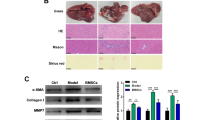
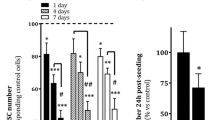
Abstract
Liver cirrhosis is characterized by hepatic dysfunction, with extensive accumulation of fibrous tissue in the liver. Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are the major source of fibrillar matrix proteins and play an important role in the progress of liver cirrhosis. In our study, the growth of HSCs is inhibited by bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs). The inhibition is irreversible and is followed by apoptosis. The effect of BMSCs on the apoptosis of HSCs is possibly via the JNK pathway activated by nerve growth factor (NGF) and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) secreted by BMSCs. Meanwhile, the apoptosis effect is enhanced by transforming growth factor-β blocking.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bortolotti F, Guido M (2007) Reversal of liver cirrhosis: a desirable clinical outcome and its pathogenic background. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 44:401–406
Desmet VJ, Roskams T (2004) Cirrhosis reversal: a duel between dogma and myth. J Hepatol 40:860–867
Kumar M, Sarin SK (2007) Is cirrhosis of the liver reversible? Indian J Pediatr 74:393–399
Cao Q, Mak KM, Ren C, Lieber CS (2004) Leptin stimulates tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in human hepatic stellate cells: respective roles of the JAK/STAT and JAK-mediated H2O2-dependant MAPK pathways. J Biol Chem 279:4292–4304
Elsharkawy AM, Oakley F, Mann DA (2005) The role and regulation of hepatic stellate cell apoptosis in reversal of liver fibrosis. Apoptosis 10:927–939
Asai K, Tamakawa S, Yamamoto M, Yoshie M, Tokusashi Y, Yaginuma Y, Kasai S, Ogawa S (2006) Activated hepatic stellate cells overexpress p75NTR after partial hepatectomy and undergo apoptosis on nerve growth factor stimulation. Liver Int 26:595–603
Yasuda H, Imai E, Shiota A, Fujise N, Morinaga T, Higashio K (1996) Antifibrogenic effect of a deletion variant of hepatocyte growth factor on liver fibrosis in rats. Hepatology 24:636–642
Saile B, Matthes N, El Armouche H, Neubauer K, Ramadori G (2001) The bcl, NfkappaB and p53/p21WAF1 systems are involved in spontaneous apoptosis and in the anti-apoptotic effect of TGF-beta or TNF-alpha on activated hepatic stellate cells. Eur J Cell Biol 80:554–561
Derubeis AR, Cancedda R (2004) Bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) in bone engineering: limitations and recent advances. Ann Biomed Eng 32:160–165
Hung SC, Chen NJ, Hsieh SL, Li H, Ma HL, Lo WH (2002) Isolation and characterization of size-sieved stem cells from human bone marrow. Stem Cells 20:249–258
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S, Marshak DR (1999) Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284:143–147
Stagg J (2007) Immune regulation by mesenchymal stem cells: two sides to the coin. Tissue Antigens 69:1–9
Rasmusson I (2006) Immune modulation by mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res 312:2169–2179
Fang B, Shi M, Liao L, Yang S, Liu Y, Zhao RC (2004) Systemic infusion of FLK1(+) mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Transplantation 78:83–88
Sakaida I, Terai S, Yamamoto N, Aoyama K, Ishikawa T, Nishina H, Okita K (2004) Transplantation of bone marrow cells reduces CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Hepatology 40:1304–1311
Luk JM, Wang PP, Lee CK, Wang JH, Fan ST (2005) Hepatic potential of bone marrow stromal cells: development of in vitro co-culture and intra-portal transplantation models. J Immunol Methods 305:39–47
Li H, Yu B, Zhang Y, Pan Z, Xu W, Li H (2006) Jagged1 protein enhances the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 341:320–325
Greenwel P, Schwartz M, Rosas M, Peyrol S, Grimaud JA, Rojkind M (1991) Characterization of fat-storing cell lines derived from normal and CCl4-cirrhotic livers. Differences in the production of interleukin-6. Lab Invest 65:644–653
Kawada N (2006) Human hepatic stellate cells are resistant to apoptosis: implications for human fibrogenic liver disease. Gut 55:1073–1084
Nykjaer A, Willnow TE, Petersen CM (2005) p75NTR—live or let die. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15:49–57
Aznar S, Lacal JC (2001) Rho signals to cell growth and apoptosis. Cancer Lett 165:1–10
Kim WH, Matsumoto K, Bessho K, Nakamura T (2005) Growth inhibition and apoptosis in liver myofibroblasts promoted by hepatocyte growth factor leads to resolution from liver cirrhosis. Am J Pathol 166:1017–1028
Matsumoto K, Tajima H, Okazaki H, Nakamura T (1992) Negative regulation of hepatocyte growth factor gene expression in human lung fibroblasts and leukemic cells by transforming growth factor-beta 1 and glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem 267:24917–24920
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Min Li from the Department of Molecular Physiology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, for revising the manuscript. This research was supported by a grant from the National 15 Hightech project (no. 2004BA745C) and a project of international cooperation (no. WB07C04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lijun Shi and Guozhong Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, L., Li, G., Wang, J. et al. Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Control the Growth of Hepatic Stellate Cells in vitro. Dig Dis Sci 53, 2969–2974 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-008-0227-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-008-0227-9