Abstract
Visceral sensory input is typically poorly localized. We hypothesized that gastric sensory neurons frequently dichotomize, innervating more than one anatomically distinct region and contributing to the poor spatial discrimination.
Methods
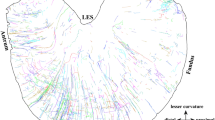
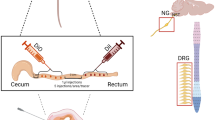
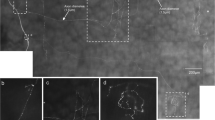
The neurochemical phenotype and projections of gastro-duodenal sensory neurons were determined in adult mice. Choleratoxin B (CTB) coupled to different fluorophors was injected into fundus, corpus, antrum, and/or distal duodenum. Immunoreactivity for TRPV1, neurofilament (N52), calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), presence of isolectin B4 (IB4) and labeling for retrograde labels was determined.
Results
Depending on the distance between injection sites, staining for two retrograde tracers was seen in 6–48% of neurons. Most dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons showed immunoreactivity for TRPV1 and CGRP. In contrast, about half of the gastric nodose ganglion (NG) neurons had TRPV1 immunoreactivity or showed IB4 labeling with only 10% CGRP-positive neurons. N52 immunoreactivity was present in one-fourth of gastroduodenal DRG and NG neurons.
Conclusion
Visceral sensory neurons have neurochemical properties and may project to more than one anatomically distinct area. Neurons with such dichotomizing axons may contribute to the poor ability to localize or discriminate visceral stimuli.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drossman DA, Li Z, Andruzzi E, et al (1993) U.S. householder survey of functional gastrointestinal disorders. Prevalence, sociodemography, and health impact. Digest Dis Sci 38(9):1569–1580
Gebhart GF (1995) Visceral nociception: consequences, modulation and the future. Eur J Anaesth Suppl 10:24–27
Mayer EA, Gebhart GF (1994) Basic and clinical aspects of visceral hyperalgesia. Gastroenterology 107(1):271–293
Tack J, Caenepeel P, Fischler B, Piessevaux H, Janssens J (2001) Symptoms associated with hypersensitivity to gastric distention in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 121(3):526–535
Blackshaw LA, Grundy D (1989) Responses of vagal efferent fibres to stimulation of gastric mechano- and chemoreceptors in the anaesthetized ferret. J Autonom Nerv Syst 27:39–45
Ozaki N, Sengupta JN, Gebhart GF (1999) Mechanosensitive properties of gastric vagal afferent fibers in the rat. J Neurophysiol 82(5):2210–2220
Sengupta JN, Kauvar D, Goyal RK (1989) Characteristics of vagal esophageal tension-sensitive afferent fibers in the opossum. J Neurophysiol 61(5):1001–1010
Sengupta JN, Saha JK, Goyal RK (1990) Stimulus-response function studies of esophageal mechanosensitive nociceptors in sympathetic afferents of opossum. J Neurophysiol 64(3):796–812
Ozaki N, Gebhart GF (2001) Characterization of mechanosensitive splanchnic nerve afferent fibers innervating the rat stomach. Am J Physiol 281(6): G1449–G1459
Blackshaw LA, Page AJ, Partosoedarso ER (2000) Acute effects of capsaicin on gastrointestinal vagal afferents. Neuroscience 96(2):407–416
Brierley SM, Jones RCW, Gebhart GF, Blackshaw LA (2004) Splanchnic and pelvic mechanosensory afferents signal different qualities of colonic stimuli in mice. Gastroenterology 127(1):166–178
Page AJ, Blackshaw LA (1998) An in vitro study of the properties of vagal afferent fibres innervating the ferret oesophagus and stomach. J Physiol (Lond) 512(3):907–916
Page AJ, Martin CM, Blackshaw LA (2002) Vagal mechanoreceptors and chemoreceptors in mouse stomach and esophagus. J Neurophysiol 87(4):2095–2103
Berthoud H-R, Lynn PA, Blackshaw LA (2001) Vagal and spinal mechanosensors in the rat stomach and colon have multiple receptive fields. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 280(5):R1371–R1381
Zagorodnyuk VP, Chen BN, Brookes SJH (2001) Intraganglionic laminar endings are mechano-transduction sites of vagal tension receptors in the guinea-pig stomach. J Physiol (Lond) 534(1):255–268
Christianson JA, Traub RJ, Davis BM (2006) Differences in spinal distribution and neurochemical phenotype of colonic afferents in mouse and rat. J Comp Neurol 494:246–259
Malykhina AP, Chao Q, Foreman RD, Akbarali HI (2004) Colonic inflammation increases Na+ currents in bladder sensory neurons. Neuroreport 15:2601–2605
Lawson SN, Crepps B, Perl ER (2002) Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity and afferent receptive properties of dorsal root ganglion neurones in guinea-pigs. J Physiol (Lond) 540(3):989–1002
Orozco OE, Walus L, Sah DWY, Pepinsky RB, Sanicola M (2001) GFRalpha3 is expressed predominantly in nociceptive sensory neurons. Eur J Neurosci 13(11):2177–2182
Stucky CL, Lewin GR (1999) Isolectin B4-positive and -negative nociceptors are functionally distinct. J. Neurosci 19(15):6497–6505
Lawson SN, Waddell PJ (1991) Soma neurofilament immunoreactivity is related to cell size and conduction velocity in rat primary sensory neurons. J Physiol 435:41–63
Wang FB, Powley TL (2000) Topographic inventories of vagal afferents in gastrointestinal muscle. J Comp Neurol 421:302–324
Pakkenberg B, Gundersen HJ (1988) Total number of neurons and glial cells in human brain nuclei estimated by the disector and the fractionator. J Microsc 150(Pt 1):1–20
Orozco OE, Walus L, Sah DWY, Pepinsky RB, Sanicola M (2001) GFRalpha3 is expressed predominantly in nociceptive sensory neurons. Eur J Neurosci 13(11):2177–2182
Sengupta JN, Saha JK, Goyal RK (1992) Differential sensitivity to bradykinin of esophageal distension-sensitive mechanoreceptors in vagal and sympathetic afferents of the opossum. J. Neurophysiol. 68:1053–1067
Ozaki N, Bielefeldt K, Sengupta JN, Gebhart GF (2002) Models of gastric hyperalgesia in the rat. Am J Physiol 283(3):G666–G676
Lamb K, Kang YM, Gebhart GF, Bielefeldt K (2003) Gastric inflammation triggers hypersensitivity to acid in awake rats. Gastroenterology 125:1410–1418
Sharkey KA, Williams RG, Dockray GJ (1984) Sensory substance P innervation of the stomach and pancreas. Gastroenterology 87:914–921
Green T, Dockray GJ (1987) Calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P in afferents to the upper gastrointestinal tract in the rat. Neurosci Lett 76:151–156
Green T, Dockray GJ (1988) Characterization of the peptidergic afferent innervation of the stomach in the rat, mouse and guinea-pig. Neuroscience 25:181–193
Altschuler SM, Bao XR, Bieger D, Hopkins DA, Miselis RR (1989) Viscerotopic representation of the upper alimentary tract in the rat: sensory ganglia and nuclei of the solitary and spinal trigeminal tracts. J Comp Neurol 283:248–268
Bielefeldt K, Zhong F, Koerber HR, Davis BM (2006) Phenotypic characterization of gastric sensory neurons in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 291(5): G987–G997
Phillips RJ, Powley TL (2000) Tension and stretch receptors in gastrointestinal smooth muscle: re-evaluating vagal mechanoreceptor electrophysiology. Brain Res Rev 34(1–2):1–26
Fox EA, Phillips RJ, Martinson FA, Baronowsky EA, Powley TL (2000) Vagal afferent innervation of smooth muscle in the stomach and duodenum of the mouse: morphology and topography. J Comp Neurol 428:558–576
Page AJ, Brierley SM, Martin CM et al (2005) Different contributions of ASIC channels 1a, 2, and 3 in gastrointestinal mechanosensory function. Gut 54:1408–1415
Jones RCW III, Xu L, Gebhart GF (2005) The mechanosensitivity of mouse colon afferent fibers and their sensitization by inflammatory mediators require transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 and acid-sensing ion channel 3. J Neurosci 25(47):10981–10989
Birder LA, Nakamura Y, Kiss S, et al (2002) Altered urinary bladder function in mice lacking the vanilloid receptor TRPV1. Nat Neurosci 5:856–860
Rong W, Hillsley K, Davis JB, Hicks G, Winchester WJ, Grundy D (2004) Jejunal afferent nerve sensitivity in wild-type and TRPV1 knockout mice. J Physiol (Lond) 560(3):867–881
Robinson DR, McNaughton PA, Evans ML, Hicks GA (2004) Characterization of the primary spinal afferent innervation of the mouse colon using retrograde labelling. Neurogastroenterol Motil 16(1):113–124
Dütsch M, Eichhorn U, Wörl J, Wank M, Berthoud H-R, Neuhuber WL (1998) Vagal and spinal afferent innervation of the rat esophagus: a combined retrograde tracing and immunohistochemical study with special emphasis on calcium-binding proteins. J Comp Neurol 398:289–307
Hwang SJ, Min Oh J, Valtschanoff JG (2005) Expression of the vanilloid receptor TRPV1 in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons supports different roles of the receptor in visceral and cutaneous afferents. Brain Res 1047(2):261–266
Kashiba H, Senba E, Ueda Y, Tohyama M (1991) Cell size and cell type analysis of calcitonin gene-related peptide-containing cutaneous and splanchnic sensory neurons in the rat. Peptides 12(1):101–106
Schafers M, Geis C, Svensson CI, Luo ZD, Sommer C (2003) Selective increase of tumour necrosis factor-alpha in injured and spared myelinated primary afferents after chronic constrictive injury of rat sciatic nerve. Eur J Neurosci 17(4):791–804
Koerber HR, Woodbury CJ (2002) Comprehensive phenotyping of sensory neurons using an ex vivo somatosensory system. Physiol Behav 77(4–5):589–594
Su X, Gebhart GF (1998) Mechanosensitive pelvic nerve afferent fibers innervating the colon of the rat are polymodal in character. J Neurophysiol 80(5):2632–2644
Kang Y-M, Bielefeldt K, Gebhart GF (2004) Sensitization of mechanosensitive gastric vagal afferent fibers in the rat by thermal and chemical stimuli and gastric ulcers. J Neurophysiol 91(5):1981–1989
Winston J, Toma H, Shenoy M, Pasricha PJ (2001) Nerve growth factor regulates VR-1 mRNA levels in cultures of adult dorsal root ganglion neurons. Pain 89(2–3):181–186
Moore BA, Stewart TMR, Hill C, Vanner SJ (2002) TNBS ileitis evokes hyperexcitability and changes in ionic membrane properties of nociceptive DRG neurons. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 282(6): G1045–G1051
Zhuo H, Ichikawa H, Helke CJ (1997) Neurochemistry of the nodose ganglion. Prog Neurobiol 52(2):79–107
Ichikawa H, Helke CJ (1999) The coexistence of TrkA with putative transmitter agents and calcium-binding proteins in the vagal and glossopharyngeal sensory neurons of the adult rat. Brain Res 846(2):268–273
Wank M, Neuhuber WL (2001) Local differences in vagal afferent innervation of the rat esophagus are reflected by neurochemical differences at the level of the sensory ganglia and by different brainstem projections. J Comp Neurol 435:41–59
Bergman E, Fundin BT, Ulfhake B (1999) Effects of aging and axotomy on the expression of neurotrophin receptors in primary sensory neurons. J Comp Neurol 410:368–386
Dirajlal S, Pauers LE, Stucky CL (2003) Differential response properties of ib4-positive and -negative unmyelinated sensory neurons to protons and capsaicin. J Neurophysiol 89(1):513–524
Beyak MJ, Ramji N, Krol KM, Kawaja MD, Vanner SJ (2004) Two TTX-resistant Na+ currents in mouse colonic dorsal root ganglia neurons and their role in colitis-induced hyperexcitability. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 287(4): G845–G855
Burgard EC, Niforatos W, van Biesen T, et al (1999) P2X receptor-mediated ionic currents in dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neurophysiol 82(3):1590–1598
Dang K, Bielefeldt K, Lamb K, Gebhart GF (2005) Gastric ulcers evoke hyperexcitability and enhance P2X receptor function in rat gastric sensory neurons. J Neurophysiol 93(6):3112–3119
Prechtl JC, Powley TL (1990) The fibre composition of the abdominal vagus of the rat. Anat Embryol 181:101–115
Yu S, Undem BJ, Kollarik M (2005) Vagal afferent nerves with nociceptive properties in guinea-pig oesophagus. J Physiol (Lond) 563(3):831–842
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, F., Christianson, J.A., Davis, B.M. et al. Dichotomizing Axons in Spinal and Vagal Afferents of the Mouse Stomach. Dig Dis Sci 53, 194–203 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-9843-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-9843-z