Abstract
The exploration of repeated patterns with different lengths, also called variable-length motifs, has received a great amount of attention in recent years. However, existing algorithms to detect variable-length motifs in large-scale time series are very time-consuming. In this paper, we introduce a time- and space-efficient approximate variable-length motif discovery algorithm, Distance-Propagation Sequitur (DP-Sequitur), for detecting variable-length motifs in large-scale time series data (e.g. over one hundred million in length). The discovered motifs can be ranked by different metrics such as frequency or similarity, and can benefit a wide variety of real-world applications. We demonstrate that our approach can discover motifs in time series with over one hundred million points in just minutes, which is significantly faster than the fastest existing algorithm to date. We demonstrate the superiority of our algorithm over the state-of-the-art using several real world time series datasets.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
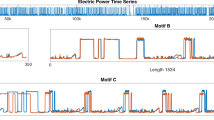
Example of Canebrake Groundcreeper records contain motif A: Athanas
Example of Streak-backed Canastero records contain motif B: Calderon-F
References
Athanas N. Xc22831. Accessible at www.xeno-canto.org/22831. Accessed 11 Aug 2008
Begum N, Keogh E (2014) Rare time series motif discovery from unbounded streams. Proc VLDB Endow 8(2):149–160
Bob P, Willem-Pier V, Sander P, Jonathon J (2005) Xeno-Canto. www.xeno-canto.org. Accessed 30 May 2005
Boesman P. Xc221161. Accessible at www.xeno-canto.org/221161
Calderon-F D. Xc301107. Accessible at www.xeno-canto.org/301107. Accessed 13 Dec 2015
Castro N, Azevedo PJ (2010) Multiresolution motif discovery in time series. In: Proceedings of the 2010 SIAM international conference on data mining. SIAM, pp 665–676
Chiu B, Keogh E, Lonardi S (2003) Probabilistic discovery of time series motifs. In: Proceedings of the ninth ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining. ACM, pp 493–498
Gao Y, Lin J, Rangwala H (2016) Iterative grammar-based framework for discovering variable-length time series motifs. In: 15th IEEE international conference on machine learning and applications (ICMLA). IEEE, pp 7–12
Gao Y, Li Q, Li X, Lin J, Rangwala H (2017) Trajviz: a tool for visualizing patterns and anomalies in trajectory. In: Joint European conference on machine learning and knowledge discovery in databases. Springer, pp 428–431
Giancarlo R, Scaturro D, Utro F (2009) Textual data compression in computational biology: a synopsis. Bioinformatics 25(13):1575–1586
Goldberger AL, Amaral LA, Glass L, Hausdorff JM, Ivanov PC, Mark RG, Mietus JE, Moody GB, Peng C-K, Stanley HE (2000) Physiobank, physiotoolkit, and physionet components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 101(23):e215–e220
Hughes JF, Skaletsky H, Pyntikova T, Graves TA, van Daalen SK, Minx PJ, Fulton RS, McGrath SD, Locke DP, Friedman C et al (2010) Chimpanzee and human Y chromosomes are remarkably divergent in structure and gene content. Nature 463(7280):536
Kent WJ, Sugnet CW, Furey TS, Roskin KM, Pringle TH, Zahler AM, Haussler D (2002) The human genome browser at UCSC. Genome Res 12(6):996–1006
Keogh E, Lonardi S, Zordan VB, Lee SH, Jara M (2005a) Visualizing the similarity of human and chimp DNA (multimedia video). http://www.cs.ucr.edu/~eamonn/DNA/
Keogh E, Lin J, Fu A (2005b) Hot sax: efficiently finding the most unusual time series subsequence. In: 2005 IEEE 5th international conference on data mining (ICDM), p 8
Krabbe N. Xc235579. Accessible at www.xeno-canto.org/235579
Li Y, Lin J, Oates T (2012) Visualizing variable-length time series motifs. In: Proceedings of the 2012 SIAM international conference on data mining. SIAM, pp 895–906
Li Y, Yiu ML, Gong Z, et al. (2015) Quick-motif: an efficient and scalable framework for exact motif discovery. In: 2015 IEEE 31st international conference on data engineering (ICDE). IEEE, pp 579–590
Lin J, Keogh E, Lonardi S, Lankford JP, Nystrom DM (2004) Visually mining and monitoring massive time series. In: Proceedings of the tenth ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining. ACM, pp 460–469
Lin J, Keogh E, Wei L, Lonardi S (2007) Experiencing sax: a novel symbolic representation of time series. Data Min Knowl Discov 15(2):107–144
Lines J, Davis LM, Hills J, Bagnall A (2012) A shapelet transform for time series classification. In: Proceedings of the 18th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining. ACM, pp 289–297
Liu B, Li J, Chen C, Tan W, Chen Q, Zhou M (2015) Efficient motif discovery for large-scale time series in healthcare. IEEE Trans Ind Inform 11(3):583–590
Locke DP, Hillier LW, Warren WC, Worley KC, Nazareth LV, Muzny DM, Yang S-P, Wang Z, Chinwalla AT, Minx P et al (2011) Comparative and demographic analysis of orang-utan genomes. Nature 469(7331):529
Mohammad Y, Nishida T (2009) Constrained motif discovery in time series. New Gener Comput 27(4):319–346
Mohammad Y, Nishida T (2014a) Exact discovery of length-range motifs. In: Intelligent information and database systems. Springer, pp 23–32
Mohammad Y, Nishida T (2014b) Scale invariant multi-length motif discovery. In: Modern advances in applied intelligence. Springer, pp 417–426
Mueen A (2013) Enumeration of time series motifs of all lengths. In: 2013 IEEE 13th international conference on data mining (ICDM). IEEE, pp 547–556
Mueen A, Keogh E (2010) Online discovery and maintenance of time series motifs. In: Proceedings of the 16th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining. ACM, pp 1089–1098
Mueen A, Keogh EJ, Zhu Q, Cash S, Westover MB (2009) Exact discovery of time series motifs. In: Proceedings of the 2009 SIAM international conference on data mining. SIAM, pp. 473–484
Mueen A, Viswanathan K, Gupta C, Keogh E (2015) The fastest similarity search algorithm for time series subsequences under Euclidean distance. http://www.cs.unm.edu/~mueen/FastestSimilaritySearch.html
Murray D, Liao J, Stankovic L, Stankovic V, Hauxwell-Baldwin R, Wilson C, Coleman M, Kane T, Firth S (2015) A data management platform for personalised real-time energy feedback. In: Proceedings of the 8th international conference on energy efficiency in domestic appliances and lighting, pp 1–15
Nevill-Manning CG, Witten IH (1997) Identifying hierarchical strcture in sequences: a linear-time algorithm. J Artif Intell Res (JAIR) 7:67–82
Nunthanid P, Niennattrakul V, Ratanamahatana CA (2011) Discovery of variable length time series motif. In: 2011 8th international conference on electrical engineering/electronics, computer, telecommunications and information technology (ECTI-CON). IEEE, pp 472–475
Patel P, Keogh E, Jessica L, Lonardi S (2002) Mining motifs in massive time series databases. In: 2003 proceedings of the 2002 IEEE international conference on data mining (ICDM). IEEE, pp 370–377
Rakthanmanon T, Campana B, Mueen A, Batista G, Westover B, Zhu Q, Zakaria J, Keogh E (2012) Searching and mining trillions of time series subsequences under dynamic time warping. In: Proceedings of the 18th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining. ACM, pp 262–270
Senin P, Malinchik S (2013) Sax-vsm: Interpretable time series classification using sax and vector space model. In: 2013 IEEE 13th international conference on data mining (ICDM). IEEE, pp 1175–1180
Senin P, Lin J, Wang X, Oates T, Gandhi S, Boedihardjo AP, Chen C, Frankenstein S, Lerner M (2014) Grammarviz 2.0: a tool for grammar-based pattern discovery in time series. In: Machine learning and knowledge discovery in databases. Springer, pp 468–472
Shieh J, Keogh E (2009) iSAX: disk-aware mining and indexing of massive time series datasets. Data Min Knowl Discov 19(1):24–57
Shokoohi-Yekta M, Chen Y, Campana B, Hu B, Zakaria J, Keogh E (2015) Discovery of meaningful rules in time series. In: Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining. ACM, pp 1085–1094
Skaletsky H, Kuroda-Kawaguchi T, Minx PJ, Cordum HS, Hillier L, Brown LG, Repping S, Pyntikova T, Ali J, Bieri T et al (2003) The male-specific region of the human Y chromosome is a mosaic of discrete sequence classes. Nature 423(6942):825–837
Tang H, Liao SS (2008) Discovering original motifs with different lengths from time series. Knowl Based Syst 21(7):666–671
Wang X, Lin J, Senin P, Oates T, Gandhi S, Boedihardjo AP, Chen C, Frankenstein S (2016) RPM: Representative pattern mining for efficient time series classification. In: 19th international conference on extending database technology (EDBT), pp 185–196
Yeh C-CM, Zhu Y, Ulanova L, Begum N, Ding Y, Dau HA, Silva DF, Mueen A, Keogh E (2016) Matrix profile i: All pairs similarity joins for time series: a unifying view that includes motifs, discords and shapelets. In: 2016 IEEE 16th international conference on data mining (ICDM), pp 1317–1322
Zhu Y, Schall-Zimmerman Z, Senobari NS, Yeh C-CM, Funning G, Mueen A, Brisk P, Keogh EJ (2016) Matrix profile ii: exploiting a novel algorithm and gpus to break the one hundred million barrier for time series motifs and joins. In: 2016 IEEE 16th international conference on data mining (ICDM), pp 739–748
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editors: Kurt Driessens, Dragi Kocev, Marko Robnik-Šikonja, Myra Spiliopoulou.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Lin, J. Exploring variable-length time series motifs in one hundred million length scale. Data Min Knowl Disc 32, 1200–1228 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10618-018-0570-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10618-018-0570-1