Abstract
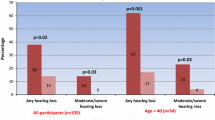
Isolated case reports in which symptomatic hearing loss develops suddenly during the course of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) have been reported, but the presence of subclinical sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) associated with IBD has been investigated in only two preliminary studies.In order to research this further, we aimed to investigate the presence of subclinical SNHL in IBD by comparison with a control group and to examine possible relations between the bowel disease parameters and hearing loss.Otoscopy, tympanometry, and pure tone audiometry were carried out in 39 patients with IBD (21 Crohn's disease [CD], 18 ulcerative colitis [UC]) and 25 healthy age- and sex-matched controls. All patients and control subjects had normal otoscopy findings and tympanometry was unremarkable, excluding middle ear disease and conductive hearing loss. Analysis of each frequency examined showed that the average hearing thresholds were increased significantly in the study group compared to those of the control group at higher frequencies (2, 4, and 8 kHz). When these parameters were compared with the control group according to subgroups of IBD, a significant difference was determined for the UC group at frequencies of 2, 4, and 8 kHz and for the CD group only at the frequency of 4 kHz. Although there was a trend of increment in SNHL as the age of the patient and duration and extent of UC increased, no significant correlation was observed between SNHL and these parameters or sex, activity, involvement site, medication history of IBD, and coexistence of other extraintestinal manifestations. In conclusion, it was demonstrated that a subclinical SNHL may be associated with UC and somewhat with CD, affecting mainly the high frequencies. In light of this finding, it may be advisable to investigate labyrinth functions as well as other extraintestinal manifestations in patients with IBD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Orchard TR, Jewel DP: Extraintestinal manifestations: skin, joints and mucocutaneous manifestations. In Kirsner's Inflammatory Bowel Disease, 6th ed. Sartor RB, Sandborn WJ (eds). Philadelphia, Saunders, 2004, pp 658–672
Rogler G, Schölmerich J: Extraintestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. Med Klin (Munich) 99:123–130, 2004
Billings P: Experimental autoimmune hearing loss. J Clin Invest 113:1114–1117, 2004
Mathews J, Kumar BN: Autoimmune sensorineural hearing loss. Clin Otolaryngol 28:479–488, 2003
Nemoto H, Iguchi H, Ichikawa Y, Wakata N, Kurihara T: Ulcerative colitis presenting as sensorineural deafness, brainstem encephalopathy, and white matter lesions. Neurologist 10:165–168, 2004
Kanra G, Kara A, Secmeer G, Ozen H, Gurakan F, Akcoren Z, Atas A: Sensorineural hearing loss as an extra-intestinal manifestation of ulcerative colitis in an adolescent girl with pyoderma gangrenosum. Eur J Pediatr161:216–218, 2002
Jacob A, Ledingham JG, Kerr AI, Ford MJ: Ulcerative colitis and giant cell arteritis issociated with sensorineural deafness. J Laryngol Otol 104:889–890, 1990
Kumar BN, Walsh RM, Wilson PS, Carlin WV: Sensorineural hearing loss and ulcerative colitis. J Laryngol Otol 111:277–278, 1997
Bachmeyer C, Leclerc-Landgraf N, Laurette F, Coutarel P, Cadranel JF, Medioni J, Dhote R, Mougeot-Martin M: Acute autoimmune sensorineural hearing loss associated with Crohn's disease. Am J Gastroenterol 93:2565–2567, 1998
Summers RW, Harker L: Ulcerative colitis and sensorineural hearing loss: is there a relationship? J Clin Gastroenterol 4:251–252, 1982
Dowd A, Rees WD: Treatment of sensorineural deafness associated with ulcerative colitis. Br Med J 295:26, 1987
Hollanders D: Sensorineural deafness—-A new complication of ulcerative colitis? Postgrad Med J 62:753–755, 1986
Weber RS, Jenkins HA, Coker NJ: Sensorineural hearing loss associated with ulcerative colitis. A case report. Arch Otolaryngol 110:810–812, 1984
Staecker H, Lefebvre PP: Autoimmune sensorineural hearing loss improved by tumor necrosis factor-alpha blockade: a case report. Acta Otolaryngol 122:684–687, 2002
Spier BJ, Wyman JB, Reichelderfer M, Schwartz DC: Acute sensorineural hearing loss as an early manifestation of indeterminate colitis. Dig Dis Sci 49:1275–1279, 2004
Loft DE, Dowd AB, Khan MHZ, Mulligan TA, Rees WDW: Auditory dysfunction in inflammatory bowel disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1:129–132, 1989
Kumar BN, Smith MS, Walsh RM, Green JR: Sensorineural hearing loss in ulcerative colitis. Clin Otolaryngol 25:143–145, 2000
Harvey RF, Bradshaw JM: A simple index of Crohn's disease activity. Lancet 1:514, 1980
Sutherland LR, Martin F, Greer S, Robinson M, Greenberger N, Saibil F, Martin T, Sparr J, Prokipchuk E, Borgen L: 5-Aminosalycylic acid enema in the treatment of distal ulcerative colitis, proctosigmoiditis, and proctitis. Gastroenterology 92:1894–1898, 1987
Levitan HL: The etiologic significance of deafness in ulcerative colitis. Int J Psychiatry Med 4:379–387, 1973
McCabe BF: Autoimmune sensorineural hearing loss. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 113:526–530, 1979
Ruckenstein MJ: Autoimmune inner ear disease. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 12:426–430, 2004
Hoistad DL, Schachern PA, Paparella MM: Autoimmune sensorineural hearing loss: a human temporal bone study. Am J Otolaryngol 19:33–39, 1998
Cadoni G, Agostino S, Manna R, De Santis A, Fetoni AR, Vulpiani P, Ottaviani F: Clinical associations of serum antiendothelial cell antibodies in patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 113:797–801, 2003
Yoo TJ, Du X, Kwon SS: Molecular mechanism of autoimmune hearing loss. Acta Otolaryngol 548 (Suppl):3–9, 2002
Ozcan M, Karakus MF, Gunduz OH, Tuncel U, Sahin H: Hearing loss and middle ear involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 22:16–19, 2002
Tumiati B, Casoli P, Parmeggiani A: Hearing loss in the Sjogren syndrome. Ann Intern Med 126:450–453, 1997
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akbayir, N., ÇAliŞ, A.B., Alkim, C. et al. Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Subclinical Extraintestinal Manifestation. Dig Dis Sci 50, 1938–1945 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-2964-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-2964-3