal cancer liver metastases. Gut. 2006;55:iii1–iii8.
Pawlik TM, Choti MA. Surgical therapy for colorectal metastases to the liver. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007;11:1057–1077.
Flavahan WA, Gaskell E, Bernstein BE. Epigenetic plasticity and the hallmarks of cancer. Science. 2017;357:6348.
Dawson MA. The cancer epigenome: Concepts, challenges, and therapeutic opportunities. Science. 2017;355:1147–1152.
Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ. MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16:203–222.
Rupaimoole R, Calin GA, Lopez-Berestein G, Sood AK. miRNA deregulation in cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2016;6:235–246.
Hur K, Toiyama Y, Okugawa Y, et al. Circulating microRNA-203 predicts prognosis and metastasis in human colorectal cancer. Gut. 2017;66:654–665.
Zhang JX, Mai SJ, Huang XX, et al. MiR-29c mediates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human colorectal carcinoma metastasis via PTP4A and GNA13 regulation of beta-catenin signaling. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:2196–2204.
Chen DL, Wang ZQ, Zeng ZL, et al. Identification of microRNA-214 as a negative regulator of colorectal cancer liver metastasis by way of regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 expression. Hepatology. 2014;60:598–609.
Jones PA, Issa JP, Baylin S. Targeting the cancer epigenome for therapy. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17:630–641.
Kim M, Costello J. DNA methylation: an epigenetic mark of cellular memory. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49:e322.
Kelly AD, Issa JJ. The promise of epigenetic therapy: reprogramming the cancer epigenome. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2017;42:68–77.
Hur K, Cejas P, Feliu J, et al. Hypomethylation of long interspersed nuclear element-1 (LINE-1) leads to activation of proto-oncogenes in human colorectal cancer metastasis. Gut. 2014;63:635–646.
Ebert MP, Mooney SH, Tonnes-Priddy L, et al. Hypermethylation of the TPEF/HPP1 gene in primary and metastatic colorectal cancers. Neoplasia. 2005;7:771–778.
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P, Gretz N. miRWalk–database: prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by “walking” the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 2011;44:839–847.
Dweep H, Gretz N, Sticht C. miRWalk database for miRNA-target interactions. Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1182:289–305.
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, et al. DAVID: database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 2003;4:P3.
The Gene Ontology Consortium. The Gene Ontology (GO) project in 2006. Nucleic Acids Research. 2006;34:D322–D326.
Kanehisa M, Goto S. KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28:27–30.
Derosa G, Sahebkar A, Maffioli P. The role of various peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and their ligands in clinical practice. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233:153–161.
Matera AG, Wang Z. A day in the life of the spliceosome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:108–121.
Carethers JM, Jung BH. Genetics and genetic biomarkers in sporadic colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:1177–1190.e1173.
Budi EH, Duan D, Derynck R. Transforming growth factor-beta receptors and smads: regulatory complexity and functional versatility. Trends Cell Biol. 2017;27:658–672.
Nusse R, Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell. 2017;169:985–999.
Onstenk W, Sieuwerts AM, Mostert B, et al. Molecular characteristics of circulating tumor cells resemble the liver metastasis more closely than the primary tumor in metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:59058–59069.
Lupp A, Klenk C, Rocken C, Evert M, Mawrin C, Schulz S. Immunohistochemical identification of the PTHR1 parathyroid hormone receptor in normal and neoplastic human tissues. Eur J Endocrinol. 2010;162:979–986.
Teraoku H, Morine Y, Ikemoto T, et al. Role of thrombospondin-1 expression in colorectal liver metastasis and its molecular mechanism. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2016;23:565–573.
Acknowledgment
This study is supported by Grants from Public Welfare Foundation of Liaoning Province (No. 2015005002), Fund for Scientific Research of The First Hospital of China Medical University (FHCMU-FSR), and the National Science and Technology Support Program (2015BAI13B07).
Availability of data and materials
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LJW, SLP, SSX, and ZQ participated in the statistical analysis and wrote the manuscript. LJW and LH downloaded and processed the raw data. YY and XCZ conceived the study, participated in its design and coordination, and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Li, H., Sun, L. et al. Epigenetic Alternations of MicroRNAs and DNA Methylation Contribute to Liver Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer. Dig Dis Sci 64, 1523–1534 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-018-5424-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-018-5424-6