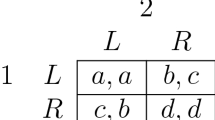Abstract
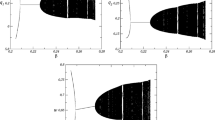
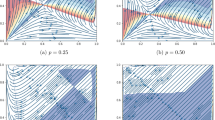
We introduce a framework to analyze the interaction of boundedly rational heterogeneous agents repeatedly playing a participation game with negative feedback. We assume that agents use different behavioral rules prescribing how to play the game conditionally on the outcome of previous rounds. We update the fraction of the population using each rule by means of a general class of evolutionary dynamics based on imitation, which contains both replicator and logit dynamics. Our model is analyzed by a combination of formal analysis and numerical simulations and is able to replicate results from the experimental and computational literature on these types of games. In particular, irrespective of the specific evolutionary dynamics and of the exact behavioral rules used, the dynamics of the aggregate participation rate is consistent with the symmetric mixed strategy Nash equilibrium, whereas individual behavior clearly departs from it. Moreover, as the number of players or speed of adjustment increase the evolutionary dynamics typically becomes unstable and leads to endogenous fluctuations around the steady state. These fluctuations are robust with respect to behavioral rules that try to exploit them.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
Anderson S. P., Engers M. (2007) Participation games: Market entry, coordination, and the beautiful blonde. Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization 63: 120–137
Arthur W. B. (1994) Inductive reasoning and bounded rationality. American Economic Review 84: 406–411
Bell A. M. (2001) Reinforcement learning rules in a repeated game. Computational Economics 18: 89–111
Benaïm M., Weibull J. W. (2003) Deterministic approximation of stochastic evolution in games. Econometrica 71: 873–903
Bottazzi G., Devetag G. (2003) A laboratory experiment on the minority game. Physica A 324: 124–132
Bottazzi G., Devetag G. (2007) Competition and coordination in experimental minority games. Journal of Evolutionary Economics 17: 241–275
Brianzoni S., Cerqueti R., Michetti E. (2010) A dynamic stochastic model of asset pricing with heterogeneous beliefs. Computational Economics 35: 165–188
Brock W. A., Hommes C. H. (1997) Rational routes to randomness. Econometrica 65: 1059–1095
Brock W. A., Hommes C. H. (1998) Heterogeneous beliefs and routes to chaos in a simple asset pricing model. Journal of Economic Dynamics & Control 22: 451–481
Brock W. A., Dindo P., Hommes C. H. (2006) Adaptive rational equilibrium with forward looking agents. International Journal of Economic Theory 2: 241–278
Challet D., Zhang Y. C. (1997) Emergence of cooperation and organization in an evolutionary game. Physica A 246: 407–418
Challet D., Zhang Y. C. (1998) On the minority game: Analytical and numerical studies. Physica A 246: 514–532
Chiarella C., He X.-Z. (2002) Heterogeneous beliefs, risk and learning in a simple asset pricing model. Computational Economics 19: 95–132
Dindo, P. (2007). Bounded rationality and heterogeneity in economic dynamic models. PhD Thesis University of Amsterdam, Tinbergen Institute Research Series 396.
Droste E., Hommes C., Tuinstra J. (2002) Endogenous fluctuations under evolutionary pressure in Cournot competition. Games and Economic Behavior 40: 232–269
Duffy J., Hopkins E. (2005) Learning, information and sorting in market entry games: Theory and evidence. Games and Economic Behavior 51: 31–62
Erev I., Rapoport A. (1998) Coordination, ‘magic’, and reinforcment learning in a market entry game. Games and Economic Behavior 23: 146–175
Franke R. (2003) Reinforcement learning in the El Farol model. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization 15: 367–388
Fudenberg D., Levine D. K. (1998) The theory of learning in games. MIT Press, Cambridge
Fudenberg D., Tirole J. (1991) Game theory. MIT Press, Cambridge
Haltiwanger J., Waldman M. (1985) Rational expectations and the limits of rationalty: An analysis of heterogeneity. American Economic Review 75: 326–340
Heemeijer, P. (2009). Expectation formation in dynamic market experiments. PhD Thesis University of Amsterdam, Tinbergen Institute Research Series 450.
Hofbauer J., Sandholm W. J. (2007) Evolution in games with randomly disturbed payoffs. Journal of Economic Theory 132: 47–69
Hofbauer J., Sandholm W. J. (2009) Stable games and their dynamics. Journal of Economic Theory 144: 1665–1693
Hommes C. H. (1998) On the consistency of backward-looking expectations: The case of the cobweb. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization 33: 333–362
Iida Y., Akiyama T., Uchida T. (1992) Experimental analysis of dynamic route choice behavior. Transportation Research B 26: 17–32
Lahkar R., Sandholm W. H. (2008) The projection dynamic and the geometry of population games. Games and Economic Behavior 64: 565–590
Li T.-Y., Yorke J. A. (1975) Period three implies chaos. American Mathematical Monthly 82: 985–999
Meyer D. J., Huyck J. B., Van Battalio R. C., Saving T. R. (1992) History’s role in coordinating decentralized allocation decisions. Journal of Political Economy 100: 292–316
Neugart M., Tuinstra J. (2003) Endogenous fluctuations in the demand for education. Journal of Evolutionary Economics 13: 29–51
Rapoport A., Seale D., Erev I., Sundali J. (1998) Equilibrium play in large groups market entry games. Management Science 44: 119–141
Rota Bulò S., Bomze I.M. (2011) Infection and immunization: A new class of evolutionary game dynamics. Games and Economic Behavior 71(1): 193–211
Sandholm W. H. (2003) Evolution and equilibrium under inexact information. Games and Economic Behavior 44: 343–378
Schlag K. H. (1998) Why imitate, and if so, how? A boundedly rational approach to multi-armed bandits. Journal of Economic Theory 78: 130–156
Selten R., Chmura T., Pitz T., Kube S., Schreckenberg M. (2007) Commuters route choice behavior. Games and Economic Behavior 58: 394–406
Sonnemans J., Hommes C., Tuinstra J., van de Velden H. (2004) The instability of a heterogeneous cobweb economy: A strategy experiment in expectation formation. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization 54: 453–481
Sundali J. A., Rapoport A., Seale D. A. (1995) Coordination in market entry games with symmetric players. Organizational Behaviour and Human Decision Processes 64: 203–218
Taylor P., Jonker L. (1978) Evolutionary stable strategies and game dynamics. Mathematical Biosciences 40: 145–156
Weibull J. W. (1995) Evolutionary game theory. MIT Press, Cambridge
Zambrano E. (2004) The interplay between analytics and computation in the study of congestion externalities: The case of the El Farol problem. Journal of Public Economic Theory 6: 375–395
Zwick R., Rapoport A. (2002) Tacit coordination in a decentralized market entry game with fixed capacity. Experimental Economics 5: 253–272
Acknowledgments
We thank Cees Diks, Cars Hommes, Bill Sandholm, Yang Zhang and an anonymous referee for constructive comments and Peter Heemeijer for providing us with the experimental data used in Sect. 2. Opinions and errors remain ours. Pietro Dindo acknowledges financial support from the European Commission 6th FP (Contract CIT3-CT-2005-513396) Project: DIME - Dynamics of Institutions and Markets in Europe.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Previous versions of this paper have circulated under the title “A behavioral model for participation games with negative feedback”.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Dindo, P., Tuinstra, J. A Class of Evolutionary Models for Participation Games with Negative Feedback. Comput Econ 37, 267–300 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10614-011-9253-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10614-011-9253-3
Keywords
- Participation games
- Heterogeneous behavioral rules
- Revision protocol
- Replicator dynamics
- Logit dynamics
- Nonlinear dynamics