Abstract
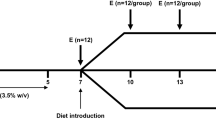
The aim of this study was to assess the effect of polyunsaturated fatty acids supplied in the diet on intestinal mucosa repair in a rat model of protein-energy malnutrition. Rats were fed either a standard semipurified diet or the same diet containing lactose as the only source of carbohydrate to cause protein-energy malnutrition. Diarrhea was induced within 24 h and was maintained for 2 weeks, after which both groups of rats were fed for 1 week either the standard diet or the standard diet supplemented with different sources of fatty acids, such as olive oil (OO), fish oil (FO), and purified phospholipids from pig brain (BPL). The lactose-enriched diet caused loss of enterocyte microvilli, lymphocyte infiltration, supranuclear cytoplasmic vesiculation, decreased number of goblet cells, low-density enlarged mitochondria, and less cristae. The FO diet improved the pathology score according to the histological and ultrastructural analysis, with an increased number of goblet cells, ratio of microvilli length to crypt depth, and percentage of intraepithelial lymphocytes compared to those found in rats with protein-energy malnutrition. We previously reported that chronic diarrhea depletes the antioxidant defense in rat intestine; we now show that both, the FO and the BPL diets, increase GSH levels in colon and that some antioxidant enzyme activities vary according to the source of fatty acids, with higher catalase and superoxide dismutase by the FO diet in jejunum, increased catalase by the BPL diet in jejunum, and elevated glutathione peroxidase by the OO diet in colon. The fatty acid profile of intestinal mucosa reflects the source of fat in the diet, with the lowest ratio of n-6/n-3 for rats fed the FO diet. These results suggest that dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids, particularly those in the n-3 series, may play an important role in intestinal repair in chronic diarrhea due to protein-energy malnutrition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kelly DA: Nutrition and growth in patients with chronic liver disease. Indian J Pediatr 62:533–544, 1995
Deitch EA, Berg R: Bacterial translocation from the gut: a mechanism of infection. J Burn Care Rehabil 8:475–482, 1987
Butzner JD, Gall DG: Impact of refeeding on intestinal development and function in infant rabbits subjected to protein-energy malnutrition. Pediatr Res 27:245–251, 1990
Butzner JD, Butler DG, Miniats OP, Hamilton JR: Impact of chronic protein-calorie malnutrition on small intestinal repair after acute viral enteritis: a study in gnotobiotic piglets. Pediatr Res 19:476–481, 1985
Ott M, Wegner A, Caspary WF, Lembcke B: Intestinal absorption and malnutrition in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Z Gastroenterol 31:661–665, 1993
Heel KA, Kong SE, McCauley RD, Erber WN, Hall JC: The effect of minimum luminal nutrition on mucosal cellularity and immunity of the gut. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 13:1015–1019, 1998
Nieto N, Lopez-Pedrosa JM, Mesa MD, Torres MI, Fernandez MI, Rios A, Suarez MD, Gil A: Chronic diarrhea impairs intestinal antioxidant defense system in rats at weaning. Dig Dis Sci 45:2044–2050, 2000
Nieto N, Torres MI, Fernandez MI, Giron MD, Rios A, Suarez MD, Gil A: Experimental ulcerative colitis impairs antioxidant defense system in rat intestine. Dig Dis Sci 45:1820–1827, 2000
Deitch EA, Taylor M, Grisham M, Ma L, Bridges W, Berg R: Endotoxin induces bacterial translocation and increases xanthine oxidase activity. J Trauma 29:1679–1683, 1989
Deitch EA, Ma WJ, Ma L, Berg R, Specian RD: Endotoxin-induced bacterial translocation: a study of mechanisms. Surgery 106:292–299; discussion 299–300, 1989
Rana SV, Gupta D, Katyal R, Singh K: Mild-to-moderate malnutrition alters glutathione, gamma-glutamyl-transpeptidase and glycine uptake in small intestinal brush-border vesicles of rhesus monkeys. Ann Nutr Metab 45:143–147, 2001
Akimoto Y, Kreppel LK, Hirano H, Hart GW: Localization of the O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase in rat pancreas. Diabetes 48:2407–2413, 1999
Dahm LJ, Jones DP: Secretion of cysteine and glutathione from mucosa to lumen in rat small intestine. Am J Physiol 267:G292–300, 1994
Gilbert HF: Catalysis of thiol/disulfide exchange: single-turnover reduction of protein disulfide-isomerase by glutathione and catalysis of peptide disulfide reduction. Biochemistry 28:7298–7305, 1989
Kelly FJ: Glutathione content of the small intestine: regulation and function. Br J Nutr 69:589-596, 1993
Martensson J, Steinherz R, Jain A, Meister A: Glutathione ester prevents buthionine sulfoximine-induced cataracts and lens epithelial cell damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:8727–8731, 1989
Franco VH, Hotta JK, Jorge SM, dos Santos JE: Plasma fatty acids in children with grade III protein-energy malnutrition in its different clinical forms: marasmus, marasmic kwashiorkor, and kwashiorkor. J Trop Pediatr 45:71–75, 1999
Marin MC, De Tomas ME, Mercuri O, Fernandez A, de Serres CT: Interrelationship between protein-energy malnutrition and essential fatty acid deficiency in nursing infants. Am J Clin Nutr 53:466–468, 1991
Holman RT, Johnson SB, Mercuri O, Itarte HJ, Rodrigo MA, De Tomas ME: Essential fatty acid deficiency in malnourished children. Am J Clin Nutr 34:1534–1539, 1981
Suarez A, Ramirez, MC, Faus, MJ, Gil, A: Dietary long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids influence tissue fatty acid composition in rats at weaning. J Nutr 126:887–897, 1996
Nieto N, Fernandez MI, Torres MI, Rios A, Suarez MD, Gil A: Dietary monounsaturated n-3 and n-6 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids affect cellular antioxidant defense system in rats with experimental ulcerative colitis induced by trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid. Dig Dis Sci 43:2676–2687, 1998
Grisham MB, Benoit JN, Granger DN: Assessment of leukocyte involvement during ischemia and reperfusion of intestine. Methods Enzymol 186:729–742, 1990
Labarca C, Paigen K: A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem 102:344–352, 1980
Tietze F: Enzymic method for quantitative determination of nanogram amounts of total and oxidized glutathione: applications to mammalian blood and other tissues. Anal Biochem 27:502–522, 1969
Carlberg I, Mannervik B: Glutathione reductase. Methods Enzymol 113:484–490, 1985
Habig WH PM, Jakoby WB.: Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139, 1974
Flohe L, Gunzler WA: Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 105:114–121, 1984
Claiborne A, Fridovich I: Purification of the o-dianisidine peroxidase from Escherichia coli B. Physicochemical characterization and analysis of its dual catalatic and peroxidatic activities. J Biol Chem 254:4245–4252, 1979
Paoletti F, Mocali A: Determination of superoxide dismutase activity by purely chemical system based on NAD(P)H oxidation. Methods Enzymol 186:209–220, 1990
Nieto N, Giron MD, Suarez MD, Gil A: Changes in plasma and colonic mucosa fatty acid profiles in rats with ulcerative colitis induced by trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid. Dig Dis Sci 43:2688–2695, 1998
Bai C, Jones DP: GSH transport and GSH-dependent detoxication in small intestine of rats exposed in vivo to hypoxia. Am J Physiol 271:G701–G706, 1996
Aw TY: Biliary glutathione promotes the mucosal metabolism of luminal peroxidized lipids by rat small intestine in vivo. J Clin Invest 94:1218–1225, 1994
Aw TY, Williams MW: Intestinal absorption and lymphatic transport of peroxidized lipids in rats: effect of exogenous GSH. Am J Physiol 263:G665–G672, 1992
Bray TM, Taylor CG: Enhancement of tissue glutathione for antioxidant and immune functions in malnutrition. Biochem Pharmacol 47:2113–2123, 1994
Darmon N, Pelissier MA, Heyman M, Albrecht R, Desjeux JF: Oxidative stress may contribute to the intestinal dysfunction of weanling rats fed a low protein diet. J Nutr 123:1068–1075, 1993
Meister A: Glutathione deficiency produced by inhibition of its synthesis, and its reversal; applications in research and therapy. Pharmacol Ther 51:155–194, 1991
Ogasawara T, Ohnhaus EE, Hoensch HP: Glutathione and its related enzymes in the small intestinal mucosa of rats: effects of starvation and diet. Res Exp Med (Berl) 189:195–204, 1989
Jahoor F, Wykes LJ, Reeds PJ, Henry JF, del Rosario MP, Frazer ME: Protein-deficient pigs cannot maintain reduced glutathione homeostasis when subjected to the stress of inflammation. J Nutr 125:1462–1472, 1995
Cornell JS, Meister A: Glutathione and gamma-glutamyl cycle enzymes in crypt and villus tip cells of rat jejunal mucosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:420–422, 1976
Lopez-Pedrosa J, Torres, MI, Fernandez, MI, Rios, A, Gil, A: Severe malnutrition alters lipid composition and fatty acid profile of small intestine in newborn piglets. J Nutr 128:224–233, 1998
Lopez-Pedrosa J, Ramirez, M, Torres, MI, Gil, A: Dietary phospholipids rich in long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids improve the repair of small intestine in previously malnourished piglets. J Nutr 129:1149–1155, 1999
Doshi M, Watanabe, S, Niimoto, T, Kawashima, H, Ishikura, Y, Kiso, Y, Hamazaki, T: Effect of dietary enrichment with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) or n-9 PUFA on arachidonate metabolism in vivo and experimentally induced inflammation in mice. Biol Pharm Bull 27:319–323, 2004
Stulnig T: Immunomodulation by polyunsaturated fatty acids: mechanisms and effects. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 132:310–321, 2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by Grant CI1-CT91-0078 from the European Union.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nieto, N., Mesa, M.D., López-Pedrosa, J.M. et al. Contribution of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids to Intestinal Repair in Protein-Energy Malnutrition. Dig Dis Sci 52, 1485–1496 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-8100-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-8100-9