Abstract
Background
Both angiotensin (Ang)-II and endothelin-1 (ET-1) are involved in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are considered a key effector of liver fibrosis.
Aims
To explore the effect of Ang-II on ET-1 expression in cultured human HSCs and the underlying mechanisms.
Methods
Human HSCs were treated with Ang-II in different concentrations (0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, or 10 nM) for different lengths of time (0.5, 1, 2, 4, or 6 h) with or without transcription inhibitor actinomycin D, Ang-II type 1 (AT1) receptor blocker losartan, AT2 receptor blocker PD123177, or different kinase inhibitors.
Results
Ang-II increased the ET-1 mRNA level in a statistically significant dose- and time-dependent manner within 4 h, which led to dose-dependent up-regulation of the ET-1 protein level. Actinomycin D (1 mg/ml), losartan (50 μM), and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase inhibitor LY294002 (50 μM) abolished the promoting effect of Ang-II on ET-1 expression. Ang-II (10 nM) significantly increased the expression of α-smooth muscle actin and type I collagen in HSCs, which was abolished by losartan, LY294002, ET A receptor blocker BQ123, and ET-1 siRNA, but not PD123177 and ET B receptor blocker BQ788.
Conclusions
Ang-II induces ET-1 expression in human HSCs via the AT1 receptor by the PI3 K/Akt signaling pathway. The ET-1/ET A receptor axis could mediate the promoting effects of Ang-II on HSCs’ transdifferentiation into myofibroblast-like cells. This is the first evidence of crosstalk between the Ang-II/AT1 axis and the ET-1 system in regard to the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bataller R, Brenner DA. Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:209–218.
Arthur MJ. Reversibility of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis following treatment for hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:1525–1528.
Lim YS, Kim WR. The global impact of hepatic fibrosis and end-stage liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2008;12:733–746.
Munshi MK, Uddin MN, Glaser SS. The role of the renin-angiotensin system in liver fibrosis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2011;236:557–566.
Nabeshima Y, Tazuma S, Kanno K, et al. Anti-fibrogenic function of angiotensin II type 2 receptor in CCl4-induced liver fibrosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;346:658–664.
Bataller R, Sancho-Bru P, Gine`s P, Brenner DA. Liver fibrogenesis: a new role for the renin-angiotensin system. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005;7:1346–1355.
Yang L, Bataller R, Dulyx J, et al. Attenuated hepatic inflammation and fibrosis in angiotensin type 1a receptor deficient mice. J Hepatol. 2005;43:317–323.
Bataller R, Gines P, Nicolas JM, et al. Angiotensin II induces contraction and proliferation of human hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology. 2000;118:1149–1156.
Rockey DC. Vascular mediators in the injured liver. Hepatology. 2003;37:4–12.
Pinzani M, Milani S, De Franco R, et al. Endothelin 1 is overexpressed in human cirrhotic liver and exerts multiple effects on activated hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology. 1996;110:534–548.
Rockey DC, Fouassier L, Chung JJ, et al. Cellular localization of endothelin-1 and increased production in liver injury in the rat: potential for autocrine and paracrine effects on stellate cells. Hepatology. 1998;27:472–480.
Li J, Kuruba R, Wilson A, Gao X, Zhang Y, Li S. Inhibition of endothelin-1-mediated contraction of hepatic stellate cells by FXR ligand. PLoS One. 2010;5:e13955.
Saward L, Zahradka P. Angiotensin II activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1997;81:249–257.
Yano N, Suzuki D, Endoh M, Zhao TC, Padbury JF, Tseng YT. A novel phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent pathway for angiotensin II/AT-1 receptor-mediated induction of collagen synthesis in MES-13 mesangial cells. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:18819–18830.
Tian B, Liu J, Bitterman P, Bache RJ. Angiotensin II modulates nitric oxide-induced cardiac fibroblast apoptosis by activation of AKT/PKB. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003;285:H1105–H1112.
Kim YJ, Koo TY, Yang WS, et al. Activation of spleen tyrosine kinase is required for TNF-α-induced endothelin-1 upregulation in human aortic endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 2012;586:818–826.
Carpino G, Morini S, Ginanni Corradini S, et al. Alpha-SMA expression in hepatic stellate cells and quantitative analysis of hepatic fibrosis in cirrhosis and in recurrent chronic hepatitis after liver transplantation. Dig Liver Dis. 2005;37:349–356.
Williams EJ, Benyon RC, Trim N, et al. Relaxin inhibits effective collagen deposition by cultured hepatic stellate cells and decreases rat liver fibrosis in vivo. Gut. 2001;49:577–583.
Bataller R, Brenner DA. Activated hepatic stellate cells as a target for the treatment of liver fibrosis. Semin Liver Dis. 2001;21:437–451.
Bataller R, Sancho-Bru P, Ginès P, et al. Activated human hepatic stellate cells express the renin-angiotensin system and synthesize angiotensin II. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:117–125.
Schneider AW, Kalk JF, Klein CP. Effect of losartan, an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, on portal pressure in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1999;29:334–339.
Rockey DC, Chung JJ. Endothelin antagonism in experimental hepatic fibrosis. Implications for endothelin in the pathogenesis of wound healing. J Clin Invest. 1996;98:1381–1388.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10620_2013_2685_MOESM1_ESM.tif
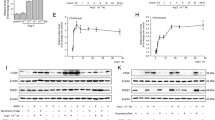
Supplementary Fig. S1. Western blot analysis of endothelin-1 (ET-1) expression in human hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) treated with ET-1 siRNA. a Human HScs transfected with control siRNA or ET-1 siRNA were treated with or without angiotensin (Ang)-II (10 nM) for 4 hours. Twenty-four hours later, cell lysates were subject to western blot analyses for ΕΤ-1 expression. Lysates from human Hscs transfected with control siRNA were used as a control (lane 1). Lane 2 ET-1 siRNA; lane 3 Ang-II (10 nM)+control siRNA; lane 4 Ang-II (10 nM)+ET-1 siRNA. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) blotting was used as a loading control. b ΕΤ-1 and GAPDH blots were measured by densitometry. The density of the ΕΤ−1 blot was normalized against that of GAPDH to obtain a relative density, which was expressed as fold changes to that of control cells (designated as 1). *P < 0.05 compared with control cells. (TIFF 122 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, C., Miao, X., Li, J. et al. Angiotensin II Induces Endothelin-1 Expression in Human Hepatic Stellate Cells. Dig Dis Sci 58, 2542–2549 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-013-2685-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-013-2685-y