Abstract
Background and Aim
Population-based endoscopic studies of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis are limited in the world. This study was aiming to describe features of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis in a representative sample of the adult in Shanghai, China.
Methods
As part of a large epidemiological study, 3,600 individuals (aged 18–80 years) were randomly selected in Shanghai, China. They were asked to undergo endoscopy and have at least four esophageal biopsies taken from 0.5 cm above the Z-line and any abnormal areas. Any eosinophil infiltration of the epithelium was defined as esophageal eosinophilia. Eosinophilic esophagitis was defined as ≥15 eosinophils/high-power field in esophageal biopsies.
Results
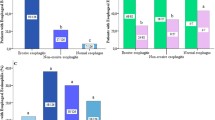
A total of 1,030 individuals accepted to have endoscopy and 1,021 individuals with biopsy results were suitable for analysis. Esophageal eosinophilia was present in 67 subjects (6.6 %). Eosinophilic esophagitis was present in four cases (0.4 %). No significant association was found between the presence of esophageal eosinophilia and reflux esophagitis, Barrett’s esophagus, symptom-defined gastroesophageal reflux disease or H. pylori infection. Most individuals with esophageal eosinophilia (80.6 %) did not have any of the upper gastrointestinal symptoms.
Conclusions
Esophageal eosinophilia was present in nearly 6.6 % of the general adult population of China; 0.4 % had eosinophilic esophagitis. Most of individuals with esophageal eosinophilia were asymptomatic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rothenberg ME, Hogan SP. The eosinophil. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:147–174.
Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Collins MH, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: a systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1342–1363.
Furuta K, Adachi K, Kowari K, et al. A Japanese case of eosinophilic esophagitis. J Gastroenterol. 2006;41:706–710.
Straumann A, Beglinger C. Eosinophilic esophagitis: the endoscopist’s enigma. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;63:13–15.
Landres RT, Kuster GG, Strum WB. Eosinophilic esophagitis in a patient with vigorous achalasia. Gastroenterology. 1978;74:1298–1301.
Dellon ES, Aderoju A, Woosley JT, Sandler RS, Shaheen NJ. Variability in diagnostic criteria for eosinophilic esophagitis: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:2300–2313.
Spergel JM, Book WM, Mays E, et al. Variation in prevalence, diagnostic criteria, and initial management options for eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases in the United States. JPGN. 2011;52:300–306.
Kapel RC, Miller JK, Torres C, Aksoy S, Lash R, Katzka DA. Eosinophilic esophagitis: a prevalent disease in the United States that affects all age groups. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:1316–1321.
Furuta GT, Straumann A. Review article: the pathogenesis and management of eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24:173–182.
Noel RJ, Putnam PE, Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic esophagitis. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:940–941.
Straumann A, Simon HU. Eosinophilic esophagitis: escalating epidemiology? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;115:418–419.
Blanchard C, Wang N, Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic esophagitis: pathogenesis, genetics, and therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;118:1054–1059.
Noel RJ, Tipnis NA. Eosinophilic esophagitis—a mimic of GERD. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2006;70:1147–1153.
Ronkainen J, Talley NJ, Aro P, et al. Prevalence of oesophageal eosinophils and eosinophilic oesophagitis in adults: the population-based Kalixanda study. Gut. 2007;56:615–620.
Cohen MS, Kaufman AB, Palazzo JP, Nevin D, Dimarino AJ Jr, Cohen S. An audit of endoscopic complications in adult eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;5:1149–1153.
Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:3 e26–20 e26; quiz 21–22.
Ferguson DD, Foxx-Orenstein AE. Eosinophilic esophagitis: an update. Dis Esophagus. 2007;20:2–8.
Lu HC, Lu CL, Chang FY. Eosinophilic esophagitis in an asymptomatic Chinese. J Chin Med Assoc. 2008;71:362–364.
Lee B, Park H, Yoon H, Kim HK, Kim HS. Three cases of eosinophilic esophagitis with dysphagia as a chief complaint Korean. J Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;36:145–149.
Attwood SE. Eosinophils and gut dysmotility. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;17:891–892.
Yan X, Wang R, Zhao Y, et al. Systematic investigation of gastrointestinal diseases in China (SILC): validation of survey methodology. BMC Gastroenterol. 2009;9:86.
Shaw MJ, Talley NJ, Beebe TJ, et al. Initial validation of a diagnostic questionnaire for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:52–57.
Cao Y, Yan X, Ma XQ, et al. Validation of a survey methodology for gastroesophageal reflux disease in China. BMC Gastroenterol. 2008;8:37.
Storskrubb T, Aro P, Ronkainen J, et al. Serum biomarkers provide an accurate method for diagnosis of atrophic gastritis in a general population: the Kalixanda study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2008;43:1448–1455.
Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, Dent J, Jones R. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:1900–1920; quiz 1943.
Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR, et al. Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut. 1999;45:172–180.
Sharma P, Dent J, Armstrong D, et al. The development and validation of an endoscopic grading system for Barrett’s esophagus: the Prague C & M criteria. Gastroenterology. 2006;131:1392–1399.
Avidan B, Sonnenberg A, Schnell TG, Sontag SJ. Hiatal hernia and acid reflux frequency predict presence and length of Barrett’s esophagus. Dig Dis Sci. 2002;47:256–264.
Drossman DA, Corazziari E, Talley N, Thompson WG, Whitehead WE. Rome II: a multinational consensus document on functional gastrointestinal disorders. Gut. 1999;45:1–81.
WHO. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet. 2004;363:157–163.
China statistical yearbook. http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2008/indexeh.htm.
Chang F, Anderson S. Clinical and pathological features of eosinophilic oesophagitis: a review. Pathology. 2008;40:3–8.
DeBrosse CW, Collins MH, Buckmeier Butz BK, et al. Identification, epidemiology, and chronicity of pediatric esophageal eosinophilia, 1982–1999. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;126:112–119.
Shi YN, Sun SJ, Xiong LS, Cao QH, Cui Y, Chen MH. Prevalence, clinical manifestations and endoscopic features of eosinophilic esophagitis: a pathological review in China. J Dig Dis. 2012;13:304–309.
Remedios M, Campbell C, Jones DM, Kerlin P. Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults: clinical, endoscopic, histologic findings, and response to treatment with fluticasone propionate. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;63:3–12.
Sgouros SN, Bergele C, Mantides A. Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults: a systematic review. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;18:211–217.
Fox VL, Nurko S, Furuta GT. Eosinophilic esophagitis: it’s not just kid’s stuff. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;56:260–270.
Attwood SE, Smyrk TC, Demeester TR, Jones JB. Esophageal eosinophilia with dysphagia. A distinct clinicopathologic syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 1993;38:109–116.
Mukkada V, Atkins D, Furuta GT. Uncertain association of Barrett’s esophagus with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6:832; author reply 832–833.
Francalanci P, De Angelis P, Minnei F, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis and Barrett’s esophagus: an occasional association or an overlap disease? Digestion. 2008;77:16–19.
Wolfsen HC, Hemminger LL, Achem SR. Eosinophilic esophagitis and Barrett’s esophagus with dysplasia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;5:A18.
Mukkada V, Atkins D, Furuta GT. Letter to the editors: uncertain association of Barrett’s esophagus with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6:832–833.
Dellon ES, Peery AF, Shaheen NJ, et al. Inverse association of esophageal eosinophilia with Helicobacter pylori based on analysis of a US pathology database. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:1586–1592.
Prasad GA, Talley NJ, Romero Y, et al. Prevalence and predictive factors of eosinophilic esophagitis in patients presenting with dysphagia: a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:2627–2632.
Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Hirano I, Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Katzka DA. ACG clinical guideline: evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:679–692; quiz 693.
Dellon ES. Diagnostics of eosinophilic esophagitis: clinical, endoscopic, and histologic pitfalls. Dig Dis (Basel, Switzerland). 2014;32:48–53.
Wang D, He Y, Li Y, et al. Dietary patterns and hypertension among Chinese adults: a nationally representative cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2011;11:925.
Acknowledgments
The study, which is part of the SILC study, was funded by AstraZeneca R&D, Mölndal, Sweden, and the program of the Key Discipline Construction of Public Health of Shanghai. We thank the respondents who gave their time and effort to participate in this study.
Conflict of interest
Xiuqiang Ma, Qin Xu, Yanling Zheng, Yanfang Zhao, Jian Lu, Rui Wang, Zhaoshen Li, and Duowu Zou declare that they have no conflict of interest. Jia He has served as the director of the Department of Health Statistics, Second Military Medical University and has received research funding from AstraZeneca.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xiuqiang Ma, Qin Xu, Yanling Zheng and Yanfang Zhao have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, X., Xu, Q., Zheng, Y. et al. Prevalence of Esophageal Eosinophilia and Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Adults: A Population-Based Endoscopic Study in Shanghai, China. Dig Dis Sci 60, 1716–1723 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-014-3512-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-014-3512-9