Abstract
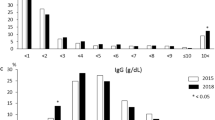
Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is rare in Asian countries compared to the West, and an exceptionally low prevalence was noted previously in Taiwan. Using the revised criteria of the IAIHG, 48 cases of AIH patients were diagnosed. All patients were consecutively diagnosed over a period of 5 years. Detailed medical histories including disease onset, hepatitis B and C, alcohol, drugs, blood transfusion, and family history of autoimmune disease were recorded. Clinical manifestations, result of steroid therapy, outcome, and survival rate were investigated and analyzed. Clinical data on AIH patients with cirrhosis and without cirrhosis were compared and analyzed for their outcome. The statistical methods used were Fisher's exact test, Wilcoxon rank sum test, and Kaplan-Meier curve. Forty-eight patients were diagnosed as AIH type 1, with a median age of 58 years and a female:male ratio of 37:11. The most common clinical features at presentation were fatigue, jaundice, and anorexia. Ninety-eight percent of patients were ANA positive, and most of the patients showed elevated values of AST, ALT, serum globulin, and bilirubin. A substantial proportion of patients presented with poor liver function at entry and 35% of patients had liver cirrhosis, with relatively prolonged PT (P=0.001) and poorer outcome (P=0.005) compared to the noncirrhotics. As a whole there was a favorable treatment response and the overall survival rate was 85%. We conclude that the incidence of AIH in Taiwan is much higher than previously presumed and AIH type 1 is the predominant type of the disease. Although a substantial proportion of AIH patients presented with poor hepatic function at entry, as a whole there was a favorable clinical outcome.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez F, Berg PA, Bianchi FB, Bianchi L, Burroughs AK, Cancado EL, Chapman RW, Cooksley WGE, Czaja AJ, Desmet VJ, Donaldson PT, Eddleston ALWF, Fainboim L, Heathcote J, Homberg J-C, Hoofnagle JH, Kakumu S, Krawitt EL, Mackay IR, MacSween RNM, Maddrey WC, Manns MP, McFarlane IG, Meyer zum Buschenfelde K-H, Mieli-Vergani G, Nakanuma Y, Nishioka M, Penner E, Porta G, Portmann BC, Reed WD, Rodes J, Schalm SW, Scheuer PJ, Schrumpf E, Seki T, Toda G, Tsuji T, Tygstrup N, Vergani D, Zeniya M (1999) International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Report: review of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol 31:929–938
International Working Party (1995) Terminology of chronic hepatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 90:181–189
Czaja AJ (2005) Current concepts in autoimmune hepatitis. Ann Hepatol 4(1):6–24
Boberg KM, Adland E, Jahnsen J, Raknerud N, Stiris M, Bell H (1998) Incidence and prevalence of primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and autoimmune hepatitis in a Norwegian population. Scand J Gastroenterol 33:99–103
Toda G, Zeniya M, Watanabe F, Imawari M, Kiyosawa K, Nishioka M, Tsuji T, Omata M (1997) Present status of autoimmune hepatitis in Japan-correlating the characteristics with international criteria in an area with a high rate of HCV infection. J Hepatol 26:1207–1212
Lee YM, Teo EK, NG TM, Khor C, Fock KM (2001) Autoimmune hepatitis in Singapore: A rare syndrome affecting middle-aged women. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:1384–138
Gupta R, Agarwal SR, Jain M, Malhotra V, Sarin SK (2001) Autoimmune hepatitis in the Indian subcontinent: 7 years experience. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:1144–1148
Koay LB, Sun CS, Hsu SI, Chen JJ, Lin CY (2001) Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis micmicking crytogenic hepatitis. Gastroenterol J Taiwan 18:132–138
Huang HC, Huang YS, Wu JC, Tsay SH, Huo TI, Wang YJ, Lo JC, Chen CY, Li CP, Chang FY, Lee SD (2002) Characteristics of autoimmune hepatitis in Taiwan: the 11 year experiences of a medical center. Chinese Med J (Taipei) 65:563–569
Qiu DK, Ma X (2003) Relationship between human leukocyte antigen-DRBI and autoimmune hepatitis type 1 in Chinese patients. J. Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:63–67
Johnson PJ, Mcfarlane IG (1993) Meeting report: International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group. Hepatology 18:998–1005
Czaja AJ, Carpenter HA (1996) Validation of scoring system for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. Dig Dis Sci 41:305–314
Nishioka M, Morshed SA, McFarlane IG (1998) Geographical variation in the frequency and characteristics of autoimmune liver diseases. In: Krawitt EL, Wiesner RH, Nishioka M (eds) Autoimmune liver diseases, 2nd ed. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 413–424
Boberg KM (2002) Prevalence and epidemiology of autoimmune hepatitis. Clin Liver Dis 6:347–359
Sherlock S, Dooley J (1993) Chronic autoimmune hepatitis. In: Diseases of the liver and biliary system. Blackwell Science, Oxford, pp 299–306
Parker DR, Kingham JGC (1997) Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis is primarily a disease of later life. Q J Med 90:289–296
Ferrari R, Pappas G, Agostinelli D, Muratori P, Muratori L, Lenzi M, Verucchi G, Cassani E, Chiodo F, Bianchi FB (2004) Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis: patterns of clinical presentation and differential diagnosis of the ‘acute’ type. Q J Med 97(7):407–417
Krawitt EL (1996) Autoimmune hepatitis. N Eng J Med 334:897–903
Czaja AJ, Mann MP (1995) The validity and importance of subtypes of autoimmune hepatitis: a point of view. Am J Gastroenterol 90:1206–1211
Homberg J-C, Abuaf N, Bernard O, Islam S, Alvarez F, Khalil SH, Poupon R, Darnis F, Levy V-G, Grippon P, Opolon P, Bernuau J, Benhamou J-P, Alagille D (1987) Chronic active hepatitis associated with anti-liver/kidney microsome type 1: a second type of “autoimmune” hepatitis. Hepatology 7:1333–1339
Manns MP (1997) Recent developments in autoimmune liver diseases. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 12(Suppl):s256–s271
Whittingham S, Mackay IR, Irwin J (1966) Autoimmune hepatitis: immunofluorescence reactions with cytoplasm of smooth muscle and glomerular cells. Lancet 1:1333–1335
Czja AJ, Cassani F, Cataleta M (1966) Frequency and significance of antibodies to actin in type 1 autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 24:1068–1073
Mcfarlane IG (1998) The relationship between autoimmune markers and different clinical syndromes in autoimmune hepatitis. Gut 42:599–602
Czja AJ, Donaldson PT, Lohse AW (2002) Antibodies to soluble liver antigen/liver pancreas and HLA risk factors for type 1 autoimmune hepatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 97:413–419
Targan SR, Landers C, Vidrich A (1995) High-titer antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in type-1 autoimmune hepatitis. Gastroenterology 108:1159–1166
Obermayer-Straub P, Strassburg CP, Manns MP (2000) Autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol 32(Suppl 1):181–197
Czaja AJ, Doherty DG, Donalson PT (2002) Genetic bases of autoimmune hepatitis. Dig Dis Sci 47:2139–2150
Donaldson PT, Doherty DG, Hayllar KM, McFarlane IG, Johnson PJ, Williams R (1991) Susceptibility to autoimmune chronic active hepatitis: human leukocyte antigens DR4 and A1-B8-DR3 are independent risk factors. Hepatology 13:701–706
Czaja AJ, Carpenter HA, Santrach PJ, Moore SB (1993) Significance of HLA DR4 in type 1 autoimmune hepatitis. Gastroenterology 105:1502–1507
Seki T, Kiyosawa K, Inoko H, Ota M (1990) Association of autoimmune hepatitis with HLA-Bw54 and DR4 in Japanese patients. Hepatology 12:1300–1304
Czaja AJ, Strettell MDJ, Thomson LJ, Santrach PJ, Moore SB, Donaldson PT, William R (1997) Associations between alleles of the major histocompatibility complex and type 1 autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 25:317–323
Czaja AJ (1996) Diagnosis and therapy of autoimmune liver disease. Med Clin North Am 80:973–994
Roberts SK, Therneau TM, Czaja AJ (1996) Prognosis of histological cirrhosis in type ∣ autoimmune hepatitis. Gastroenterology 110:848–857
Omagari K, Kinoshita H, Kato Y, Nakata K, Kanematsu T, Kusumoto Y, Mori I (1999) Clinical features of 89 patients with autoimmune hepatitis in Nagasaki Prefecture, Japan. J Gastroenterol 34:221–226
Czaja AJ, Carpenter HA (2004) Decreased fibrosis during corticosteroid therapy of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatol 40:646–652
Cotler SJ, DeLellis R, Kaplan MM (2001) Reversibility of cirrhosis in autoimmune hepatitis with corticosteroid therapy. J Clin Gasteroenterol 32:428–430
Mohamadnejad M, Malekzadeh R, Nasseri-Moghaddam S, Hagh-Azali S, Rakhshani N, Tavangar SM, Sedaghat M, Alimohamadi SM (2005) Impact of immunosuppressive treatment on liver fibrosis in autoimmune hepatitis. Dig Dis Sci 50:547–551
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koay, LB., Lin, CY., Tsai, SL. et al. Type 1 Autoimmune Hepatitis in Taiwan: Diagnosis Using the Revised Criteria of the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group. Dig Dis Sci 51, 1978–1984 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-9068-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-9068-y