Abstract
Background
Barrier function is essential for the maintenance of normal intestinal function. Dysregulation of the intestinal barrier underlies a wide range of disorders.
Aim
Previously, we found that sodium butyrate (NaB) decreased the molecular permeability of intestinal barrier in vivo model, but the mechanism by which NaB facilitated the tightness of tight junctions (TJs) in small intestinal epithelium needed further studies.
Methods
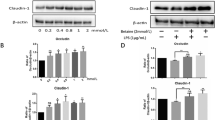
In vitro culture of the cdx2-IEC monolayer was used to mimic barrier function. The TJs were assessed by transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) and paracellular flux of fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated dextran 40,000 (FD-40), Western blot, Q-RT-PCR, and immunofluorescence. Promoter and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays were also done to analyze the Claudin-1 gene.
Results
NaB decreased FD-40 flux, increased TEER and TJ protein Claudin-1 expression, induced ZO-1 and Occludin redistribution in cellular membrane, and reversed the damage effect after calcium (Ca2+) switch assay. Silencing Claudin-1 prevented protective function of NaB from enhancing intestinal barrier integrity. Further studies demonstrated that NaB increased Claudin-1 transcription by facilitating the interaction between transcription factor SP1 and a specific motif within the promoter region of Claudin-1. This SP1 binding motif was located upstream of the coding region (−138 to −76 bp) and indispensable for the transcription of Claudin-1 following NaB treatment. ChIP assay confirmed the association between SP1 and Claudin-1 promoter, and the elimination of the SP1 binding site by point mutation resulted in a significant loss of Claudin-1 transcription after NaB dealing.
Conclusions
NaB enhanced intestinal barrier function through increasing Claudin-1 transcription via facilitating the association between SP1 and Claudin-1 promoter.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Turner JR. Molecular basis of epithelial barrier regulation: from basic mechanisms to clinical application. Am J Pathol. 2006;169:1901–1909.
Shin K, Fogg VC, Margolis B. Tight junctions and cell polarity. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:207–235.
Matter K, Aijaz S, Tsapara A, Balda MS. Mammalian tight junctions in the regulation of epithelial differentiation and proliferation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17:453–458.
Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM. The molecular physiology of tight junction pores. Physiology. 2004;19:331–338.
Bansal V, Costantini T, Kroll L, et al. Traumatic brain injury and intestinal dysfunction: uncovering the neuro-enteric axis. J Neurotrauma. 2009;26:1353–1359.
Costantini TW, Loomis WH, Putnam JG, et al. Burn-induced gut barrier injury is attenuated by phosphodiesterase inhibition: effects on tight junction structural proteins. Shock. 2009;31:416–422.
Hollander D. Intestinal permeability, leaky gut, and intestinal disorders. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 1999;1:410–416.
Hsueh W, Caplan MS, Tan X, MacKendrick W, Gonzalez-Crussi F. Necrotizing enterocolitis of the newborn: pathogenetic concepts in perspective. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 1998;1:2–16.
Hamer HM, Jonkers D, Venema K, Vanhoutvin S, Troost FJ, Brummer RJ. Review article: the role of butyrate on colonic function. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;27:104–119.
Suh E, Traber PG. An intestine-specific homeobox gene regulates proliferation and differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16:619–625.
Puthia MK, Sio SW, Lu J, Tan KS. Blastocystis ratti induces contact-independent apoptosis, F-actin rearrangement, and barrier function disruption in IEC-6 cells. Infect Immun. 2006;74:4114–4123.
Cox DS, Raje S, Gao H, Salama NN, Eddington ND. Enhanced permeability of molecular weight markers and poorly bioavailable compounds across Caco-2 cell monolayers using the absorption enhancer, zonula occludens toxin. Pharm Res. 2002;19:1680–1688.
Dhawan P, Singh AB, Deane NG, et al. Claudin-1 regulates cellular transformation and metastatic behavior in colon cancer. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:1765–1776.
Dufresne J, Cyr DG. Activation of an SP binding site is crucial for the expression of Claudin 1 in rat epididymal principal cells. Biol Reprod. 2007;76:825–832.
Newmark HL, Lupton JR, Young CW. Butyrate as a differentiating agent: pharmacokinetics, analogues and current status. Cancer Lett. 1994;78:1–5.
Smiricky-Tjardes MR, Grieshop CM, Flickinger EA, Bauer LL, Fahey GC Jr. Dietary galactooligosaccharides affect ileal and total-tract nutrient digestibility, ileal and fecal bacterial concentrations, and ileal fermentative characteristics of growing pigs. J Anim Sci. 2003;81:2535–2545.
De Preter V, Geboes KP, Bulteel V, et al. Kinetics of butyrate metabolism in the normal colon and in ulcerative colitis: the effects of substrate concentration and carnitine on the β-oxidation pathway. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011;34:526–532.
Furuse M. Molecular basis of the core structure of tight junctions. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010;2:a002907.
Kim SO, Choi BT, Choi IW, et al. Anti-invasive activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors via the induction of Egr-1 and the modulation of tight junction-related proteins in human hepatocarcinoma cells. BMB Rep. 2009;42:655–660.
Bordin M, D’Atri F, Guillemot L, Citi S. Histone deacetylase inhibitors up-regulate the expression of tight junction proteins. Mol Cancer Res. 2004;2:692–701.
Harten SK, Shukla D, Barod R, et al. Regulation of renal epithelial tight junctions by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene involves occludin and Claudin 1 and is independent of E-cadherin. Mol Biol Cell. 2009;20:1089–1101.
Krishnan M, Singh AB, Smith JJ, et al. HDAC inhibitors regulate Claudin-1 expression in colon cancer cells through modulation of mRNA stability. Oncogene. 2010;29:305–312.
Furuse M, Fujita K, Hiiragi T, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S. Claudin-1 and -2: novel integral membrane proteins localizing at tight junctions with no sequence similarity to occludin. J Cell Biol. 1998;141:1539–1550.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Professor Xian Wang and Associate Professor Ming-Jiang Xu for offering laboratory and technical assistance on several assays, Min-ji Wei for HPLC assay, Professor Qiang Zhang for detection of TEER, and Elizabeth T. Chang for the language assistance. This work was funded by National natural science foundation of China, Number 31040041.
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, HB., Wang, PY., Wang, X. et al. Butyrate Enhances Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function via Up-Regulation of Tight Junction Protein Claudin-1 Transcription. Dig Dis Sci 57, 3126–3135 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2259-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2259-4