Abstract
Background
The ability of adolescents to regulate their emotions and take advantage of their parents’ guidance may affect how they experience their transition to adulthood and their tendency to develop current and future mental health problems. The present study had two aims; first, to test the effectiveness of interpersonal emotion- regulation (ER) compared to self-ER. Second, to examine how interaction between parent/adolescent anxiety influences the effectiveness of interpersonal compared to self-ER.
Methods
39 couples of parents (13 males; 26 females, 39–61 years of age) and adolescents (17 males; 22 females, 13–18 years of age) participated in the study. Adolescents viewed negative emotional images with low or high intensity. For each image, they were instructed to either choose and apply a regulatory strategy (i.e., self ER) or to apply a regulatory strategy chosen by their parents (i.e., interpersonal ER).
Results
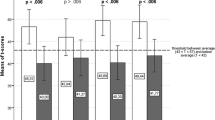
It was found that in low anxiety parents- low anxiety adolescents, the effectiveness of self and interpersonal ER were equal. In low-anxiety parents- high-anxiety adolescents, on the other hand, there was a significant advantage to interpersonal compared to self-ER. In high-anxiety parents, there was a significant advantage to self, compared to interpersonal ER in reducing distress, independent of the level of anxiety experienced by the adolescent.
Conclusions
The study has significant clinical implications, providing a behavioral tool to decrease distress in highly anxious individuals during the challenging times of pre-adulthood.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldao, A. (2013). The future of emotion regulation research: Capturing context. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 8, 155–172.
Aldao, A., & Nolen-Hoeksema, S. (2010). Specificity of cognitive emotion regulation strategies: A transdiagnostic examination. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 48, 974–983.
Bariola, E., Gullone, E., & Hughes, E. K. (2011). Child and adolescent emotion regulation: The role of parental emotion regulation and expression. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 14(2), 198–212.
Blos, P. (1979). The adolescent passage. New York: International Universities Press.
Bonanno, G. A., & Burton, C. L. (2013). Regulatory flexibility: An individual differences perspective on coping and emotion regulation. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 8, 591–612.
Branje, S. (2018). Development of parent–adolescent relationships: Conflict interactions as a mechanism of change. Child Development Perspectives, 12, 171–176.
Carthy, T., Horesh, N., Apter, A., & Gross, J. J. (2010). Patterns of emotional reactivity and regulation in children with anxiety disorders. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 32, 23–36.
Cisler, J., Olatunji, B., Feldner, M., & Forsyth, J. (2010). Emotion regulation and the anxiety disorders: An integrative review. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 32, 68–82.
Cohen, J. (1992). A power primer. Psychological Bulletin, 112, 155–159
Costa, N. M., & Weems, C. F. (2005). Maternal and child anxiety: Do attachment beliefs or children’s perceptions of maternal control mediate their association? Social Development, 14, 576–590.
Daniel, K. E., Baee, S., Boukhechba, M., Barnes, L. E., & Teachman, B. A. (2019). Do I really feel better? Effectiveness of emotion regulation strategies depends on the measure and social anxiety. Depression and Anxiety, 36, 1182–1190.
De Goede, I., Branje, S., & Meeus, W. (2009). Developmental changes in adolescents’ perceptions of relationships with their parents. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 38, 75–88.
Eisenberg, N., & Spinrad, T. L. (2004). Emotion-related regulation: Sharpening the definition. Child Development, 75, 334–339.
Eisenberg, N., Spinrad, T. L., & Eggum, N. D. (2010). Emotion-related self-regulation and its relation to children’s maladjustment. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 6, 495–525.
Fabes, R. A., Leonard, S. A., Kupanoff, K., & Martin, C. L. (2001). Parental coping with children’s negative emotions: Relations with children’s emotional and social responding. Child Development, 72, 907–920.
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A. G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social behavioral and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39(2), 175–191. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03193146
Fliek, L., Roelofs, J., van Breukelen, G., & Muris, P. (2019). A longitudinal study on the relations among fear-enhancing parenting, cognitive biases, and anxiety symptoms in non-clinical children. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 50, 631–646.
Gökdağ, C. (2021). How does interpersonal emotion regulation explain psychological distress? The roles of Attachment style and social support. Personality and Individual Differences, 176, 110763.
Goldfield, G. S., & Legg, C. (2006). Dietary restraint, anxiety, and the relative reinforcing value of snack food in non-obese women. Eating Behaviors, 7, 323–332.
Gross, J. J. (2014). Emotion regulation: Conceptual and empirical foundations. In J. J. Gross (Ed.), Handbook of emotion regulation (pp. 3–24). New York: Guilford.
Keijsers, L., Frijns, T., Branje, S. J. T., & Meeus, W. (2009). Developmental links of adolescent disclosure parental solicitation and control with delinquency: Moderation by parental support. Developmental Psychology, 45, 1314–1327.
Knight, L. K., Stoica, T., Fogleman, N. D., & Depue, B. E. (2019). Convergent neural correlates of empathy And anxiety during socioemotional processing. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 13, 1–15.
Lang, P. J., Bradley, M. M., & Cuthbert, B. N. (2008). International affective picture system (IAPS): Affective ratings of pictures and instruction manual. Technical Report A-8.
Levy-Gigi, E., & Shamay-Tsoory, S. G. (2017). Help me if you can: Evaluating the effectiveness of interpersonal compared to intrapersonal emotion regulation in reducing distress. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 55, 33–40.
Messina, I., Calvo, V., Masaro, C., Ghedin, S., & Marogna, C. (2021). Interpersonal emotion regulation: From research to Group Therapy. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 636919.
Miller-Slough, R. L., & Dunsmore, J. C. (2016). Parent and friend emotion socialization in adolescence: Associations with psychological adjustment. Adolescent Research Review, 1(4), 287–305.
Niven, K. (2022). Does interpersonal emotion regulation ability change with age? Human Resource Management Review, 32(3), 100847.
Noller, P. (1995). Parent–adolescent relationships. In M. A. Fitzpatrick, & A. L. Vangelisti (Eds.), Explaining family interactions (pp. 77–111). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Nozaki, Y., & Mikolajczak, M. (2020). Extrinsic emotion regulation. Emotion, 20(1), 10–15.
Olatunji, B. O., Berg, H. E., & Zhao, Z. (2017). Emotion regulation of fear and disgust: Differential effects of reappraisal and suppression. Cognition and Emotion, 31(2), 403–410. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699931.2015.1110117
Patel, N., Stoodley, C., Pine, D. S., Grillon, C., & Ernst, M. (2017). Interaction of induced anxiety and verbal working memory: Influence of trait anxiety. Learning & Memory, 24 407–413.
Patton, G. C., Sawyer, S. M., Santelli, J. S., Ross, D. A., Afifi, R., Allen, N. B.,… Viner, R. M. (2016). Our future: A Lancet commission on adolescent health and wellbeing.The Lancet, 387, 2423– 2478.
Pierce, G. R., Sarason, I. G., & Sarason, B. R. (1991). General and relationship-based perceptions of social support: Are two constructs better than one? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61, 1028–1039.
Rasing, S. P. A., Braam, M. W. G., Brunwasser, S. M., Janssens, M. A. M., Creemers, D., H. M., & Scholte, R. H. J. (2019). Depression and anxiety symptoms in female adolescents: Relations with parental psychopathology and parenting behavior. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 1, 1–16.
Reinholdt-Dunne, M. L., Mogg, K., Esbjorn, B. H., & Bradley, B. P. (2012). Effects of age and anxiety on processing threat cues in healthy children. Journal of Experimental Psychopathology, 3, 30–41.
Remmes, C. R., & Ehrenreich-May, J. (2014). Parental emotion regulation strategy use and responses to youth negative affect. Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy, 28, 34–45.
Riediger, M., & Klipker, K. (2014). Emotion regulation in adolescence.
Schäfer, J., Naumann, E., Homes, E. A., Tuschen-Caffier, B., & Samson, A. C. (2017). Emotion regulation strategies in depressive and anxiety symptoms in youth: A meta-analytic review. Journal of and Youth Adolescence, 46, 261–276.
Schwartz-Mette, R. A., Lawrence, H. R., Shankman, J., Fearey, E., & Harrington, R. (2021). Intrapersonal emotion regulation difficulties and maladaptive interpersonal behavior in adolescence. Research on child and adolescent psychopathology, 49(6), 749–761. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-020-00739-z.
Shafir, R., Guarino, T., Lee, I. A., & Sheppes, G. (2017). Emotion regulation choice in an evaluative context: The moderating role of self-esteem. Cognition and Emotion, 31, 1725–1732.
Shamay-Tsoory, S. G., & Levy-Gigi, E. (2021). You name it: Interpersonal affect labeling diminishes distress in romantic couples. Behavior Therapy, 52(2), 455–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beth.2020.06.004
Sheppes, G., Scheibe, S., Suri, G., Radu, P., Blechert, J., & Gross, J. J. (2014). Emotion regulation choice: A conceptual framework and supporting evidence. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 143, 163–181.
Sheppes, G., Suri, G., & Gross, J. J. (2015). Emotion regulation and psychopathology. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 11(1), 379–405. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032814-112739
Smetana, J. G., Yau, J., & Hanson, S. (1991). Conflict resolution in families with adolescents. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 1, 189–206.
Spielberger, C. D., Gorsuch, R. L., Lushene, R., Vagg, P. R., & Jacobs, G. A. (1983). Manual for the state-trait anxiety inventory. Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press.
Stocker, C. M., Richmond, M. K., & Rhoades, G. K. (2007). Family emotional processes and adolescents’ adjustment. Social Development, 16, 310–325.
Suveg, C., & Zeman, J. (2004). Emotion regulation in children with anxiety disorders. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 33, 750–759.
Troy, A. S., Shallcross, A. J., & Mauss, I. B. (2013). A person-by-situation approach to emotion regulation. Psychological Science, 24(12), 2505–2514. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797613496434
Vered, R., Haim-Nachum, S., & Levy-Gigi, E. (2021). Acting against your own interests: The tension between emotion regulation preference and efficacy and its implications for individuals with depressive symptoms. PloS ONE, 16(7), e0254213. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0254213.
Williams, W. C., Morelli, S. A., Ong, D. C., & Zaki, J. (2018). Interpersonal emotion regulation: Implications for affiliation, perceived support, relationships, and well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 115(2), 224–254.
Xia, L. X., Gao, X., Wang, Q., & Hollon, S. D. (2014). The relations between interpersonal self-support traits and emotion regulation strategies: A longitudinal study. Journal of Adolescence, 37(6), 779–786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2014.05.007
Young, K. S., Sandman, C. F., & Craske, M. G. (2019). Positive and negative emotion regulation in adolescence: Links to anxiety and depression. Brain Sciences, 9, 1–20.
Zimmermann, P., & Iwanski, A. (2014). Emotion regulation from early adolescence to emerging adulthood and middle adulthood: Age differences, gender differences, and emotion-specific developmental variations. International Journal of Behavior Development, 38, 182–194.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Naor-Ziv, R., Shamay-Tsoory, S. & Levy-Gigi, E. The Effectiveness of Interpersonal Emotion Regulation and the Role of Anxiety in Parent-adolescent Relationships. Cogn Ther Res 47, 648–654 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10608-023-10394-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10608-023-10394-5