Abstract
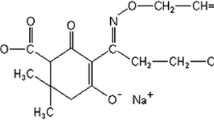
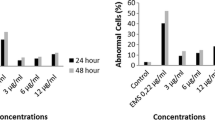
Chlorination is widely used method in the disinfection of drinking and utility water worldwide. In this study, cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of sodium hypochlorite were investigated by the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay and chromosomal aberration analysis on human peripheral lymphocytes in vitro. A significant increase in chromosomal aberration frequency was observed in all treatments of NaOCl (0.030, 0.065, 0.100, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4 μg/mL) at 24 and 48 h compared with the negative control and mitomycin C (MMC, 0.3 μg/mL), which was used as a positive control. NaOCl significantly increased the frequency of micronuclei in a dose dependent manner. The results showed that there was a significant correlation between NaOCl concentration and chromosomal aberration, micronuclei frequency, necrotic cells, apoptotic cells and binucleated cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksu P, Gul S, Ozkan O, Nur G, Kaya TO (2008) Evaluation of the acute toxicity, genotoxicity of NaOCl on blackbrow bleak (Acanthalburnus microlepis De Filippi, 1863). Fresenius Environ Bull 17(3):298–302
Bolognesi C, Buschini A, Branchi E, Carboni P, Furlini M, Martino A, Monteverde M, Poli P, Rossi C (2004) Comet and micronucleus assays in zebra mussel cells for genotoxicity assessment of surface drinking water treated with three different disinfectants. Sci Total Environ 333(1–3):127–136. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.05.018
Buschini A, Carboni P, Furlini M, Poli P, Rossi C (2004) Sodium hypochlorite-, chlorine dioxide- and peracetic acid-induced genotoxicity detected by the Comet assay and Saccharomyces cerevisiae D7 tests. Mutagenesis 19:157–162. doi:10.1093/mutage/geh012
Bystrom A, Sundqvist G (1983) Bacteriologic evaluation of the effect of 0.5 percent sodium-hypochlorite in endodontıc therapy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 55(3):307–312
Crebelli R, Conti L, Monarca S, Feretti D, Zerbini I, Zani C, Veschetti E, Cutilli D, Ottaviani M (2005) Genotoxicity of the disinfection by-products resulting from peracetic acid- or hypochlorite-disinfected sewage wastewater. Water Res 39(6):1105–1113. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2004.12.029
Demsia G, Vlastos D, Goumenou M, Matthopoulos DP (2007) Assessment of the genotoxicity of imidacloprid and metalaxyl in cultured human lymphocytes and rat bone-marrow. Mutat Res 634(1–2):32–39. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2007.05.018
Eastmond DA, Tucker JD (1989) Identifıcation of aneuploidy-inducing agents using cytokinesis-blocked human-lymphocytes and an antikinetochore antibody. Environ Mol Mutagen 13(1):34–43. doi:10.1002/em.2850130104
Emmanuel E, Keck G, Blanchard JM, Vermande P, Perrodin Y (2004) Toxicological effects of disinfections using sodium hypochlorite on aquatic organisms and its contribution to AOX formation in hospital wastewater. Environ Int 30(7):891–900. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2004.02.004
Fenech M, Crott J, Turner J, Brown S (1999) Necrosis, apoptosis, cytostasis and DNA damage in human lymphocytes measured simultaneously within the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay: description of the method and results for hydrogen peroxide. Mutagenesis 14(6):605–612. doi:10.1093/mutage/14.6.605
Gustavino B, Buschini A, Monfrinotti M, Rizzoni M, Tancioni L, Poli P, Rossi C (2005) Modulating effects of humic acids on genotoxicity induced by water disinfectants in Cyprinus carpio. Mutat Res 587(1–2):103–113. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2005.08.009
Guzzella L, Monarca S, Zani C, Feretti D, Zerbini I, Buschini A, Poli P, Rossi C, Richardson SD (2004) In vitro potential genotoxic effects of surface drinking water treated with chlorine and alternative disinfectants. Mutat Res 564(2):179–193. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2004.08.006
IARC (1991) IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. chlorinated drinking-water. IARC Lyon 52:45–159
Ishidate M, Sofuni T, Yoshikawa K, Hayashi M, Nohmi T, Sawada M, Matsuoka A (1984) Primary mutagenicity screening of food-additives currently used in Japan. Food Chem Toxicol 22(8):623–636. doi:10.1016/0278-6915(84)90271-0
Le Curieux F, Marzin D, Erb F (1993) Comparison of three short-term assays: results on seven chemicals. Potential contribution to the control of water genotoxicity. Mutat Res 319:223–236. doi:10.1016/0165-1218(93)90082-O
Meier JR, Bull RJ, Stober JA, Cimino MC (1985) Evaluation of chemicals used for drinking-water disinfection for production of chromosomal damage and sperm-head abnormalities in mice. Environ Mutagen 7(2):201–211. doi:10.1002/em.2860070208
Monarca S, Feretti D, Collivignarelli C, Guzzella L, Zerbini I, Bertanza G, Pedrazzani R (2000) The influence of different disinfectants on mutagenicity and toxicity of urban wastewater. Water Res 34(17):4261–4269. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00192-5
Monarca S, Zani C, Richardson SD, Thruston AD, Moretti M, Feretti D, Villarini M (2004) A new approach to evaluating the toxicity of genotoxicity of disinfected drinking water. Water Res 38(17):3809–3819. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2004.07.003
Ohnishi S, Murata M, Kawanishi S (2002) DNA damage induced by hypochlorite and hypobromite with reference to inflammation-associated carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett 178(1):37–42. doi:10.1016/S0304-3835(01)00812-6
Rencuzogullari E, Topaktas M (2000) Chromosomal aberrations in cultured human lymphocytes treated with the mixtures of carbosulfan, ethyl carbamate and ethyl methanesulfonate. Cytologia (Tokyo) 65(1):83–92
Roncada T, Vicentini VEP, Mantovani MS (2004) Possible modulating actions of plant extracts on the chromosome breaking activity of MMC and Ara-C in human lymphocytes in vitro. Toxicol In Vitro 18(5):617–622. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2004.02.007
Rutala WA, Weber DJ (1997) Uses of inorganic hypochlorite (bleach) in health-care facilities. Clin Microbiol Rev 10(4):597–610
White GC (1978) Chlorine decay. J Water Pollut Control Fed 50(5):8–14
Whiteman M, Jenner A, Halliwell B (1997) Hypochlorous acid-induced base modifications in isolated calf thymus DNA. Chem Res Toxicol 10(11):1240–1246. doi:10.1021/tx970086i
Wlodkowski TJ, Rosenkranz HS (1975) Mutagenicity of sodium-hypochlorite for Salmonella-typhimurium. Mutat Res 31(1):39–42
Yuzbasioglu D, Celik M, Yilmaz S, Unal F, Aksoy H (2006) Clastogenicity of the fungicide afugan in cultured human lymphocytes. Mutat Res 604(1–2):53–59. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2006.01.001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gül, S., Savsar, A. & Tayfa, Z. Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of sodium hypochlorite on human peripheral lymphocytes in vitro. Cytotechnology 59, 113–119 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-009-9201-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-009-9201-4