Abstract
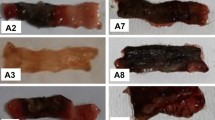
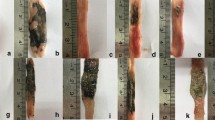
Nitric oxide has been implicated in the pathogenic mechanism of inflammatory bowel disease states. We evaluated indomethacin-induced enteropathy in rats, in relation to the expression of the inducible isoform of NO synthase (iNOS) using aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), its isomer 4-ASA (10 or 50 mg/kg/day, po), and dexamethasone, an iNOS transcription inhibitor (3 mg/kg/day, sc). Enteropathy was induced by indomethacin (7.5 mg/kg/day, sc) for two days and the small intestine was examined for lesions over the next 14 days. Indomethacin-induced small-intestinal ulcer size, mucosal myeloperoxidase activity, iNOS expression and serum nitrite/nitrate levels were maximally increased by day 4 and gradually decreased by day 14. Treatment with 5-ASA, but not 4-ASA, decreased indomethacin-induced ulcer length, myeloperoxidase activity, serum nitrite/nitrate levels and iNOS expression at day 4. Dexamethasone had a greater effect than 5-ASA in reducing myeloperoxidase activity and ulcer length by 26 and 32%, respectively. Dexamethasone also reduced serum nitrate/nitrite and iNOS expression to their basal levels. In conclusion, inhibition of iNOS expression by 5-ASA appears to be associated with diminished intestinal ulceration in indomethacin-induced enteropathy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kitagawa H, Takeder F, Kohei H (1990) Effect of endothelium derived relaxing factor on the gastric lesion induced by HCl in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 253:1133–1137
Lopez-Belmonte J, Whittle BJR, Moncada S (1993) The actions of nitric oxide donors in the prevention of induction of injury to the rat gastric mucosa. Br J Pharmacol 108:73–78
Whittle BJR, Lopez-Belmonte J, Moncada S (1992) Nitric oxide mediates rat mucosal vasodilation induced by intragastric capsaicin. Eur J Pharmacol 218:339–341
Podolsky RS, Grabowski M, Milner R, Ritchie WP, Dempsey DT (1994) Capsaicin-induced gastric hyperemia and protection are NO dependent. J Surg Res 57:438–442
Brown KW, Hanson PJ, Whittle BJR (1922) Nitric oxide donors increase mucus gel thickness in rat stomach. Eur J Pharmacol 223:103–104
Holzer P, Lippe IT, Tabrizi AL, Lenard L Jr, Bartho L (1997) Dual excitatory and inhibitory effect on nitric oxide on peristalsis in the guinea pig intestine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280:154–161
Lyons CR (1995) The role of nitric oxide in inflammation. Adv Immunol 60:323–371
Grisham MB, Jourd’heuil D, Wink DA (1999) Nitric oxide. I. Physiological chemistry of nitric oxide and its metabolites: Implication in inflammation. Am J Physiol 276:G315–G321
Miller MJS, Sandoval M (1999) Nitric Oxide III. A molecular prelude to inflammation. Am J Physiol 276:G795–G799
Rachmilewitz D, Karmeli F, Okon E, Bursztyn M (1995) Experimental colitis is ameliorated by inhibition of nitric oxide synthase activity. Gut 37:247–255
Nandi J, Parasher G, Frenklakh L, Goodman D, Siddiqui T, Oler A, Levine RA (2000) Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOs) in rat intestinal mucosa by indomethacin. Gastroenterology 118:A4290
Kimura H, Miura S, Shigematsu T, Ohkubo N, Tsuzuki Y, Kurose I, Higuchi H, Akiba Y, Hokari R, Hirokawa M, Serizawa H, Ishii H (1997) Increased nitric oxide production and inducible nitric oxide synthase activity in colonic mucosa of patients with active ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Dig Dis Sci 42:1047–1054
Singer II, Kawka DW, Scott S, Weidner JR, Mumford RA, Riehl TE, Stenson WF (1996) Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and nitrotyrosine in colonic epithelium in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 111:871–885
Battarbee HD, Grisham MB, Johnson GG, Zavecz JH (1996) Superior mesenteric artery blood flow and indomethacin-induced intestinal injury and inflammation. Am J Physiol 271:(Gastrointest Liver Physiol 34):G605–G612
Robert A (1975) An intestinal disease produced experimentally by prostaglandin deficiency. Gastroenterology 69:1045–1047
Salvemini D, Misko TP, Masferrer JL, Seibert K, Currie MG, Needleman P (1993) Nitric oxide activates cyclooxygenase enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7240–7244
Santucci L, Fiorucci S, Giansanti M, Buonori PM, DiMatteo FM, Morelli A (1994) Pentoxifylline prevents indomethacin induced acute mucosal damage in rats: role of tumour necrosis factor alpha. Gut 35:909–915
Bertrand V, Guimbund R, Tulliez M, Mauprivez C, Sogni P, Couturier D, Giroud JP, Chaussade S, Chauvelot-Moachon L (1998) Increase in tumor necrosis factor-α production linked to toxicity of indomethacin in the rat small intestine. Br J Pharmacol 124:1385–1394
Saud B, Nandi J, Ong G, Finocchiaro S, Levine RA (2005) Inhibition of TNF-α improves indomethacin-induced enteropathy in rats by modulating iNOS expression. Dig Dis Sci 50:1677–1683
Parasher G, Frenklakh L, Siddiqui T, Nandi J, Levine RA (2001) Nitric oxide inhibitors ameliorate indomethacin-induced enteropathy in rats. Dig Dis Sci 46:2536–2541
Yang Z, Nandi J, Wang J, Bosco G, Gregory M, Chung C, Xie Y, Yang X, Camporesi EM (2006) Hyperbaric oxygenation ameliorates indomethacin-induced enteropathy in rats by modulating TNF- α and IL-1β production. Dig Dis Sci 51:1426–1433
Kennedy M, Wilson L, Szabo C, Salzman AL (1999) 5-aminosalicylic acid inhibits iNOS transcription in human intestinal epithelial cells. Int J Mol Med 4:437–443
Nandi J, Saud B, Palma DT, Levine RA (2003) 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) improves indomethacin (INDO)-induced enteropathy by inhibiting iNOS transcription in rats. FASEB J 17:A659
Grisham MB, Benoit JN, Granger DN (1996) Assessment of leukocyte involvement during ischemia and re-perfusion of intestine. Methods Enzymol 186:729–742
Takahashi S, Fujita T, Yamamoto A (2000) Role of cyclooxygenase-2 in Helicobacter pylori-induced gastritis in Mongolian gerbils. Am J Physiol 279:G791–G798
Wallace JL, Cohen MM (1984) Gastric mucosal protection with chronic mild restraint: Role of endogenous prostaglandins. Am J Physiol 247:G127–G132
Veerabagu MP, Opara EI, Meguid MM, Nandi J, Olar A, Holtzapple PG, Levine RA (1996) Mode of food intake reduction in Lewis rat with indomethacin-induced ulcerative ileitis. Physiol Behav 60:381–387
Chen K, Hirota S, Wasa M, Okada A (1999) Expression of NOS II and its role in experimental small bowel ulceration in rats. Surgery 126:553–561
Tanaka A, Hase S, Miyazawa T, Ohno R, Takeuchi K (2002) Role of cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 and COX-2 inhibition in nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced intestinal damage in rats: relation to various pathogenic events. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303:1248–1254
Konaka A, Nishijima M, Tanaka A, Kunikata T, Kato S, Tekeuchi K (1999) Nitric oxide, superoxide radicals and mast cells in pathogenesis of indomethacin-induced small intestinal lesions in rats. J Physiol Pharmacol 50:25–38
Bjarnasson I, Hayllar J, Mac Pherson AJ, Russel AS (1993) Side effects of nonsteroid antiinflammatory drugs on the small and large intestine in humans. Gastroenterology 104:1832–1847
Yamada T, Deitch E, Specian RD, Perry MA, Sartor RB, Grisham MB (1993) Mechanisms of acute and chronic intestinal inflammation induced by indomethacin. Inflammation 17:641–662
Veerabagu MP, Meguid MM, Olar A, Holtzapple PG, Levine RA (1996) Interavenous nucleosides and nucleotide promote healing of small bowel ulcers in experimental entrocolitis. Dig Dis Sci 41:1452–1457
Whittle BJR, Laszlo F, Evans SM, Moncada S (1995) Induction of nitric oxide synthase and microvascular injury in the rat jejunum provoked by indomethacin. Br J Pharmacol 116:2286–2290
Hori M, Kita M, Torihashi S, Miyamoto S, Ong KJ, Sato K, Ozaki H, Karaki H (2001) Upregulation of iNOS by Cox-2 in muscularis resident macrophage of rat intestine stimulated with LPS. Am J Physiol 280:G930–G938
Takeuchi K, Yokota A, Tanaka A, Takahira Y (2006) Factors involved in upregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase in rat small intestine following administration of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Dig Dis Sci 51(7):1250–1259
Kim S, Huri D, Snyder S (2005) Inducible nitric oxide synthase binds, s-nitrosylates, and activates cyclooxygenase-2. Science 310:1966–1970
Wahl C, Liptay S, Adler G, Schmid R (1998) Sulfasalazine: a potent and specific inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B. J Clin Invest 101:1163–1174
Crotty B, Rosenberg WMC, Aronson JK, Jewell DP (1992) Inhibition of binding of interferon-gamma to its receptor by salicylates used in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 33:1353–1357
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nandi, J., Saud, B., Zinkievich, J.M. et al. 5-Aminosalicylic Acid Improves Indomethacin-Induced Enteropathy by Inhibiting iNOS Transcription in Rats. Dig Dis Sci 53, 123–132 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-9832-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-9832-2