Abstract
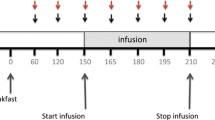
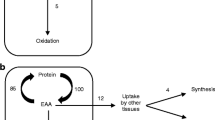
Arginine is a conditionally essential amino acid and exerts anabolic effects. We studied the effects of enteral arginine on whole-body and duodenal protein metabolism. Eight healthy fasted volunteers received randomly a 5-hr enteral infusion of either arginine (Arg; 20 g) or an isonitrogenous amino acid mixture (AA) and an IV infusion of [13C]leucine. Duodenal biopsies were performed. Whole-body protein turnover and duodenal protein synthesis (FSR) were calculated from GC/MS-assessed enrichment. The mRNA levels for major components of proteolytic pathways, ubiquitin, cathepsin D, and m-calpain, were evaluated by RT-PCR. Results were compared using paired Wilcoxon test. Endogenous, oxidative, and nonoxidative leucine fluxes were not different after Arg and AA infusions, respectively. Duodenal mucosal protein FSR (71% ± 26% vs 81% ± 30%/day) and mRNA levels of ubiquitin, cathepsin D, and m-calpain were also similar after Arg and AA infusions. We conclude that in healthy subjects, arginine infusion exerts no effect on whole-body and duodenal protein metabolism. Whether arginine might specifically affect these parameters in catabolic or inflammatory situations remains to be determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nieves C Jr, Langkamp-Henken B (2002) Arginine and immunity: a unique perspective. Biomed Pharmacother 56:471–482
de Jonge WJ, Kwikkers KL, te Velde AA, van Deventer SJ, Nolte MA, Mebius RE, Ruijter JM, Lamers MC, Lamers WH (2002) Arginine deficiency affects early B cell maturation and lymphoid organ development in transgenic mice. J Clin Invest 110:1539–1548
Wu G, Morris SM Jr (1998) Arginine metabolism: nitric oxide and beyond. Biochem J 336:1–17
Lecleire S, Coëffier M, Leblond J, Lemoulan S, Hubert A, Petit A, Ducrotté P, Déchelotte P, Marion R (2005) Modulation of nitric oxide and cytokines production by L-arginine in human gut mucosa. Clin Nutr 24:353–359
Marion R, Coeffier M, Lemoulan S, Gargala G, Ducrotte P, Dechelotte P (2005) L-Arginine modulates CXC chemokines in the human intestinal epithelial cell line HCT-8 by the NO pathway. Biochimie 87:1048–1055
Wu G, Meininger CJ, Knabe DA, Bazer FW, Rhoads JM (2000) Arginine nutrition in development, health and disease. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 3:59–66
Barbul A, Lazarou SA, Efron DT, Wasserkrug HL, Efron G (1990) Arginine enhances wound healing and lymphocyte immune responses in humans. Surgery 108:331–336, discussion 336–337
Di Lorenzo M, Bass J, Krantis A (1995) Use of L-arginine in the treatment of experimental necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg 30:235–240, discussion 240–241
Chung DH, Evers BM, Townsend CM Jr, Huang KF, Herndon DN, Thompson JC (1993) Role of polyamine biosynthesis during gut mucosal adaptation after burn injury. Am J Surg 165:144–149
Minuskin ML, Lavine ME, Ulman EA, Fisher H (1981) Nitrogen retention, muscle creatine and orotic acid excretion in traumatized rats fed arginine and glycine enriched diets. J Nutr 111:1265–1274
Merimee TJ, Lillicrap DA, Rabinowitz D (1965) Effect of arginine on serum-levels of human growth-hormone. Lancet 2:668–670
Woolfson AM, Heatley RV, Allison SP (1979) Insulin to inhibit protein catabolism after injury. N Engl J Med 300:14–17
Takagi K, Tashiro T, Yamamori H, Mashima Y, Nakajima N, Sunaga K (1995) Recombinant human growth hormone and protein metabolism of burned rats and esophagectomized patients. Nutrition 11:22–26
Sitren HS, Fisher H (1977) Nitrogen retention in rats fed on diets enriched with arginine and glycine. 1. Improved N retention after trauma. Br J Nutr 37:195–208
Bruins MJ, Soeters PB, Lamers WH, Deutz NE (2002) L-Arginine supplementation in pigs decreases liver protein turnover and increases hindquarter protein turnover both during and after endotoxemia. Am J Clin Nutr 75:1031–1044
Cui XL, Iwasa M, Iwasa Y, Ohmori Y, Yamamoto A, Maeda H, Kume M, Ogoshi S, Yokoyama A, Sugawara T, Funada T (1999) Effects of dietary arginine supplementation on protein turnover and tissue protein synthesis in scald-burn rats. Nutrition 15:563–569
Leon P, Redmond HP, Stein TP, Shou J, Schluter MD, Kelly C, Lanza-Jacoby S, Daly JM (1991) Arginine supplementation improves histone and acute-phase protein synthesis during gram-negative sepsis in the rat. J Parenter Enteral Nutr 15:503–508
Wakabayashi Y, Yamada E, Yoshida T, Takahashi H (1994) Arginine becomes an essential amino acid after massive resection of rat small intestine. J Biol Chem 269:32667–32671
Adegoke OA, McBurney MI, Samuels SE, Baracos VE (2003) Modulation of intestinal protein synthesis and protease mRNA by luminal and systemic nutrients. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 284:G1017–G1026
Coeffier M, Claeyssens S, Hecketsweiler B, Lavoinne A, Ducrotte P, Dechelotte P (2003) Enteral glutamine stimulates protein synthesis and decreases ubiquitin mRNA level in human gut mucosa. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 285:G266–G273
Bouteloup-Demange C, Boirie Y, Dechelotte P, Gachon P, Beaufrere B (1998) Gut mucosal protein synthesis in fed and fasted humans. Am J Physiol 274:E541–E546
Bouteloup-Demange C, Claeyssens S, Maillot C, Lavoinne A, Lerebours E, Dechelotte P (2000) Effects of enteral glutamine on gut mucosal protein synthesis in healthy humans receiving glucocorticoids. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 278:G677–G681
Claeyssens S, Bouteloup-Demange C, Gachon P, Hecketsweiler B, Lerebours E, Lavoinne A, Déchelotte P (2000) Effect of enteral glutamine on leucine, phenylalanine and glutamine metabolism in hypercortisolemic subjects. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 278:E817–E824
Nakshabendi IM, Downie S, Russell RI, Rennie MJ (1996) Increased rates of duodenal mucosal protein synthesis in vivo in patients with untreated coelia disease. Gut 39:176–179
Rennie MJ, Edwards RH, Halliday D, Matthews DE, Wolman SL, Millward DJ (1982) Muscle protein synthesis measured by stable isotope techniques in man: the effects of feeding and fasting. Clin Sci (Lond) 63:519–523
Gianotti L, Braga M, Nespoli L, Radaelli G, Beneduce A, Di Carlo V (2002) A randomized controlled trial of preoperative oral supplementation with a specialized diet in patients with gastrointestinal cancer. Gastroenterology 12:1763–1770
Ishibashi Y, Hanyu N, Suzuki Y, Yanai S, Tashiro K, Usuba T, Iwabuchi S, Takahashi T, Takada K, Ohkawa K, Urashima M, Yanaga K (2004) Quantitative analysis of free ubiquitin and multi-ubiquitin chain in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett 211:111–117
Lakshmikuttyamma A, Selvakumar P, Kanthan R, Kanthan SC, Sharma RK (2004) Overexpression of m-calpain in human colorectal adenocarcinomas. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13:1604–1609
Welters CF, Dejong CH, Deutz NE, Heineman E (1999) Effects of parenteral arginine supplementation on the intestinal adaptive response after massive small bowel resection in the rat. J Surg Res 85:259–266
Osowska S, Moinard C, Neveux N, Loi C, Cynober L (2004) Citrulline increases arginine pools and restores nitrogen balance after massive intestinal resection. Gut 53:1781–1786
Palmer JP, Benson JW, Walter RM, Ensinck JW (1976) Arginine-stimulated acute phase of insulin and glucagon secretion in diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest 58:565–570
Calbet JA, MacLean DA (2002) Plasma glucagon and insulin responses depend on the rate of appearance of amino acids after ingestion of different protein solutions in humans. J Nutr 132:2174–2182
Paddon-Jones D, Sheffield-Moore M, Zhang XJ, Volpi E, Wolf SE, Aarsland A, Ferrando AA, Wolfe RR (2004) Amino acid ingestion improves muscle protein synthesis in the young and elderly. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 286:E321–E328
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by grants from the Rouen Hospital for Clinical Research (PHRC régional 2002; 02/060 HP) and from Nutrialis MRT 00 p0708. R.M. was supported by a grant from the French-speaking Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (SFNEP). The skillful assistance of Brigitte Maurer (Laboratory of Medical Biochemistry, CHU Rouen) for isotope analysis is gratefully acknowledged. The authors thank the Laboratory of Physiology (Pr. Philippe Denis) for13CO2 analysis, the Hospital Pharmacy for isotope preparations (Pr. Philippe Arnaud, Dr. Nathalie Donnadieu), and the Endoscopy Unit of the Gastroenterology Department (Pr. Eric Lerebours) for helpful assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The first two authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Claeyssens, S., Lecleire, S., Leblond, J. et al. Lack of Effect of Acute Enteral Arginine Infusion on Whole-Body and Intestinal Protein Metabolism in Humans. Dig Dis Sci 52, 1826–1832 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9628-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9628-9