Abstract
Introduction
This study investigated the expression of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and interleukin-4 (IL-4) in the esophageal biopsies from patients with reflux esophagitis (RE) and Barrett’s esophagus (BE) and their relationships with endoscopic grading and histologic grading.
Methods
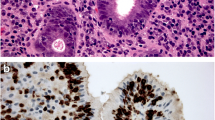
Ninety individuals were recruited (30 RE, 30 BE, and 30 normal control) and underwent upper gastrointestinal endoscopy with esophageal biopsy. Immunohistochemistry was used to semi-quantitatively detect the expression of IFN-γ and IL-4 in the specimens.
Results
IFN-γ was overexpressed in BE and RE compared with the control (P < 0.01), whereas IL-4 was up-regulated in BE compared with RE and control (P < 0.01). A positive correlation between the level of IFN-γ and the endoscopic grading (r = 0.509, P < 0.01) and histologic grading of RE (r = 0.493, P < 0.01) was observed.
Conclusions
Th1 and Th2 immune responses play different roles in the development of RE and BE. Th1 immune response is the major pathway for RE development, whereas both Th1 and Th2 immune responses are implicated in BE pathogenesis. The expression of IFN-γ is associated with the endoscopic and histologic grading of RE.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shapiro M, Green C, Faybush EM, et al. The extent of oesophageal acid exposure overlap among the different gastro-oesophageal reflux disease groups. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;23:321–329.
Shalauta MD, Saad R. Barrett’s esophagus. Am Fam Physician. 2004;69:2113–2118.
Fitzgerald RC, Onwuegbusi BA, Bajaj-Elliott M, et al. Diversity in the oesophageal phenotypic response to gastro-oesophageal reflux: immunological determinants. Gut. 2002;50:451–459.
Moons LM, Kusters JG, Bultman E, et al. Barrett’s oesophagus is characterized by a predominantly humoral inflammatory response. J Pathol. 2005;207:269–276.
El Chartouni C, Rehli M. Comprehensive analysis of TLR4-induced transcriptional responses in interleukin 4-primed mouse macrophages. Immunobiology. 2010;215:780–787.
Teloni R, Giannoni F, Rossi P, et al. Interleukin-4 inhibits cyclo-oxygenase-2 expression and prostaglandin E production by human mature dendritic cells. Immunology. 2007;120:83–89.
Schroder K, Hertzog PJ, Ravasi T, et al. Interferon-gamma: an overview of signals, mechanisms and functions. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;75:163–189.
Choi P, Reiser H. IL-4: role in disease and regulation of production. Clin Exp Immunol. 1998;113:317–319.
Borghaei RC, Rawlings PL Jr, Mochan E. Interleukin-4 suppression of interleukin-1-induced transcription of collagenase (MMP-1) and stromelysin 1 (MMP-3) in human synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41:1398–1406.
Corcoran ML, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Brown PD, et al. Interleukin 4 inhibition of prostaglandin E2 synthesis blocks interstitial collagenase and 92-kDa type IV collagenase/gelatinase production by human monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:515–519.
Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR, et al. Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut. 1999;45:172–180.
Ismail-Beigi F, Horton PF, Pope CE II. Histological consequences of gastroesophageal reflux in man. Gastroenterology. 1970;58:163–174.
Lin Y, Buckhaults PJ, Lee JR, et al. Association of the actin-binding protein transgelin with lymph node metastasis in human colorectal cancer. Neoplasia. 2009;11:864–873.
Isomoto H, Wang A, Mizuta Y, et al. Elevated levels of chemokines in esophageal mucosa of patients with reflux esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:551–556.
O’Riordan JM, Abdel-latif MM, Ravi N, et al. Proinflammatory cytokine and nuclear factor kappa-B expression along the inflammation-metaplasia-dysplasia-adenocarcinoma sequence in the esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100:1257–1264.
Yamaguchi T, Yoshida N, Tomatsuri N, et al. Cytokine-induced neutrophil accumulation in the pathogenesis of acute reflux esophagitis in rats. Int J Mol Med. 2005;16:71–77.
Yoshida N, Uchiyama K, Kuroda M, et al. Interleukin-8 expression in the esophageal mucosa of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2004;39:816–822.
Fitzgerald RC, Abdalla S, Onwuegbusi BA, et al. Inflammatory gradient in Barrett’s oesophagus: implications for disease complications. Gut. 2002;51:316–322.
Farthing MJ, Fitzgerald R, Zhang ZW. Acid, helicobacter and immunity: a new paradigm for oesophagogastric cancer. J Physiol Paris. 2001;95:423–427.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Janssen Grant of China (YQZ, JRC01) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (YL, 30901782).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ying-Qiang Zhong and Ying Lin authors are contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, YQ., Lin, Y. & Xu, Z. Expression of IFN-γ and IL-4 in the Esophageal Mucosa of Patients with Reflux Esophagitis and Barrett’s Esophagus and Their Relationship with Endoscopic and Histologic Grading. Dig Dis Sci 56, 2865–2870 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-011-1696-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-011-1696-9