Abstract
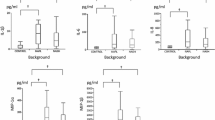
Pentoxifylline (POF) is a new candidate for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Its effects on the cytokine production in patients with NASH are not completely understood. This study was designed to investigate the effect of POF on TNF-α production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) in patients with NASH. After preliminary experiments in healthy control subjects to determine the range of POF concentration to be used in NASH patients, PBMCs from patients with NASH (n = 13) were cultured in the presence of lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 100 ng/ml) and various concentrations of POF for 24 hr. Concentrations of TNF-α in culture supernatants were measured by ELISA and the transcriptional activity was determined by RT-PCR. As dictated by the results of our preliminary study in PBMC from healthy control subjects, we treated LPS stimulated PBMCs from NASH patients with 10, 100, and 500 μg/ml of POF. Stimulation of PBMCs from NASH patients with LPS resulted in a strong up-regulation of TNF-α production from median 355.9 (interquartile range, 206.7–463.5) pg/ml to 1,670 pg/ml (interquartile range, 1,121–2,414) pg/ml. In this LPS-stimulated culture system, POF caused a dose-dependent suppression of TNF-α levels (P < 0.001, ANOVA on ranks for repeated measures). TNF-α levels in culture supernatants decreased to 870.3 (range, 598.3–2,077) pg/ml with 10 μg/ml of POF treatment, and to levels similar to those obtained in baseline unstimulated cultures (133.4 (range, 95.8–1518.5) pg/ml) at 100 μg/ml. At 500 μg/ml, POF suppressed TNF-α production to levels significantly lower than that obtained in unstimulated (baseline) culture supernatants (76.3 (range, 33–94.5) pg/ml; P = 0.001). The mRNA expression was consistent with the effects on protein concentration. Demographic characteristics of the patients, laboratory results, such as AST, ALT, alkaline phosphatase, GGT, and triglyceride levels, and the liver histology did not seem to influence the in vitro TNF-α response of the PBMCs from NASH patients. POF can significantly decrease the LPS-stimulated TNF-α production by PBMCs in NASH patients. Our results support the notion that POF might be a good candidate for the treatment of NASH.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bugianesi E, Leone N, Vanni E, Marchesini G, Brunello F, Carucci P, Musso A, Paolis P, Capussotti L, Salizzoni M, Rizzetto M (2002) Expanding the natural history of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: from cryptogenic cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 123:134–140
Marchesini G, Brizi M, Bianchi G (2001) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. A feature of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 50:1844–1850
Valenti L, Fracanzani AL, Dongiovanni P, Santorelli G, Branchi A, Taioli E, Fiorelli G, Fargion S (2002) Tumor necrosis factor a promoter polymorphisms and insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 122:274–280
Hotamisligil GS, Peraldi P, Budavari A, Ellis R, White MF, Spiegelman BM (1996) IRS-1 mediated inhibition of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity in TNF-a and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Science 371:665–668
Wigg AJ, Roberts-Thomson IC, Dymock RB, McCarthy PJ, Grose RH, Cummins AG (2001) The role of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, intestinal permeability, endotoxaemia, and tumour necrosis factor a in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Gut 48:206–211
Kugelmas M, Hill DB, Vivian B, Marsano L, McClain CJ (2003) Cytokines and NASH: a pilot study of the effects of lifestyle modification and vitamin E. Hepatology 38:413–419
Crespo J, Cayon A, Fernandez-Gil P, Hernandez-Guerra M, Mayorga M, Dominguez-Diez A, Fernandez-Escalante JC, Pons-Romero F (2001) Gene expression of tumor necrosis factor α and TNF-receptors, p55 and p75, in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients. Hepatology 34:1158–1163
Akriviadis E, Botla R, Briggs W, Han S, Reynolds T, Shakil O (2000) Pentoxifylline improves short-term survival in severe acute alcoholic hepatitis: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 119:1637–1648
Satapathy SK, Gang S, Chauhan R, Sakhuja P, Malhotra V, Sharma BC, Sarin SK (2004) Beneficial effects of tumor necrosis factor-α inhibition by pentoxifylline on clinical, biochemical, and metabolic parameters of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 99:1946–1952
Brunt EM, Janney CG, Di Bisceglie AM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Bacon BR (1999) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J Gastroenterol 94:2467–2474
Schandené L, Vandenbussche P, Crusiaux A, Alégre ML, Abramowicz D, Dupont E, et al, (1992) Differential effects of pentoxifylline on the production of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF a) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) by monocytes and T cells. Immunology 76:30–34
Mander T, Hill S, Hughes A, Rawlins P, Clark C, Gammon G, Foxwell B, Moore M (1997) Differential effects on the TNF-α production by pharmacological agents with varying molecular sites of action. Int J Immunopharmac 19:451–462
Anonymous (2002) Nonalcoholic steatosis and steatohepatitis IV. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease abnormalities in macrophage function and cytokines. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 282:G1–G5
Windmeier C, Gressner AM (1997) Pharmacological aspects of pentoxifylline with emphasis on its inhibitory actions on hepatic fibrogenesis. Gen Pharmac 29:181–196
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by a grant from Marmara University Research Fund (HEA-076/051201).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duman, D.G., Ozdemir, F., Birben, E. et al. Effects of Pentoxifylline on TNF-α Production by Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Dig Dis Sci 52, 2520–2524 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9723-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9723-y