Abstract
Background
miR-30a expression is down-regulated and regulates tumor suppressors in various cancers.
Aim
We investigated the mechanisms underlying the biological role of miR-30a in CRC.
Methods
MicroRNA, mRNA, and protein expression were analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR and Western blot. The migration and invasion abilities of CRC were determined by wound healing assay, and trans-well migration and invasion. A luciferase reporter assay was used to confirm the targets of miR-30a.
Results
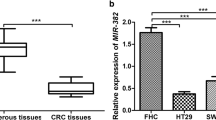
miR-30a expression was significantly down-regulated in CRC tissues and in CRC tissue with lymph node metastasis compared to CRC tissue without metastasis. Overexpression of miR-30a suppressed migration and invasion through insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) in CRC cells. miR-30a suppresses IGF1R protein expression and inhibits β-catenin or p-AKT and increases E-cadherin expression. The IGF1R expression level is also up-regulated in CRC tumors and inversely correlated with miR-30a in CRC specimens.
Conclusions
miR-30a functions as a tumor-suppressive miRNA, which may provide a therapeutic strategy for metastasis of CRC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee JM, Lee JH, Roh MS, et al. The prognostic significance of fascin expression in colorectal carcinoma. Intest Res. 2010;8:117–125.
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108.
Haggar FA, Boushey RP. Colorectal cancer epidemiology: incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2009;22:191–197.
Kopfstein L, Christofori G. Metastasis: cell-autonomous mechanisms versus contributions by the tumor microenvironment. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006;63:449–468.
Ambros V, Lee RC, Lavanway A, Williams PT, Jewell D. MicroRNAs and other tiny endogenous RNAs in C. elegans. Curr Biol. 2003;13:807–818.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297.
Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:597–610.
Price C, Chen J. MicroRNAs in cancer biology and therapy: current Status and Perspectives. Genes Dis. 2014;1:53–63.
William KKW, Joseph JYS. MicroRNA dysregulations in gastrointestinal cancers: pathophysiological and clinical perspectives. Intest Res. 2012;10:324–331.
Liu M, Huang F, Zhang D, et al. Heterochromatin protein HP1gamma promotes colorectal cancer progression and is regulated by miR-30a. Cancer Res. 2015;75:4593–4604.
Tang R, Liang L, Luo D, et al. Downregulation of MiR-30a is associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:2514–2520.
Fu J, Xu X, Kang L, et al. miR-30a suppresses breast cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting Eya2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;445:314–319.
Liu Z, Chen L, Zhang X, et al. RUNX3 regulates vimentin expression via miR-30a during epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2014;18:610–623.
Wen XP, Ma HL, Zhao LY, Zhang W, Dang CX. MiR-30a suppresses non-small cell lung cancer progression through AKT signaling pathway by targeting IGF1R. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2015;61:78–85.
Guo F, Chen H, Chang J, Zhang L. Mutation R273H confers p53 a stimulating effect on the IGF-1R-AKT pathway via miR-30a suppression in breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;78:335–341.
Xie M, Qin H, Luo Q, et al. MicroRNA-30a regulates cell proliferation and tumor growth of colorectal cancer by targeting CD73. BMC Cancer. 2017;17:305.
Liu L, Meng T, Wang QS et al. Association of Beclin-1 and microRNA-30a expression with the severity and treatment response of colorectal cancer. Genet Mol Res. 2016. doi:10.4238/gmr.15027704.
Zhong M, Bian Z, Wu Z. miR-30a suppresses cell migration and invasion through downregulation of PIK3CD in colorectal carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem.. 2013;31:209–218.
Wei W, Yang Y, Cai J, et al. MiR-30a-5p suppresses tumor metastasis of human colorectal cancer by targeting ITGB3. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39:1165–1176.
Shen H, Xing C, Cui K, et al. MicroRNA-30a attenuates mutant KRAS-driven colorectal tumorigenesis via direct suppression of ME1. Cell Death Differ. 2017;24:1253–1262.
Park YR, Kim SL, Lee MR, et al. MicroRNA-30a-5p (miR-30a) regulates cell motility and EMT by directly targeting oncogenic TM4SF1 in colorectal cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017. doi:10.1007/s00432-017-2440-4.
Cao H, Xu E, Liu H, Wan L, Lai M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer metastasis: a system review. Pathol Res Pract. 2015;211:557–569.
Zhou JJ, Zheng S, Sun LF, Zheng L. MicroRNA regulation network in colorectal cancer metastasis. World J Biol Chem. 2014;5:301–307.
Bouyssou JM, Manier S, Huynh D, et al. Regulation of microRNAs in cancer metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1845:255–265.
Hartog H, Wesseling J, Boezen HM, van der Graaf WT. The insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in cancer: old focus, new future. Eur J Cancer. 2007;43:1895–1904.
Davies M, Gupta S, Goldspink G, Winslet M. The insulin-like growth factor system and colorectal cancer: clinical and experimental evidence. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2006;21:201–208.
Vanamala J, Reddivari L, Radhakrishnan S, Tarver C. Resveratrol suppresses IGF-1 induced human colon cancer cell proliferation and elevates apoptosis via suppression of IGF-1R/Wnt and activation of p53 signaling pathways. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:238.
Hassan AB, Macaulay VM. The insulin-like growth factor system as a therapeutic target in colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2002;13:349–356.
Zhang QY, Wang L, Song ZY, Qu XJ. Knockdown of type I insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibits human colorectal cancer cell growth and downstream PI3 K/Akt, WNT/beta-catenin signal pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015;73:12–18.
Knowlden JM, Jones HE, Barrow D, et al. Insulin receptor substrate-1 involvement in epidermal growth factor receptor and insulin-like growth factor receptor signalling: implication for Gefitinib (‘Iressa’) response and resistance. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008;111:79–91.
Li B, Ge L, Li M, Wang L, Li Z. miR-448 suppresses proliferation and invasion by regulating IGF1R in colorectal cancer cells. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8:3013–3022.
Su J, Liang H, Yao W, et al. MiR-143 and MiR-145 regulate IGF1R to suppress cell proliferation in colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 2014;9:e114420.
Acknowledgments
This project is supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning (NRF-2015R1D1A3A01016026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YCL carried out the molecular genetic studies and drafted the manuscript. YRP participated in the sequenced alignment and drafted the manuscript. SLK helped to draft the Materials and methods, STL preformed the statistical analysis. SWK conceived of the study and coordination and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval
The human sample and clinical data used in this study were provided by the Biobank of Chonbuk National University Hospital, a member of the Korea Biobank Network, which is supported by the Ministry of Health, Welfare, and Family Affairs. This work was supported by Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Chonbuk National University-Biomedical Research Institute of Chonbuk National University Hospital (IRB No; CUH-2016-04-018-002).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y.C., Park, Y.R., Kim, S.L. et al. MicroRNA-30a Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Metastasis Through Down-Regulation of Type I Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor. Dig Dis Sci 62, 3040–3049 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4763-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4763-z