Abstract
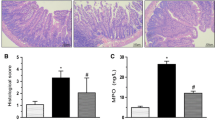
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of abnormal intestinal oligopeptide transporter (PepT1) on rat colon inflammation by transportion of N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP). We induced upregulation of PepT1 in the colon of rats by 80% small bowel resection and examined colonic PepT1 di-tripeptide transport activity. By Western blot analysis, PepT1 was clearly detected in the colon of bowel resection rats, while it was absent from the colon of bowel transection and reanastomosis rats. The experiment with cephalexin colon perfusion showed that the arterial cephalexin concentration in resection rats was five to nine times that in transection rats. Inhibition of PepT1 by Gly–Gly completely abolished cephalexin absorption from the colon of resection rats. We found that 10 μM fMLP perfusion in the colon of resection rats for 4 hr significantly increased myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and caused colon wall damage. In contrast, 10 μM fMLP perfusion in the colon of transection rats did not induce any inflammation. A 5 mM Gly–Gly perfusion completely inhibited the MPO activity and colonic wall damage induced by 10 μM fMLP. We conclude that colonic PepT1 induced by bowel resection may provide a mechanism for oligopeptide transport and may serve as a potential cause of colonic mucosa damage by transport of the bacterial product fMLP in rat colon.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adibi SA (2003) Regulation of expression of the intestinal oligopeptide transporter (Pept-1) in health and disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 285:G779–G788
Rubio-Aliaga I, Daniel H (2002) Mammalian peptide transporters as targets for drug delivery. Trends Pharmacol Sci 23:434–440
Xiao-Yan Chu, Gloria P, Anchez-Castano S, Kazutaka Higaki, Doo-Man OH, Cheng-Pang Hsu, Gordon L (2001) Amidon. Correlation between epithelial cell permeability of cephalexin and expression of intestinal oligopeptide transporter. J PET 299:575–582
Buyse M, Tsocas A, Walker F, Merlin D, Bado A (2002) PepT1-mediated fMLP transport induces intestinal inflammation in vivo. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283:C1795–C1800
Chadwick VS, Mellor DM, Myers DB, Seldon AC, Keshavarzian MF, Hobson CH (1988) Production of peptides inducing chemotaxis and lysosomal enzyme release in human neutrophils by intestinal bacteria in vitro and in vivo. Scand J Gastroenterol 23:121–128
Painter RG, Sklar LA, Jesaitis AJ, Schmitt M, Cochrane CG (1984) Activation of neutrophils by N-formyl chemotactic peptides. Fed Proc 43:2737–2742
Marasco WA, Phan SH, Krutzsch H, Showell HJ, Feltner DE, Nairn R, Becker EL, Ward PA (1984) Purification and identification of formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine as the major peptide neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 259:5430–5439
Merlin D, Steel A, Gewirtz AT, Si-Tahar M, Hediger MA, Madara JL (1998) hPepT1-mediated epithelial transport of bacteria-derived chemotactic peptides enhances neutrophil–epithelial interactions. J Clin Invest 102:2011–2018
Merlin D, Si-Tahar M, Sitaraman SV, Eastburn K, Williams I, Liu X, Hediger MA, Madara JL (2001) Colonic epithelial hPepT1 expression occurs in inflammatory bowel disease: transport of bacterial peptides influences expression of MHC class 1 molecules. Gastroenterology 120:1666–1679
Fei Y-J, Kanai Y, Nussberger S, Ganapathy V, Leibach FH, Romero MF, Singh SK, Boron WF, Hediger MA (1994) Expression cloning of a mammalian proton-coupled oligopeptide transporter. Nature 368:563–566
Liang R, Fei Y-J, Prasad P, Ramamoorthy S, Han H, Yang-Feng TL, Hediger MA, Ganapathy V, Leibach F (1995) Human intestinal H+/peptide cotransporter. Cloning, functional expression and chromosomal localization. J Biol Chem 270:6456–6463
Saito H, Okuda M, Terada T, Sasaki S, Inui K (1995) Cloning and characterization of the rat H+/peptide cotransporter mediating absorption of ß-lactam antibiotics in the intestine and kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 275:1631–1637
Freeman TC, Bentsen BS, Thwaites DT, Simmons NL (1995) H+/di-tripeptide transporter (PepT1) expression in the rabbit intestine. Eur J Physiol 430:394–400
Ford D, Howard A, Hirst BH (2003) Expression of the peptide transporter hPepT1 in human colon: a potential route for colonic protein nitrogen and drug absorption. Histochem Cell Biol 119:37–43
Christoph von Ritter, Sekizuka E, Grisham MB, Granger DN (1988) The chemotactic N-formyl-methionyl-leucylphenylalanine peptide increases mucosal permeability in the distal ileum of the rat. Gastroenterology 95:651–656
Rome S, Barbot L, Windsor E, Kapel N, Tricottet V, Huneau J-F, Reynes M, Gobert JG, Tomé D (2002) The regionalization of PepT1, NBAT and EAAC1 transporters in the small intestine of rats are unchanged from birth to adulthood. J Nutr 132:1009–1011
Tanaka H, Miyamoto KI, Morita K, Haga H, Segawa H, Shiraga T, Fujioka A, Kouda T, Taketani Y, Hisano S, Fukui Y, Kitagawa K, Takeda E (1998) Regulation of the PepT1 peptide transporter in the rat small intestine in response to 5-fluorouracil-induced injury. Gastroenterology 114:714–723
Akarawut W, Lin C-J, Smith DE (1998) Noncompetitive inhibition of glycylsarcosine transport by quinapril in rabbit renal brush border membrane vesicles: effect on high-affinity peptide transporter. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287:684–690
Hong S, Smith DE, Brosius FC III (2001) Developmental expression of PEPT1 and PEPT2 in rat small intestine, colon, and kidney. Pediatr Res 49:789–795
Brosius FC III, Liu Y, Nguyen N, Sun D, Bartlett J, Schwaiger M (1997) Persistent myocardial ischemia increases GLUT1 glucose transporter expression in both ischemic and nonischemic heart regions. J Mol Cell Cardiol 29:1675–1685
Hong S, Smith DE, Yang T, Huang YG, Schnermann JB, Brosius FC III (1999) Localization of PEPT1 and PEPT2 proton-coupled oligopeptide transporter mRNA and protein in rat kidney. Am J Physiol 276(Renal Physiol 45):F658–F665
Ziegler TR, Fernandez-Estivariz C, Gu LH, Bazargan N, Umeakunne K, Wallace TM, Diaz EE, Rosado KE, Pascal RR, Galloway JR, Wilcox JN, Leader LM (2002) Distribution of the H+/peptide transporter PepT1 in human intestine: upregulated expression in the colonic mucosa of patients with short-bowel syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr 75:922–930
Hu M, Amidon GL (1988) Passive and carrier-mediated intestinal absorption components of captopril. J Pharm Sci 77:1007–1011
Gangopadhyay A, Thamotharan M, Adibi SA (2002) Regulation of oligopeptide transporter (Pept-1) in experimental diabetes. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 283:G133–G138
Barbot L, Windsor E, Rome S, Tricottet V, Reynes M, Topouchian A, Huneau JF, Gobert JG, Tome D, Kapel N (2003) Intestinal peptide transporter PepT1 is over-expressed during acute cryptosporidiosis in suckling rats as a result of both malnutrition and experimental parasite infection. Parasitol Res 89:364–370
Curtis KJ, Kim JM, Perdomo JM, Silk DB, Whitehead JS (1978) Protein digestion and absorption in the rat. J Physiol 274:409–419
Fuller MF, Reeds PJ (1998) Nitrogen cycling in the gut. Annu Rev Nutr 18:385–411
Buyse M, Berlioz F, Guilmeau S, Tsocas A, Voisin T, Péranzi G, Merlin D, Laburthe M, Lewin MJM, Rozé C, Bado A (2001) PepT1-mediated epithelial transport of dipeptides and cephalexin is enhanced by luminal leptin in the small intestine. J Clin Invest 108:1483–1494
Sadlack B, Merz H, Schorle H, Schimpl A, Feller AC, Horak I (1993) Ulcerative colitis-like disease in mice with a disrupted interleukin-2 gene. Cell 75:253–261
Matsuda H, Fuijama Y, Andoh A, Ushijama T, Kajinami T, Bamba T (2000) Characterisation of antibody responses against rectal mucosa-associated bacterial flora in patients with ulcerative colitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 15:61–68
Burke DA, Axon ATR (1987) Ulcerative colitis and Escherichia coli with adhesive properties. J Clin Pathol 40:782–786
Karlinger K, Gyorke T, Mako E, Mester A, Tarjan Z (2000) The epidemiology and the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Eur J Radiol 35:154–167
Brandwein SL, McCabe RP, Cong Y, Waites KB, Ridwan BU, Dean PA, Ohkusa T, Birkenmeier EH, Sundberg JP, Elson CO (1997) Spontaneously colitic C3H/HeJBir mice demonstrate selective antibody reactivity to antigens of the enteric bacterial flora. J Immunol 159:44–52
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by Grant 30371392 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30371392).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, B., Song, D., Xue, H. et al. Abnormal Expression of the Peptide Transporter PepT1 in the Colon of Massive Bowel Resection Rat: A Potential Route for Colonic Mucosa Damage by Transport of fMLP. Dig Dis Sci 51, 2087–2093 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-9067-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-9067-z