Abstract
Background
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is involved in many acute and chronic inflammatory diseases. However, its role in intrahepatic bile duct (IBD) cell damage associated with severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) remains unclear.
Aims
This study was aimed to identify the role of MIF and its underlying mechanisms in SAP complicated by IBD cell damage.
Methods
Forty-eight specific-pathogen-free male Wistar rats were randomly divided into four groups (N = 12): a sham operation group (SO group) and three SAP model groups (SAP-3h, SAP-6h, and SAP-12h). Immunohistochemistry was used to detect the expression of MIF and P38 in IBD cells. MIF mRNA expression in IBD cells was observed using real-time fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR). In addition, Western blotting was performed to detect the protein expression of P38, phosphorylated P38 (P-P38), nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB p65), and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α). Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays were used to analyze the levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in the IBD of rats.
Results
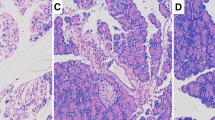
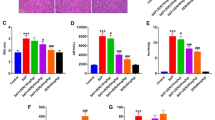
Compared with the SO group, the expression of MIF in the IBD was significantly upregulated both at mRNA and at protein levels in the SAP group. Besides, the protein expression levels of P38, P-P38, NF-κB, p65, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in the IBD in rats were also significantly increased in the SAP group and the levels increased gradually as acute pancreatitis progressed (all P < 0.05).
Conclusions
MIF may promote the IBD injury and inflammatory reaction in SAP via activating the P38-MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MIF:
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor
- SAP:
-
Severe acute pancreatitis
- IBD:
-
Intrahepatic bile duct
- SPF:
-
Specific pathogen-free
- SO:
-
Sham operation
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- MODS:
-
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
- MOF:
-
Multiple organ failure
- SIRS:
-
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome
- ARDS:
-
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
- AP:
-
Acute pancreatitis
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- ICAM:
-
Intercellular adhesion molecule
- VCAM:
-
Vascular cell adhesion protein
- MCP:
-
Monocyte chemoattractant protein
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- IOD:
-
Integral optical density
- SEM:
-
Standard error of the mean
- OD:
-
Optical density
- PL:
-
Phospholipase
- PAF:
-
Platelet-activating factor
References
Mayer J, Rau B, Gansauge F, et al. Inflammatory mediators in human acute pancreatitis: clinical and pathophysiological implications. Gut. 2000;47:546–552.
Nieminen A, Maksimow M, Mentula P, et al. Circulating cytokines in predicting development of severe acute pancreatitis. Crit Care. 2014;18:R104.
Dambrauskas Z, Giese N, Gulbinas A, et al. Different profiles of cytokine expression during mild and severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:1845–1853.
Barnes MA, McMullen MR, Roychowdhury S, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor contributes to ethanolinduced liver injury by mediating cell injury, steatohepatitis and steatosis. Hepatology. 2013;57:1980–1991.
Larson DF, Horak K. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: controller of systemic inflammation. Crit Care. 2006;10:138–140.
Rahman SH, Menon KV, Holmfield JH, et al. Serum macrophage migration inhibitory factor is an early marker of pancreatic necrosis in acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 2007;245:282–289.
Gao L, Flores C, Fan-Ma S, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in acute lung injury: expression. Biomarker and associations. Transl Res. 2007;150:18–29.
Rahman SH, Menon KV, Holmfield JH, et al. Serum macrophage migration inhibitory factor is an early marker of pancreatic necrosis in acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 2007;245:282–289.
Reid PT, Donnelly SC, Haslett C. Inflammatory predictors for the development of the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Thorax. 1995;50:1023–1026.
Kevill KA, Bhandari V, Kettunen M, et al. A role for macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. J Immunol. 2008;180:601–608.
Donnelly SC, Haslett C, Reid PT, et al. Regulatory role for macrophage migration inhibitory factor in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat Med. 1997;3:320–323.
Adamali H, Armstrong ME, McLaughlin AM, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor enzymatic activity, lung inflammation, and cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;186:162–169.
Payen D, Lukaszewicz AC, Legrand M, et al. A multicentre study of acute kidney injury in severe sepsis and septic shock: association with inflammatory phenotype and HLA genotype. PLoS One. 2012;7:e35838.
Lehmann LE, Book M, Hartmann W, et al. A MIF haplotype is associated with the outcome of patients with severe sepsis: a case control study. J Transl Med. 2009;7:100.
Dambrauskas Z, Giese N, Gulbinas A, et al. Different profiles of cytokine expression during mild and severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:1845–1853.
Aeberli D, Yang Y, Mansell A, et al. Endogenous macrophage migration inhibitory factor modulates glucocorticoid sensitivity in macrophages via effects on MAP kinase phosphatase-1 and p38 MAP kinase. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:974–981.
Ishiguro Y, Ohkawara T, Sakuraba H, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor has a proinflammatory activity via the p38 pathway in glucocorticoid-resistant ulcerative colitis. Clin Immunol. 2006;120:335–341.
Erik T, Deborah EW, Isaac S. Dominant negative p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase expression inhibits NF-kappaB activation in AR42J cells. Pancreatology. 2010;10:119–128.
Cuzzocrea S, Malleo G, Genovese T, et al. Effects of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibition on the development of cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in mice. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:2811–2821.
Schmidt J, Rattner DW, Lewandrowski K, et al. A better model of acute pancreatitis for evaluating therapy. Ann Surg. 1992;215:44–56.
Suzuki S, Toledo-Pereyra LH, Rodriguez FJ, et al. Neutrophil infiltration as an important factor in liver ischemia and reperfusion injury. Modulating effects of FK506 and cyclosporine. Transplantation. 1993;5:1265–1272.
Ono K, Han J. The p38 signal transduction pathway: activation and function. Cell Signal. 2000;12:1–13.
Lee JC, Laydon JT, Mcdonnell PC, et al. A protein kinase involved in the regulation of inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis. Nature. 1994;372:739–746.
Raingeaud J, Gupta S, Rogers JS, et al. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and environmental stress cause p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by dual phosphorylation on tyrosine and threonine. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:7420–7426.
Saccani S, Pantano S, Natoli G. p38-Dependent marking of inflammatory genes for increased NF-kappa B recruitment. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:69–75.
Kefaloyianni E, Gaitanaki C, Beis I. ERK1/2 and p38-MAPK signalling pathways, through MSK1, are involved in NF-kappaB transactivation during oxidative stress in skeletal myoblasts. Cell Signal. 2006;18:2238–2251.
Szabo G, Romics LJ, Frendl G. Liver in sepsis and systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Clin Liver Dis. 2002;6:1045–1066.
Takahashi K, Koga K, Linge HM, et al. Macrophage CD74 contributes to MIF-induced pulmonary inflammation. Respir Res. 2009;10:33.
Mazzon E, Impellizzeri D, Di Paola R, et al. Effects of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway inhibition on the development of cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in mice. Pancreas. 2012;41:560–570.
Amin MA, Haas CS, Zhu K, et al. Migration inhibitory factor up-regulates vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 via Src, PI3 kinase, and NFkappaB. Blood. 2006;107:2252–2261.
Paszt A, Eder K, Szabolcs A, et al. Effects of glucocorticoid agonist and antagonist on the pathogenesis of l-arginine-induced acute pancreatitis in rat. Pancreas. 2008;36:369–376.
Murr MM, Yang J, Fier A, et al. Pancreatic elastase induces liver injury by activating cytokine production within Kupffer cells via nuclear factor-Kappa B. J Gastrointest Surg. 2002;6:474–480.
Murr MM, Yang J, Fier A, et al. Regulation of Kupffer cell TNF gene expression during experimental acute pancreatitis: the role of p38-MAPK, ERK1/2, SAPK/JNK, and NF-kappaB. J Gastrointest Surg. 2003;7:20–25.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank professor Mingxia Fan, the director of experiment animal central of Renmin hospital of Wuhan university, for whose technical assistance and contribute to animal feeding and model making, and specimen collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Zhao, KL., Hu, WJ. et al. Macrophage Migration Inhibitor Promoted the Intrahepatic Bile Duct Injury in Rats with Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci 64, 759–772 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-018-5379-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-018-5379-7