Abstract
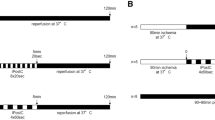
Ischemia and reperfusion (IR) injury of the liver is associated with impaired bile secretion, but the effects of ischemic preconditioning (IPC) and intermittent ischemia (INT) on bile flow are unknown. A rat model of segmental (60%–70%) hepatic ischemia and reperfusion was employed to test the effects of IPC and INT on bile flow. Continuous clamping for 45 min (CC) substantially reduced bile flow, and this did not recover after 60 min of reperfusion. IPC and INT caused a significant recovery of bile flow. The elevation in plasma liver marker enzymes induced by CC was not reduced by IPC and INT. Light microscopy showed mild hepatocyte damage in all groups. In the CC group, the amount of F-actin localized around the bile canaliculi in the ischemic lobes was less than that in the nonischemic lobes, but this difference was not observed in the IPC and INT groups. It is concluded that IPC and INT substantially alleviate the decrease in bile flow induced by ischemia. Bile flow may be useful in the assessment of IR injury.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Selzner N, Rudiger H, Graf R, Clavien PA (2003) Protective strategies against ischemic injury of the liver. Gastroenterology 125:917–936
Ben-Ari Z, Pappo O, Mor E (2003) Intrahepatic cholestasis after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 9:1005–1018
Jaeschke H (2003) Molecular mechanisms of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury and preconditioning. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 284:G15–G26
Teoh NC, Farrell GC (2003) Hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury: pathogenic mechanisms and basis for hepatoprotection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:891–902
Glantzounis G, Salacinski H, Yang W, Davidson B, Seifalian A (2005) The contemporary role of antioxidant therapy in attenuating liver ischemia-reperfusion injury: a review. Liver Transplant 11:1031–1047
Caldwell CC, Okaya T, Martignoni A, Husted T, Schuster R, Lentsch AB (2005) Divergent functions of CD4+T lymphocytes in acute liver inflammation and injury after ischemia/reperfusion. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 289:G969–G976
Nieuwenhuijs V, De Bruijn M, Padbury R, Barritt G (2006) Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury: roles of Ca2+ and other intracellular mediators of impaired bile flow and hepatocyte damage. Dig Dis Sci 51:1087–1102.
Belghiti J, Noun R, Malafosse R, Jagot P, Sauvanet A, Pierangeli F, Marty J, Farges O (1999) Continuous versus intermittant portal triad clamping for liver resection: a controlled study. Ann Surg 229:369–375
Vajdova K, Heinrich S, Tian Y, Graf R, Clavien PA (2004) Ischemic preconditioning and intermittent clamping improve murine hepatic microcirculation and Kupffer cell function after ischemic injury. Liver Transpl 10:520–528
Clavien PA, Selzner M, Rudiger HA, Graf R, Kadry Z, Rousson V, Jochum W (2003) A prospective randomized study in 100 consecutive patients undergoing major liver resection with versus without ischemic preconditioning. Ann Surg 238:843–850
Clavien PA, Yadav S, Sindram D, Bentley RC (2000) Protective effects of ischemic preconditioning for liver resection performed under inflow occlusion in humans. Ann Surg 232:155–162
Iwasaki Y, Tagaya N, Hattori Y, Yamaguchi K, Kubota K (2002) Protective effect of ischemic preconditioning against intermittent warm-ischemia-induced liver injury. J Surg Res 107:82–92
Nuzzo G, Giuliante F, Vellone M, De Cosmo G, Ardito F, Murazio M, D’Acapito F, Giovannini I (2004) Pedicle clamping with ischemic preconditioning in liver resection. Liver Transpl 10:S53–S57
Rudiger HA, Kang KJ, Sindram D, Riehle HM, Clavien PA (2002) Comparison of ischemic preconditioning and intermittent and continuous inflow occlusion in the murine liver. Ann Surg 235:400–407
Peralta C, Hotter G, Closa D, Gelpi E, Bulbena O, Rosello-Catafau J (1997) Protective effect of preconditioning on the injury associated to hepatic ischemia-reperfusion in the rat: role of nitric oxide and adenosine. Hepatology 25:934–937
Makuuchi M, Mori T, Gunven P, Yamazaki S, Hasegawa H (1987) Safety of hemihepatic vascular occlusion during resection of the liver. Surg Gynecol Obstet 164:155–158
Koti R, Seifalian A, Davidson B (2003) Protection of the liver by ischemic preconditioning: a review of mechanisms and clinical applications. Dig Surg 20:383–396
Kamiike W, Burdelski M, Steinhoff G, Ringe B, Lauchart W, Pichlmayr R (1988) Adenine nucleotide metabolism and its relation to organ viability in human liver transplantation. Transplantation 45:138–143
Sumimoto K, Inagaki K, Yamada K, Kawasaki T, Dohi K (1988) Reliable indices for the determination of viability of grafted liver immediately after orthotopic transplantation. Bile flow rate and cellular adenosine triphosphate level. Transplantation 46:506–509
Accatino L, Pizarro M, Solis N, Arrese M, Koenig CS (2003) Bile secretory function after warm hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat. Liver Transpl 9:1199–1210
Bowers BA, Branum GD, Rotolo FS, Watters CR, Meyers WC (1987) Bile flow—an index of ischemic injury. J Surg Res 42:565–569
Oshio C, Phillips MJ (1981) Contractility of bile canaliculi: implications for liver function. Science 212:1041–1042
Tsukada N, Ackerley CA, Phillips MJ (1995) The structure and organization of the bile canalicular cytoskeleton with special reference to actin and actin-binding proteins. Hepatology 21:1106–1113
Benkoel L, Dodero F, Hardwigsen J, et al. (2001) Effect of ischemia-reperfusion on bile canalicular F-actin microfilaments in hepatocytes of human liver allograft: image analysis by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Dig Dis Sci 46:1663–1667
Benkoel L, Chanussot F, Dodero F, et al. (1998) Modification of Ca2+, Mg2+-ATPase and F-actin distribution in hepatocytes of cyclosporine A treated rats. Effect of soyabean lecithin and triacylglycerol. Cell Mol Biol 44:1221–1227
Benkoel L, Chanussot F, Dodero F, De La Maisonneuve C, Bongrand P, Benoliel AM, Lambert R, Brisse J, Chamlin A (2000) Effect of dietary lipid (soybean lecithin and triacylglycerol) on hepatic F-actin microfilaments in cyclosporine A-treated rats: image analysis by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Dig Dis Sci 45:1096–1102
Loranger A, Tuchweber B, Youseff I, Marceau N (1995) Biliary secretion and actin-cytokeratin filament distribution in rat hepatocytes during phalloidin-induced cholestasis. Biochem Cell Biol 73:641–649
Hasselgren PO, Fornander J, Jagenburg R, Sundstrom E (1982) Effects of live ischemia on hepatic protein synthesis in vitro and in vivo. Acta Physiol Scand 114:143–148
Wang Y, Gregory RB, Barritt GJ (2000) Regulation of F-actin and endoplasmic reticulum organisation by the trimeric G-protein Gi2 in rat hepatocytes: implication for the activation of store-operated Ca2+ inflow. J Biol Chem 275:22229–22237
Serafin A, Rosello-Catafau J, Prats N, Xaus C, Gelpi E, Peralta C (2002) Ischemic preconditioning increases the tolerance of Fatty liver to hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat. Am J Pathol 161:587–601
Ferguson DJ, Anderson TJ (1981) Ultrastructural observations on cell death by apoptosis in the ``resting'' human breast. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol 393:193–203
Boyer JL (2003) Bile formation and cholestasis. In: Schift ER, Sorrell MF, Maddrey WC (eds). Schift’s diseases of the liver. Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, p 139
Cutrin JC, Cantino D, Biasi F, et al. (1996) Reperfusion damage to the bile canaliculi in transplanted human liver. Hepatology 24:1053–1057
Shinohara H, Tanaka A, Kitai T, Yanabu N, Inomoto T, Satoh S, Hatano E, Yamaoka Y, Hirao K (1996) Direct measurement of hepatic idocyanine green clearance with near-infrared spectroscopy: separate evaluation of uptake and removal. Hepatology 23:137–144
Szijarto A, Hahn O, Lotz G, Schaff Z, Madarasz, Kupcsulik P (2006) Effect of ischemic preconditioning on rat liver microcirculation monitored with laser Doppler flowmetry. J Surg Res 131:150–157
Yin DP, Sankary HN, Chong AS, Ma LL, Shen J, Foster P, Williams JW (1998) Protective effect of ischemic preconditioning on liver preservation-reperfusion injury in rats. Transplantation 66:152–157
Hasegawa T, Malle E, Farhood A, Jaeschke H (2005) Generation of hypochlorite-modified proteins by neutrophils during ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat liver: attenuation by ischemic preconditioning. Am J Physiol 289:G760–G767
Cottart CH, Do L, Blanc MC, Vaubourdolle M, Descamps G, Durand D, Galen FX, Clot JP (1999) Hepatoprotective effect of endogenous nitric oxide during ischemia-reperfusion in the rat. Hepatology 29:809–813
Gurgal J, Bucci T, Farhood A, Jaeschke H (2001) Mechanism of cell death during warm hepatic ishcemia-reperfusion in rats: Apoptosis or necrosis? Hepatology 33:397–405
Yadav S, Sindram D, Perry D, Clavien PA (1999) Ischemic preconditioning protects the mouse liver by inhibition of apoptosis through a caspase-dependent pathway. Hepatology 30:1223–1231
Georgiev P, Navarini A, Eloranta J, Lang K, Kullak-Ublick G, Nocito A, Dahm F, Jochum W, Graf R, Clavien PA (2006) Cholestasis protects the liver from ischaemic injury and post-ischaemic inflammation in the mouse. Gut doi:10.1136/gut.2006.097170
Caban A, Oczkowicz G, Abdel-Samad O, Cierpka L (2006) Influence of ischemic preconditioning and nitric oxide on microcirculation and the degree of rat liver injury in the model of ischemia and reperfusion. Transpl Proc 38:196–198
Burtis CA, Ashwood ER (1999) Tietz textbook of clinical chemistry. 3rd ed. W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia, p 641
van Der Bilt JD, Kranenburg O, Nijkamp MW, Smakman N, Veenendaal LM, te Velde EA, Voest EE, Van Diest PJ, Rinkes IHMB (2005) Ischemia/reperfusion accelerates the outgrowth of hepatic micrometastases in a highly standardized murine model. Hepatology 42:165–175
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Ms. Rachael Hughes for skilled technical assistance, Mr. Brad Rumbelow and SouthPath (Flinders Medical Centre) for the measurement of liver marker enzymes, Dr. Graham White for advice on interpretation of data for plasma liver marker enzymes, Ms. Kylie Lange for advice on the statistical analysis, and Ms. Amanda Palmer for assistance in preparation of the manuscript. This research was supported by grants from the Flinders Medical Centre Foundation and Flinders University of South Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nieuwenhuijs, V.B., de Bruijn, M.T., Schiesser, M. et al. Ischemic Preconditioning and Intermittent Ischemia Preserve Bile Flow in a Rat Model of Ischemia Reperfusion Injury. Dig Dis Sci 52, 1159–1167 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9520-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9520-7