Abstract
In this paper, we develop novel numerical methods based on the multi-point flux approximation (MPFA) method to solve the degenerated partial differential equation (PDE) arising from pricing two-assets options. The standard MPFA is used as our first method and is coupled with a fitted finite volume in our second method to handle the degeneracy of the PDE and the corresponding scheme is called fitted MPFA method. The convection part is discretized using the upwinding methods (first and second order) that we have derived on non uniform grids. The time discretization is performed with \(\theta \)-Euler methods. Numerical simulations show that our new schemes can be more accurate than the current fitted finite volume method proposed in the literature.










Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
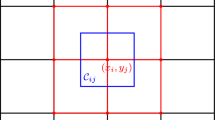
center of the control volume \(\mathcal {C}_{i,j}\).
References
Aavatsmark, I. (2002). An introduction to multipoint flux approximations for quadrilateral grids. Computational Geosciences, 6(3–4), 405–432.
Aavatsmark, I. (2007). Multipoint flux approximation methods for quadrilateral grids. In 9th International forum on reservoir simulation, Abu Dhabi (pp. 9–13).
Angermann, L., & Wang, S. (2007). Convergence of a fitted finite volume method for the penalized black–scholes equation governing european and american option pricing. Numerische Mathematik, 106(1), 1–40.
Bates, D. S. (1996). Jumps and stochastic volatility: Exchange rate processes implicit in deutsche mark options. The Review of Financial Studies, 9(1), 69–107.
Duffy, D. J. (2013). Finite Difference methods in financial engineering: A partial differential equation approach. Hoboken: Wiley.
Haug, E. G. (2007). The complete guide to option pricing formulas (Vol. 2). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Heston, S. L. (1993). A closed-form solution for options with stochastic volatility with applications to bond and currency options. The Review of Financial Studies, 6(2), 327–343.
Huang, C.-S., Hung, C.-H., & Wang, S. (2006). A fitted finite volume method for the valuation of options on assets with stochastic volatilities. Computing, 77(3), 297–320.
Huang, C.-S., Hung, C.-H., & Wang, S. (2009). On convergence of a fitted finite-volume method for the valuation of options on assets with stochastic volatilities. IMA Journal of Numerical Analysis, 30(4), 1101–1120.
Hull, J. C. (2003). Options, futures and others. Derivative (5th ed.). Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Kwok, Y.-K. (2008). Mathematical models of financial derivatives. Berlin: Springer.
LeVeque, R. J. (2004). Finite volume methods for hyperbolic problems. Cambridge Texts in Applied Mathematics, 39(1), 88–89.
Lie, K.-A., Krogstad, S., Ligaarden, I. S., Natvig, J. R., Nilsen, H. M., & Bård Skaflestad, B. (2012). Open-source matlab implementation of consistent discretisations on complex grids. Computational Geosciences, 16(2), 297–322.
Persson, J., & Sydow, L. V. (2007). Pricing European multi-asset options using a space-time adaptive FD-method. Computing and Visualization in Science, 10(4), 173–183.
Sandve, T. H., Berre, I., & Nordbotten, J. M. (2012). An efficient multi-point flux approximation method for discrete fracture-matrix simulations. Journal of Computational Physics, 231(9), 3784–3800.
Stephansen, A. F. (2012). Convergence of the multipoint flux approximation l-method on general grids. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 50(6), 3163–3187.
Tambue, A. (2016). An exponential integrator for finite volume discretization of a reaction–advection–diffusion equation. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 71(9), 1875–1897.
Wang, S. (2004). A novel fitted finite volume method for the Black–Scholes equation governing option pricing. IMA Journal of Numerical Analysis, 24(4), 699–720.
Wilmott, P. (2005). The best of Wilmott 1: Incorporating the quantitative finance review. Hoboken: Wiley.
Wilmott, P., Dewynne, J., & Howison, S. (1993). Option pricing: Mathematical models and computation. Oxford: Oxford Financial Press.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Robert Bosch Stiftung through the AIMS ARETE Chair programme (Grant No 11.5.8040.0033.0).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koffi, R.S., Tambue, A. A Fitted Multi-point Flux Approximation Method for Pricing Two Options. Comput Econ 55, 597–628 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10614-019-09906-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10614-019-09906-x