Abstract
Background
Although treatment of acute liver failure has been improved significantly recently, the survival rate of acute liver failure is only 5–20%. Therefore, prevention and treatment of acute liver failure are still urgent issues in the field of liver disease.
Aims
It has been demonstrated that ulinastatin could attenuate acute injury of internal organs from endotoxin. This study evaluates whether ulinastatin can prevent and/or attenuate acute liver failure induced by the combination of lipopolysaccharide and d-galactosamine (LPS/d-gal).
Methods
Sprague–Dawley rats were employed to induce acute liver failure by injection of LPS/d-gal. The liver function, inflammatory factors, oxidative stress index, and hepatic histopathological alteration were examined in the rats with and without ulinastatin treatment.
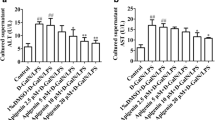
Results
In rats treated with LPS/d-gal, there were increases in the levels of ALT and AST in the serum and levels of malondialdehyde and inducible nitric oxide synthase in liver tissues. Moreover, the levels of antioxidants such as superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase were reduced in the liver. Furthermore, inflammatory factors (TNF-alpha and IL-6) and apoptotic enzyme (caspase-3) were increased in the respective serum and liver of rats treated with LPS/d-gal. However, pre-treatment of ulinastatin significantly reversed all of these parameters in the rats that received LPS/d-gal alone.
Conclusions
The finding in this study suggests that ulinastatin could be a potential agent for prevention and treatment of acute liver injury induced by LPS/d-gal.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim SH, Heo JH, Kim YS, Kang SS, Choi JS, Lee SM. Protective effect of daidzin against d-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatic failure in mice. Phytother Res. 2008;23:701–706.
Kaur G, Tirkey N, Bharrhan S, Chanana V, Rishi P, Chopra K. Inhibition of oxidative stress and cytokine activity by curcumin in amelioration of endotoxin-induced experimental hepatoxicity in rodents. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006;145:313–321.
Ravikumar V, Shivashangari KS, Devaki T. Effect of Tridax procumbens on liver antioxidant defense system during lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatitis in d-galactosamine sensitised rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 2005;269:131–136.
Mehanna A, Vitorino DC, Panis C, Blanco EE, Pinge-Filho P, Martins-Pinge MC. Cardiovascular and pulmonary effects of NOS inhibition in endotoxemic conscious rats subjected to swimming training. Life Sci. 2007;81:1301–1308.
Huang Y, Xie K, Zhang J, Dang Y, Qiong Z. Prospective clinical and experimental studies on the cardioprotective effect of ulinastatin following severe burns. Burns. 2008;34:674–680.
Cao ZL, Okazaki Y, Naito K, Ueno T, Natsuaki M, Itoh T. Ulinastatin attenuates reperfusion injury in the isolated blood-perfused rabbit heart. Ann Thorac Surg. 2000;69:1121–1126.
Gurtu V, Kain SR, Zhang G. Fluorometric and colorimetric detection of caspase activity associated with apoptosis. Anal Biochem. 1997;251:98–102.
Koizumi R, Kanai H, Maezawa A, Kanda T, Nojima Y, Naruse T. Therapeutic effects of ulinastatin on experimental crescentic glomerulonephritis in rats. Nephron. 2000;84:347–353.
Sakaguchi T, Nakamura S, Suzuki S, et al. Participation of platelet-activating factor in the lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury in partially hepatectomized rats. Hepatology. 1999;30:959–967.
Aihara T, Shiraishi M, Hiroyasu S, et al. Ulinastatin: a protease inhibitor, attenuates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by downregulating TNF-alpha in the liver. Transpl Proc. 1998;30:3732–3734.
Banerjee A, Russell WK, Jayaraman A, Ramaiah SK. Identification of proteins to predict the molecular basis for the observed gender susceptibility in a rat model of alcoholic steatohepatitis by 2-D gel proteomics. Proteomics. 2008;8:4327–4337.
Jaeschke H, Farhood A, Bautista AP, Spolarics Z, Spitzer JJ. Complement activates Kupffer cells and neutrophils during reperfusion after hepatic ischemia. Am J Physiol. 1993;264:G801–G809.
El-Beshbishy HA. Aqueous garlic extract attenuates hepatitis and oxidative stress induced by galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide in rats. Phytother Res. 2008;22:1372–1379.
Qiu RL, Zhao X, Tang YT, Yu FM, Hu PJ. Antioxidative response to Cd in a newly discovered cadmium hyperaccumulator, Arabis paniculata F. Chemosphere. 2008;74:6–12.
Hayashi Y, Abe M, Murai A, et al. Comparison of effects of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitors on plasma nitrite/nitrate levels and tissue NOS activity in septic organs. Microbiol Immunol. 2005;49:139–147.
Billiar TR, Curran RD, West MA, Hofmann K, Simmons RL. Kupffer cell cytotoxicity to hepatocytes in coculture requires l-arginine. Arch Surg. 1989;124:1416–1420. Discussion 1420–1411.
Hsieh CH, Frink M, Hsieh YC, et al. The role of MIP-1 alpha in the development of systemic inflammatory response and organ injury following trauma hemorrhage. J Immunol. 2008;181:2806–2812.
Suzuki S, Nakamura S, Serizawa A, et al. Role of Kupffer cells and the spleen in modulation of endotoxin-induced liver injury after partial hepatectomy. Hepatology. 1996;24:219–225.
Mookerjee RP, Sen S, Davies NA, Hodges SJ, Williams R, Jalan R. Tumour necrosis factor alpha is an important mediator of portal and systemic haemodynamic derangements in alcoholic hepatitis. Gut. 2003;52:1182–1187.
Yang BS, Ma YJ, Wang Y, et al. Protective effect and mechanism of stronger neo-minophagen C against fulminant hepatic failure. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:462–466.
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, et al. Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 1997;91:479–489.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China (Y207464).
Conflict of interest
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Ethical approval
The animal protocol in this experiment was approved by the committee of the Tongji University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, J., Chen, YP., Wan, R. et al. Protective Effects of Ulinastatin on Acute Liver Failure Induced by Lipopolysaccharide/d-Galactosamine. Dig Dis Sci 57, 399–404 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-011-1927-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-011-1927-0