Abstract
Background
Endoscopic bilateral self-expandable metallic stent (SEMS) placement for malignant hilar biliary obstructions (MHBOs) is technically demanding, and a second SEMS insertion is particularly challenging. A simultaneous side-by-side (SBS) placement technique using a thinner delivery system may mitigate these issues.
Aims
We aimed to examine the feasibility and efficacy of simultaneous SBS SEMS placement for treating MHBOs using a novel SEMS that has a 5.7-Fr ultra-thin delivery system.
Methods
Thirty-four patients with MHBOs underwent SBS SEMS placement between 2010 and 2016. We divided the patient cohort into those who underwent sequential (conventional) SBS placement between 2010 and 2014 (sequential group) and those who underwent simultaneous SBS placement between 2015 and 2016 (simultaneous group), and compared the groups with respect to the clinical outcomes.
Results
The technical success rates were 71% (12/17) and 100% (17/17) in the sequential and simultaneous groups, respectively, a difference that was significant (P = .045). The median procedure time was significantly shorter in the simultaneous group (22 min) than in the sequential group (52 min) (P = .017). There were no significant group differences in the time to recurrent biliary obstruction (sequential group: 113 days; simultaneous group: 140 days) or other adverse event rates (sequential group: 12%; simultaneous group: 12%).
Conclusions
Simultaneous SBS placement using the novel 5.7-Fr SEMS delivery system may be more straightforward and have a higher success rate compared to that with sequential SBS placement. This new method may be useful for bilateral stenting to treat MHBOs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sawas T, Al Halabi S, Parsi MA, Vargo JJ. Self-expandable metal stents versus plastic stents for malignant biliary obstruction: a meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;82:256–267.
Almadi MA, Barkun A, Martel M. Plastic vs. self-expandable metal stents for palliation in malignant biliary obstruction: a series of meta-analyses. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112:260–273.
Kato H, Tsutsumi K, Kawamoto H, Okada H. Current status of endoscopic biliary drainage for unresectable malignant hilar biliary structures. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;7:1032–1038.
Kawakami H, Itoi T, Kuwatani M, Kawakubo K, Kubota Y, Sakamoto N. Technical tips and troubleshooting of endoscopic biliary drainage for unresectable malignant hilar biliary obstruction. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2015;22:E12–E21.
Moon JH, Rerknimitr R, Kogure H, Nakai Y, Isayama H. Topic controversies in the endoscopic management of malignant hilar strictures using metal stent: side-by-side versus stent-in-stent techniques. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2015;22:650–656.
Chennat J, Waxman I. Initial performance profile of a new 6F self-expanding metal stent for palliation of malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72:632–636.
Law R, Baron TH. Bilateral metal stents for hilar biliary obstruction using a 6Fr delivery system: outcomes following bilateral and side-by-side stent deployment. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58:2667–2672.
Kawakubo K, Kawakami H, Kuwatani M, et al. Single-step simultaneous side-by-side placement of a self-expandable metallic stent with a 6-Fr delivery system for unresectable malignant hilar biliary obstruction: a feasibility study. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2015;22:151–155.
Bismuth H, Castaing D, Traynor O. Resection or palliation: priority of surgery in the treatment of hilar cancer. World J Surg. 1988;12:39–47.
Isayama H, Hamada T, Yasuda I, et al. TOKYO criteria 2014 for transpapillary biliary stenting. Dig Endosc. 2015;27:259–264.
Mukai T, Yasuda I, Nakashima M, et al. Metallic stents are more efficacious than plastic stents in unresectable malignant hilar biliary strictures: a randomized controlled trial. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2013;20:214–222.
Vienne A, Hobeika E, Gouya H, et al. Prediction of drainage effectiveness during endoscopic stenting of malignant hilar strictures: the role of liver volume assessment. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72:728–735.
Lee TH, Moon JH, Park SH. Bilateral metallic stenting in malignant hilar obstruction. Clin Endosc. 2014;47:440–446.
Naitoh I, Hayashi K, Nakazawa T, et al. Side-by-side versus stent-in-stent deployment in bilateral endoscopic metal stenting for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Dig Dis Sci. 2012;57:3279–3285.
Kim KM, Lee KH, Chung YH, et al. A comparison of bilateral stenting methods for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Hepatogastroenterology. 2012;59:341–346.
Kogure H, Isayama H, Nakai Y, et al. High single-session success rate of endoscopic bilateral stent-in-stent placement with modified large cell Niti-S stents for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Dig Endosc. 2014;26:93–99.
Lee TH, Park DH, Lee SS, et al. Technical feasibility and revision efficacy of the sequential deployment of endoscopic bilateral side-by-side metal stents for malignant hilar biliary strictures: a multicenter prospective study. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58:547–555.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
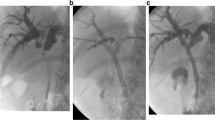
Sequential side-by-side placement of self-expandable metallic stents for high-grade malignant hilar biliary obstruction. After inserting 2 guidewires into the left and right intrahepatic bile ducts, the first stent was inserted and placed in the right hepatic duct. Next, the second stent was inserted and placed in the left hepatic duct alongside the first stent over the other guidewire. (MPG 33610 kb)
Simultaneous side-by-side self-expandable metallic stent placement for high-grade malignant hilar biliary obstruction. After inserting 2 guidewires into the left and right intrahepatic bile ducts, 2 5.7-Fr delivery systems were simultaneously inserted over each guidewire through the duodenoscope’s 4.2-mm working channel. Next, 2 stents were simultaneously placed in a side-by-side configuration, aligning the distal stent ends above the duodenal papilla. (MPG 41932 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, T., Ishii, N., Kobayashi, Y. et al. Simultaneous Versus Sequential Side-by-Side Bilateral Metal Stent Placement for Malignant Hilar Biliary Obstructions. Dig Dis Sci 62, 2542–2549 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4691-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4691-y